Why Do We Need Callback Functions?
In traditional synchronous programming, we directly call functions and wait for their return results. This pattern is simple and intuitive, but when faced with time-consuming operations (such as I/O operations, network requests, etc.), the thread gets blocked, leading to low resource utilization.
Callback functions are key to solving the following problems:
- Decoupling: Separating functionality implementation from invocation
- Asynchronous Processing: Avoiding blocking the main thread
- Extensibility: Allowing different callers to customize processing logic
Workflow of Callback Functions
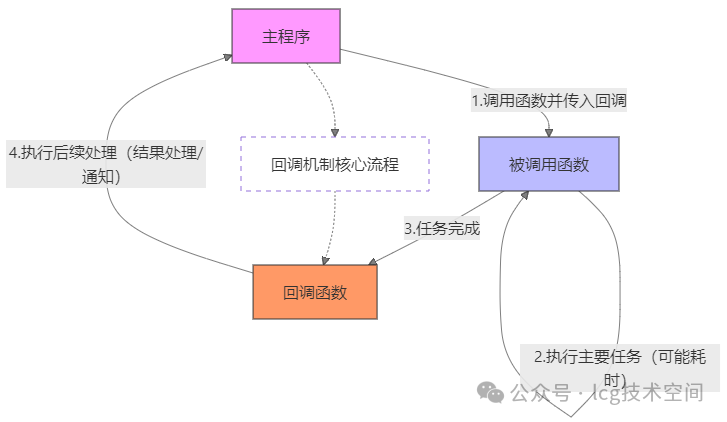
Types of Callback Functions
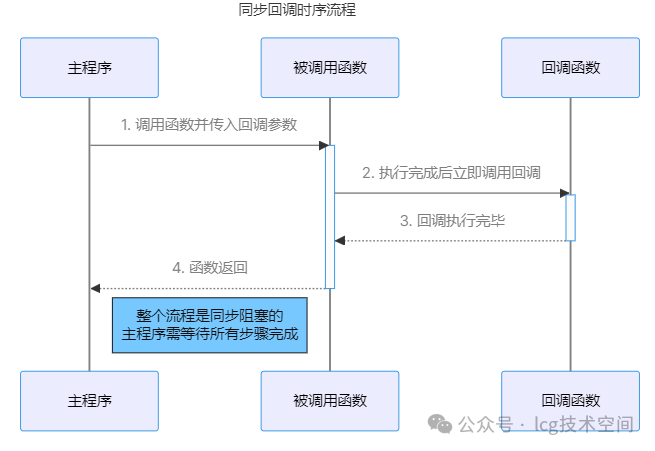
Synchronous Callback Flowchart
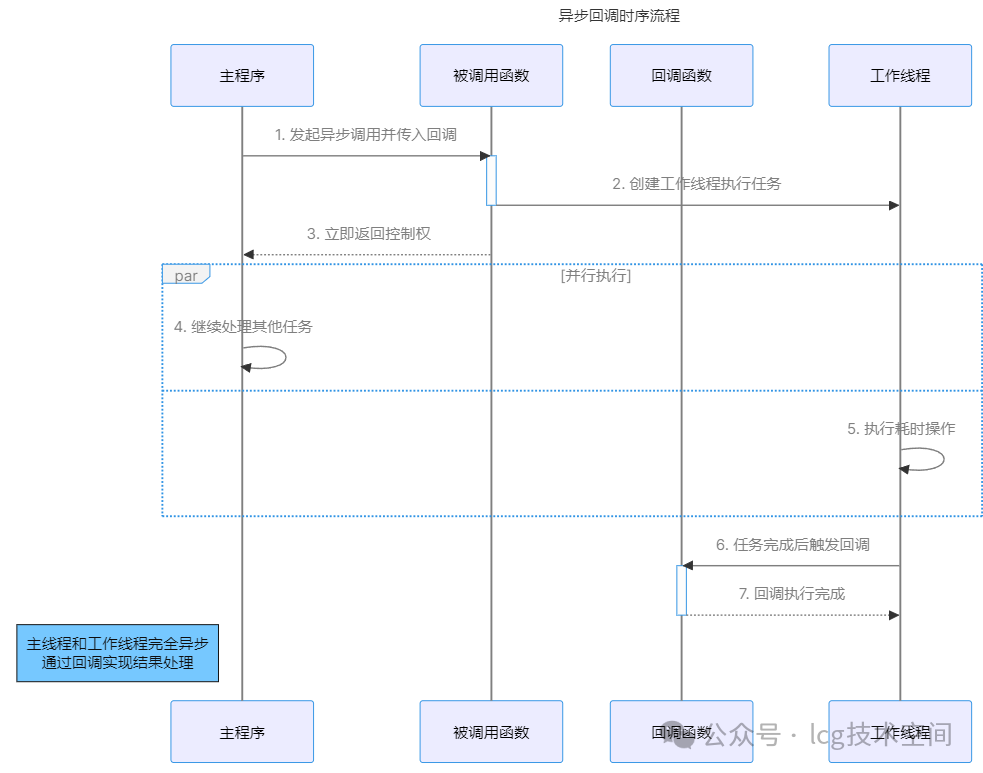
Asynchronous Callback Flowchart
Example Analysis: Tomorrow’s Youtiao App Case
Problems with Synchronous Calls
// Synchronous version
void make_youtiao(int num) {
// Time-consuming production process
for(int i=0; i<num; 10="" <="" blocks="" calling="" code="" complete="" each="" for="" i++)="" make_youtiao(10000);="" making="" method="" minutes="" must="" production="" sell();="" to="" wait="" youtiao...="" {="" }=""></num;>Callback Function Solution
// Callback function version
void make_youtiao(int num, std::function<void()> callback) {
// Time-consuming production process
for(int i=0; i<num; "youtiao="" <="" <<="" [](){="" after="" call="" callback="" callback();="" calling="" code="" complete="" complete,="" each="" i++)="" is="" make_youtiao(10000,="" making="" method="" production="" sales"="" sell();="" starting="" std::cout="" std::endl;="" youtiao...="" {="" }="" });=""></num;></void()>Asynchronous Callback Implementation
#include <thread>
#include <functional>
void async_make_youtiao(int num, std::function<void()> callback) {
std::thread([num, callback](){
// Execute time-consuming operation in a new thread
for(int i=0; i<num; "main="" "youtiao="" <="" <<="" [](){="" after="" async_make_youtiao(10000,="" call="" callback="" callback();="" calling="" code="" complete,="" completion="" continues="" detach="" each="" executing="" i++)="" independently="" making="" method="" other="" production="" run="" sales"="" sell();="" starting="" std::cout="" std::endl;="" tasks..."="" thread="" to="" youtiao...="" {="" }="" }).detach();="" });=""></num;></void()></functional></thread>Several Ways to Implement Callbacks in C++
- Function Pointers
typedef void (*Callback)(int);
void process(Callback cb) {
// Processing...
cb(42); // Call callback
}
- std::function
void process(std::function<void(int)> cb) {
// Processing...
cb(42); // Call callback
}
</void(int)>- Lambda Expressions
process([](int result) {
std::cout << "Got result: " << result << std::endl;
});
- Class Member Functions as Callbacks
class Processor {
public:
void handleResult(int result) {
std::cout << "Result: " << result << std::endl;
}
};
Processor p;
process(std::bind(&Processor::handleResult, &p, std::placeholders::_1));
Best Practices for Callback Functions
- Error Handling
void async_op(std::function<void(error*, data*)=""> callback) {
try {
Data* data = do_work();
callback(nullptr, data); // On success, error is null
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
callback(new Error(e.what()), nullptr);
}
}
</void(error*,>- Resource Management
void with_file(const std::string& path,
std::function<void(file*)> processor) {
FILE* f = fopen(path.c_str(), "r");
if (!f) throw std::runtime_error("File open failed");
try {
processor(f);
} catch (...) {
fclose(f);
throw;
}
fclose(f);
}
</void(file*)>- Thread-Safe Callbacks
class EventHandler {
std::mutex mtx;
std::function<void()> callback;
public:
void setCallback(std::function<void()> cb) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
callback = cb;
}
void trigger() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
if(callback) callback();
}
};
</std::mutex></std::mutex></void()></void()>Conclusion
Callback functions are a core mechanism of asynchronous programming, allowing the “logic for handling completion” to be passed as parameters, achieving:
- Non-blocking calls, improving system throughput
- Module decoupling, allowing the caller to decide subsequent processing
- Efficient resource utilization, avoiding thread idling
In C++, we can implement callbacks in various ways, from simple function pointers to modern <span>std::function</span> and lambda expressions. Understanding and correctly using callback functions is an important step towards becoming an efficient C++ programmer.