 Utilize artificial intelligence effectively to accelerate undergraduate learning! Using AI is not equivalent to plagiarism; many students are merely satisfied with copying! This phenomenon must be stopped!The concept of convolution is very important and is the foundation of signal processing! Make sure to review the knowledge about convolution in textbooks multiple times!After class, it is necessary to repeatedly review the content of the program to master the use of functions! Everyone starts programming with C language, and in the second year, they encounter MATLAB software. How much time have you spent on programming in total? Relying solely on classroom time is far from enough to learn simulation well, and some even cannot remember the functions.The current learning situation is quite alarming, as most students attending classes are just using AI to cope with assignments. It is both helpless and heartbreaking! Students do not heed your advice, and by the time they graduate, they find themselves empty-handed, regretting it too late!In the last class, the teacher provided a demonstration program for the echo generator. So how can students write a MATLAB function to generate a simple echo effect that contains only one echo? What parameters are involved? Please recall carefully!Chapter Four is here!
Utilize artificial intelligence effectively to accelerate undergraduate learning! Using AI is not equivalent to plagiarism; many students are merely satisfied with copying! This phenomenon must be stopped!The concept of convolution is very important and is the foundation of signal processing! Make sure to review the knowledge about convolution in textbooks multiple times!After class, it is necessary to repeatedly review the content of the program to master the use of functions! Everyone starts programming with C language, and in the second year, they encounter MATLAB software. How much time have you spent on programming in total? Relying solely on classroom time is far from enough to learn simulation well, and some even cannot remember the functions.The current learning situation is quite alarming, as most students attending classes are just using AI to cope with assignments. It is both helpless and heartbreaking! Students do not heed your advice, and by the time they graduate, they find themselves empty-handed, regretting it too late!In the last class, the teacher provided a demonstration program for the echo generator. So how can students write a MATLAB function to generate a simple echo effect that contains only one echo? What parameters are involved? Please recall carefully!Chapter Four is here!
Main content: Continuous LTI systems and unit impulse response, zero-state response of continuous-time systems, and related MATLAB functions. Some of this content has already been covered in the previous chapter. Let’s first look at the definition of linear time-invariant systems!

Please carefully watch the video of students programming live, and there will also be guidance from me later! A small error in the previous chapter’s program has been identified!
The essence of the sinc function is an ideal low-pass filter!

At this time, please recall how to write a custom sinc function, with results equivalent to MATLAB’s built-in function.


1. Experiment Objectives
(1) Familiarize with the response and characteristics of continuous LTI systems under typical excitation signals;
(2) Master the method for solving the unit impulse response of continuous LTI systems;
(3) Focus on mastering the convolution method to calculate the zero-state response of continuous-time systems;
(4) Familiarize with the calling format and function of related MATLAB functions;
(5) Be able to perform time-domain analysis of systems using MATLAB.

The system’s response generally includes two parts: the response generated by the current input (zero-state response) and the response generated by historical inputs (initial state) (zero-input response). For low-order systems, the response can generally be obtained through analytical methods. However, for high-order systems, manual calculations can be quite difficult, and MATLAB’s powerful computational capabilities can easily determine various responses of the system, such as impulse response, step response, zero-input response, zero-state response, and total response.
1. Direct Solution Method
The involved MATLAB functions are: impulse (impulse response), step (step response), roots (zero-input response), lsim (zero-state response), etc.
In MATLAB, the system’s differential equation must be input in the form of a coefficient vector. Therefore, before using it, the system’s differential equation must be transformed to obtain its transfer function. The coefficients of the denominator polynomial and numerator polynomial are represented by vectors a and b (arranged in descending powers of s).
This method can only be used for theoretical learning to enhance students’ problem-solving abilities. It is not feasible for practical applications!


3. Involved MATLAB Functions
1. impulse function
Function: Calculate and plot the system’s impulse response.
Calling format: impulse(sys): where sys can be a system function established using the commands tf, zpk, or ss.
impulse(sys, t): Calculate and plot the system’s impulse response over the time defined by vector t.
Y = impulse(sys, t): Save the system’s output values.
2. step function
Function: Calculate and plot the system’s step response curve.
Calling format: step(sys): where sys can be a system established using the commands tf, zpk, or ss.
step(sys, t): Calculate and plot the system’s step response over the time defined by vector t.
3. lsim function
Function: Calculate and plot the zero-state response of the system under arbitrary input.
Calling format: lsim(sys, x, t): where sys can be a system function established using the commands tf, zpk, or ss, x is the system’s input, and t defines the time range;
lsim(sys, x, t, zi): Calculate the total response of the system under arbitrary input and zero state, where sys must be in state-space form, and zi is the system’s initial state.
4. roots function
Function: Calculate the roots of a homogeneous polynomial.
Calling format: r = roots(b): Calculate the roots of polynomial b, where r is the roots of the polynomial.
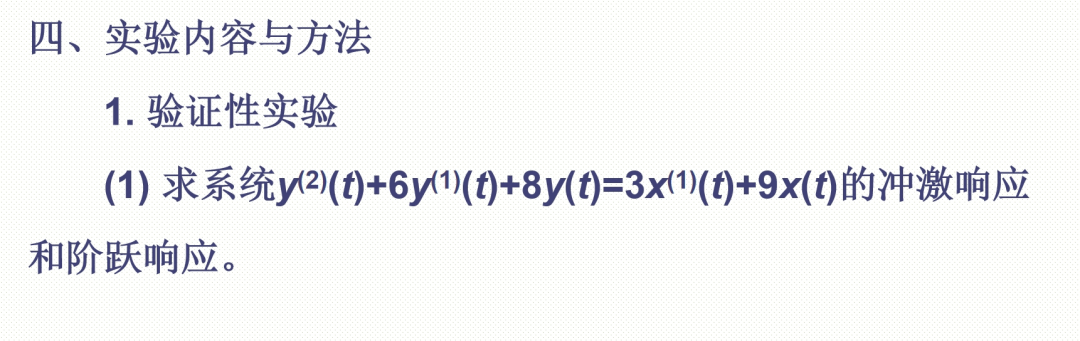










Thought Questions!
(1) What are the mathematical models of continuous-time systems?
(2) The zero-state response of a linear time-invariant system is the convolution of the input signal with the impulse response; what is the basis for this?
(3) Why can the system’s impulse response h(t) be considered both the zero-state response and the zero-input response?
Please write your answers in the comments section! To be continued!

Revision History
20250223 Completed the first draft;
20250406 Revised content;