

-
To be honest, the computer science major has already “dominated the world”!
-
Talent training programs for the “Data Science and Big Data Technology” major
-
Talent training programs for the Cybersecurity major
-
Artificial Intelligence major and Intelligent Science and Technology major training programs

 整理 | 刘燕、冬梅 来源:AI前线(ID:ai-front)The impact of the MATLAB ban is beginning to show. National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition prohibits the use of MATLAB
整理 | 刘燕、冬梅 来源:AI前线(ID:ai-front)The impact of the MATLAB ban is beginning to show. National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition prohibits the use of MATLAB
The National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition is about to start, but students from Harbin Institute of Technology have found that they cannot use MATLAB to participate.
Recently, a netizen, Mr. A (pseudonym), revealed on Zhihu that the organizing committee of the National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition has preliminarily determined that the teams from Harbin Institute of Technology cannot use MATLAB, which is owned by MathWorks. Harbin Institute of Technology students have expressed that they are currently unable to apply for the MATLAB version specifically for the mathematical modeling competition.
Another student from Harbin Institute of Technology stated on Zhihu that this news was announced by the teacher responsible for the modeling competition at their school, and it has basically been confirmed that Harbin Institute of Technology is not allowed to use MATLAB in this year’s National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition.
The National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition is currently the largest mathematical modeling competition in the world, established in 1992, held annually, and is one of the first 19 competitions included in the “Ranking of College Discipline Competitions”.
MATLAB software is known as the “artifact for engineering” and is a leading mathematical technology application software in the industry, powerful in algorithm development, data visualization, data analysis, and numerical computation. It is an essential tool for engineering students and is one of the most commonly used software in mathematical modeling competitions. Many engineering colleges in China teach students how to use MATLAB as their first lesson after enrollment. For engineering students, the role of MATLAB in their data analysis and modeling is irreplaceable by other software.
On June 17 of this year, Harbin Institute of Technology issued a notice for the registration of the 2020 National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition, requiring participating teams to carefully read and understand the “Regulations and Participation Rules of the National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition (2019 Revised Edition)” and to strictly follow the relevant requirements for participation.
It is worth mentioning that the notice did not mention any matters related to the use of MathWorks or MATLAB. MathWorks is also one of the sponsors of the National College Student Mathematical Modeling Competition.
Prohibiting the use of MATLAB for participation is evidently unfair to Harbin Institute of Technology, as competitors from other universities can still use MATLAB normally. Many students from Harbin Institute of Technology have expressed dissatisfaction with the organizing committee’s decision, with Mr. A believing that the announcement to ban MATLAB is very unfair to Harbin Institute of Technology students, and that there was no prior notice during registration, which is unreasonable and has caused losses to students who registered normally.
This may be a follow-up to the previous ban on MATLAB at Harbin Institute of Technology. In early June of this year, news that Harbin Institute of Technology and Harbin Engineering University were banned from using MATLAB sparked heated discussions.
At that time, a teacher responsible for technical support at Harbin Institute of Technology responded that since June 6, 2020, due to Harbin Institute of Technology being placed on the U.S. Department of Commerce’s entity list, faculty and students at Harbin Institute of Technology have been unable to use MATLAB normally. MATLAB‘s parent company, MathWorks, confirmed that they must comply with U.S. government regulations and can no longer provide legitimate software licenses to faculty and students at Harbin Institute of Technology and Harbin Engineering University.
After the ban was announced, some students were concerned about whether they could still use MATLAB in the national mathematical modeling competition in September. Some industry insiders had previously analyzed that the possibility of a ban in the national competition was low. Now, as the competition approaches, there are new developments, putting a lot of pressure on students from Harbin Institute of Technology.
Currently, neither the organizing committee nor Harbin Institute of Technology has made an official statement confirming whether Harbin Institute of Technology can use MATLAB in this national mathematical modeling competition, and further information is pending official notification.
Dependence on Foreign Industrial Software, Insufficient Self-Development Capability
MATLAB is widely used in algorithm development, data visualization, data analysis, and numerical computation as a high-level technical computing language and interactive environment. In addition to common functions such as matrix operations and plotting functions/data images, MATLAB can also be used to create user interfaces and call programs written in other languages (including C, C++, Java, Python, and FORTRAN).
Industrial software is like the brain of manufacturing, and its importance is self-evident. Globally, due to the early start of industrial software in developed countries, strong technical accumulation, and high specialization, they have basically monopolized the high-end industrial software field, which is technically complex. In this context, a large number of international software companies, including Oracle, Siemens, and SAP, occupy more than half of the global market share and dominate the industrial software market, while China’s market share in industrial software is about 6%.
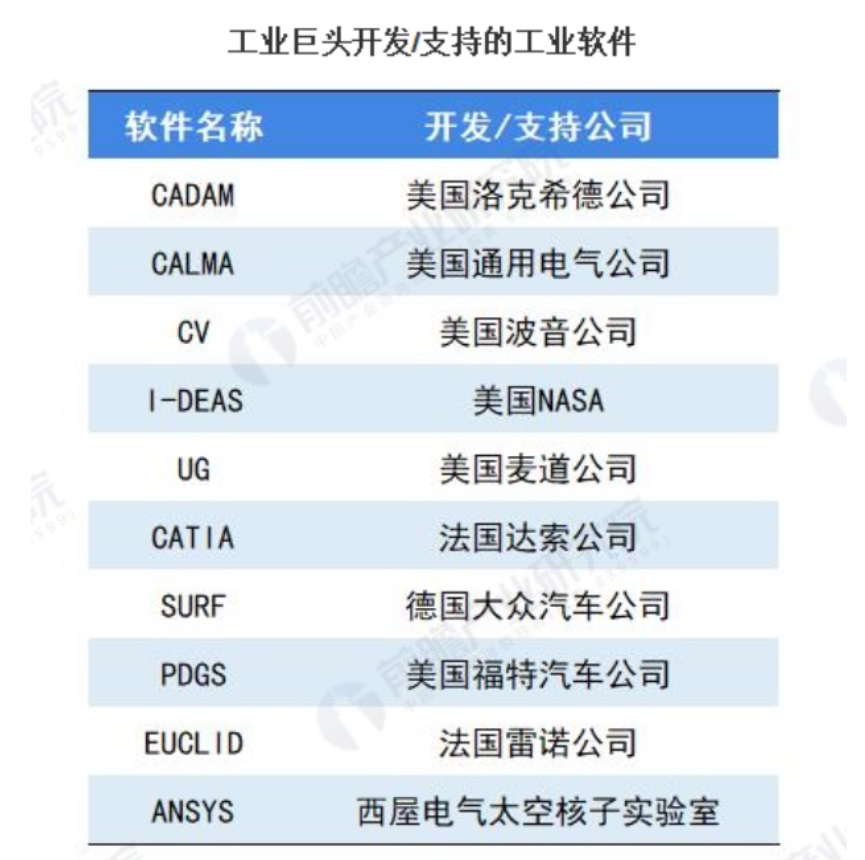
Data Source: Qianzhan Industry Research Institute
In fact, in the fields of design, processing, and analysis, our industrial software is 100% monopolized by European and American manufacturers. In engineering manufacturing, including the automotive industry, aerospace industry, electrical, and electronic information, MATLAB is the most basic computational simulation tool, and currently, there is no software in China that can fully cover the MATLAB ecosystem. In the first decade of this century, the market share of domestically produced industrial software in China sharply shrank to less than 5%. After the termination of the Ministry of Science and Technology’s “863” CIMS project in 2013, the country has not provided continuous funding support for the research and development of domestically produced industrial software.
How Difficult is it to Develop a Set of Domestic Basic Software?
After the MATLAB ban incident, many netizens discussed how long it would take to “recreate a domestic MATLAB”. Most people estimated it would take more than 5 years. While basic functional alternatives are not difficult, the challenge lies in the complex ecosystem and the accumulation of algorithms and documentation applicable to various industries or application scenarios, which are very difficult to replicate.
Moreover, most software practitioners lack the motivation and energy to undertake this work. While many developers may find some alternative solutions for personal use, making them available for everyone requires a unified display page and an easy-to-use interface. MATLAB may consider developing an alternative due to the large number of IT personnel among its users, but software like ChembioOffice, which is only used by a small number of professionals, has very few developers willing to invest time in self-development. Even if they are willing to develop, it is difficult to achieve results without a solid foundation in the relevant field.
For software and systems related to research and design, business management, production scheduling, and process control in the industrial field, we collectively refer to them as industrial software. The difficulty in developing industrial software lies in the fact that understanding IT alone is not enough; one also needs to understand domain-specific knowledge. In the software industry, industrial software accounts for a small proportion, yet it is the brain and nerve of industrial manufacturing, known as the “crown” of the industrial field, with high-end software being the “pearl” on the crown.
At the same time, foreign industrial software companies learned long ago to use various means to “suppress” domestic software. Among them, two methods are particularly covert.
The first is to cut off the source. By donating and sponsoring, they bind domestic universities and research institutes to their software in teaching and research, mainly teaching software operation, weakening the foundational education of software development, leading to a gradual decline in the capabilities of domestic universities and research institutes in the research and development of industrial software theory, algorithms, program design, and implementation.
For example, many universities now bundle finite element theory and technology courses with a certain foreign CAE simulation software, turning them into “Finite Element Theory and ×× Software”. Instructors only provide a brief introduction to finite element theory, while a large portion of the class time is spent teaching the operation of a certain foreign CAE software, and at the end of the course, students only need to use that CAE software to complete a design.
The second is to flood the Chinese market with a large number of software products, even deliberately allowing piracy, using piracy to create a dumping market that squeezes out domestic industrial software vendors, forcing them to lose their survival and growth space. They use piracy to create a low-cost temptation for domestic industrial enterprises to use their software at almost zero cost, and then adopt measures to combat piracy to collect legitimate software licensing fees and annual service fees, thus obtaining high profits.
For example, a certain automotive research center in Shanghai has only two sets of legitimate foreign CAD/CAM/CAE software after years of use, while hundreds of other sets are pirated. What this center did not realize is that these software products have been automatically sending information about their pirated usage back to foreign manufacturers through backdoors during use. Foreign manufacturers waited until the center reached over 300 sets of large-scale usage before initiating patent infringement lawsuits, resulting in a fine of 19 million yuan and forcing the center’s research and design to be firmly locked into foreign software.
Conclusion
Under the dual difficulties of insufficient domestic industrial software development capabilities and the intentional “suppression” by foreign industrial software companies, the road to developing domestically produced industrial basic software is still long. This situation forces us to increase the research and investment in domestic industrial-grade software, and all sectors of society must pay attention and quickly fill the gaps.
Further Reading: “Breaking! MATLAB banned in universities, which software will be the next to fall victim to U.S. “poisonous hands”?“

Welcome to join the Tsinghua IT communication QQ group: 976141892
Have you discovered the “look” and “like”? Click me to try it!
