Building an IoT system using a wireless I/O gateway is a complex yet orderly process. Below is a basic step-by-step guide: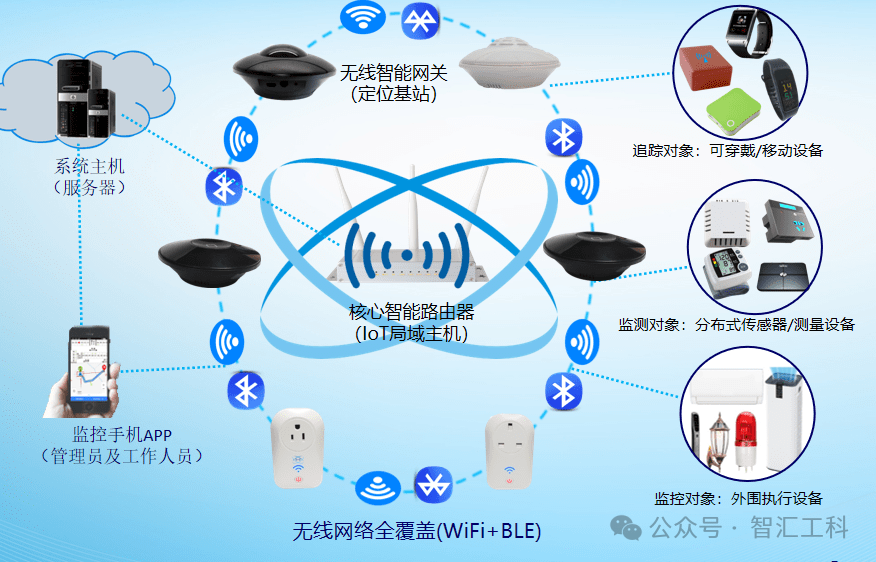
1. Define Requirements and Planning
1. Determine the application scenarios:
● Analyze the environments where the IoT gateway will be deployed, such as industrial automation, smart homes, smart cities, etc.
● Identify the specific devices and parameters that need to be monitored and controlled based on the application scenarios.
2. Device Compatibility:
● Determine the types of devices, communication protocols, and interfaces that the gateway needs to support.
● Ensure that the wireless I/O gateway is compatible with on-site sensors, actuators, and other devices.
2. Choose a Wireless I/O Gateway
1. Gateway Performance:
● Select a gateway with sufficient processing speed, low power consumption, and good scalability.
● Ensure the gateway supports necessary network interfaces, such as Wi-Fi, 4G/5G, Bluetooth, etc., to meet wireless communication needs.
2. I/O Ports:
● Ensure the gateway provides enough input/output ports to connect various sensors and actuators.
3. Data Security:
● Choose a gateway with security features such as data encryption, authentication, and access control.
3. Hardware Layout and Connections
1. On-site Layout:
● Based on the number, type, and geographical distribution of the system’s I/O points, arrange the appropriate number of wireless I/O gateways and bus expansion modules on-site.
● Connect the device components that need to be integrated into the system to these I/O modules.
2. Power Supply and Communication:
● Ensure the gateway has a stable power supply and consider backup power solutions.
● Configure the wireless communication network to ensure smooth communication between the gateway and sensors, actuators.
4. Software Configuration and Debugging
1. Application Configuration Management Platform:
● Log in to the application configuration management platform provided by the wireless I/O gateway.
● Configure and set the on-site I/O modules according to application requirements, including calibrating the physical meanings and engineering units of I/O port data, and setting the conversion relationships between analog signals and actual physical values.
2. Data Display and Alarms:
● Set the display methods for input data in the application configuration management platform, such as graphs, tables, curves, etc.
● Define the logical relationships of output data, such as threshold-based alarm signals.
3. Remote Monitoring and Management:
● Log in to the application terminal platform and use data trend charts and threshold alarms to implement remote monitoring and management of on-site devices.
5. System Testing and Optimization
1. Functional Testing:
● Ensure all gateway functions work as expected, including data collection, processing, storage, and forwarding.
2. Performance Testing:
● Evaluate the gateway’s performance under expected loads to ensure the system can operate stably.
3. Compatibility Testing:
● Verify the compatibility of the gateway with different devices to ensure the system can connect to various sensors and actuators.
4. Security Testing:
● Detect potential security vulnerabilities to ensure the data security of the system.
5. Optimization and Adjustment:
● Optimize and adjust the system based on test results to improve stability and performance.
6. Deployment and Maintenance
1. Deploy the Gateway:
● Deploy the gateway in the target environment and perform necessary configurations.
2. Real-time Monitoring:
● Monitor the operational status of the gateway in real-time to ensure its stability and security.
3. Upgrades and Maintenance:
● Regularly update software, fix vulnerabilities, and optimize performance.
● Establish partnerships and maintain close contact with device manufacturers, cloud service providers, etc., to obtain timely technical support and upgrade information.
By following the above steps, a fully functional and stable IoT system can be built using a wireless I/O gateway. In practical applications, flexible adjustments and optimizations should be made according to specific scenarios and requirements.