0 Introduction
Hello everyone! My name is Lichuang IoT, and I mainly focus on industrial automation and the Internet of Things (IoT). I have a good understanding of the industrial automation field and have developed IoT-related products. My original intention was to work on industrial IoT, but the system is too vast, and I will continue to learn independently. Therefore, I will start with a smaller system, such as building a complete smart home system, covering the entire range from hardware to software. Let’s begin with how this smart home system is constructed based on IoT. Here you can start from 0 and reach a qualitative change at 1, simply by learning the Lichuang IoT architecture with me.
To recap the previous section, “How to Build Your Own IoT System – Lichuang IoT,” we discussed the importance of IoT development, what IoT is, its application scenarios, and the learning roadmap for Lichuang IoT, which introduces the Lichuang IoT architecture. The IoT architecture is mainly divided into three layers: the perception layer, the transmission layer, and the application layer. This section will discuss the sensors in the hardware layer of the perception layer. The perception layer is the most fundamental part of IoT, akin to the human senses perceiving the world.
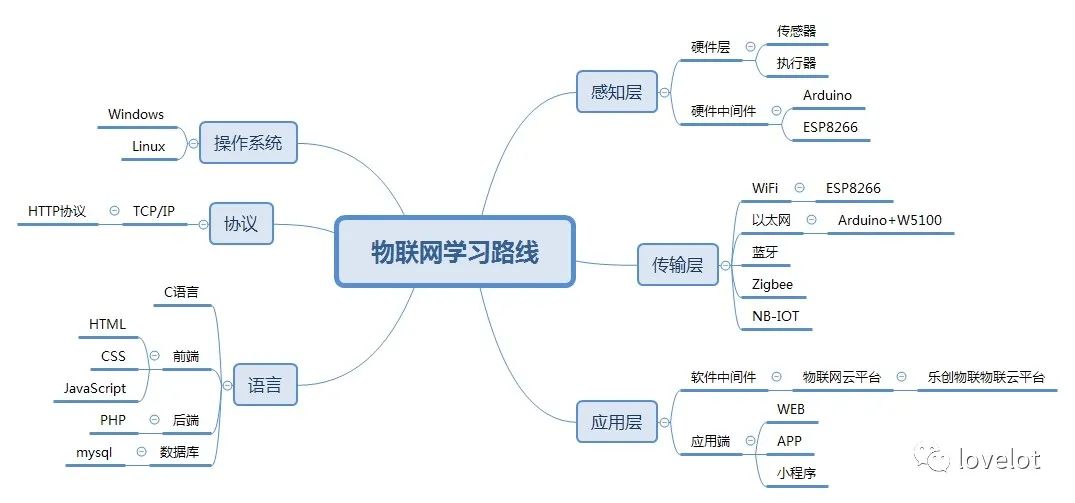
Lichuang IoT Learning Roadmap
1 Introduction to Sensors
A sensor is a component or part of a measurement system used to measure physical, chemical, biological, or other parameters. Typically, sensors can provide a signal in the form of equivalent voltage or current, which can be used for detection, processing, storage, and forwarding. Sensor technology has had a significant impact on modern industries, and there are many sensors available in the market. The measurement objects and physical conversion principles of sensors.

Sensor
According to the national standard GB7665-19871, a sensor can perceive specified measurement information and convert it into an output signal according to certain rules. The general signal output is a standard signal (0~10mA, 4-20mA, 0~5V, 0~10V). It consists of three parts: a sensitive element, a conversion element, and a measurement circuit.
There are many classifications of sensors. Based on the input physical quantity, they can be divided into: displacement sensors, pressure sensors, speed sensors, temperature sensors, and gas sensors; based on the working principle, they can be divided into: resistive, inductive, capacitive, and potential types; based on the nature of the output signal, they can be divided into: analog sensors and digital sensors. Analog sensors output analog signals, while digital sensors output digital signals.
2 Hot Research Areas in Sensors
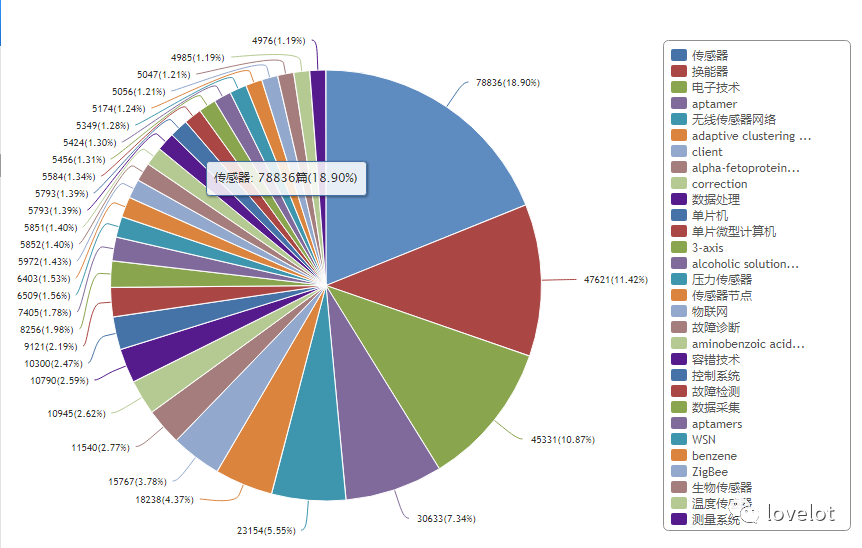
CNKI Sensor Articles
1) Wireless Sensors
In recent years, wireless sensors and sensor networks have developed rapidly, widely applied in environmental monitoring, on-site detection and control in manufacturing, smart homes, intelligent transportation, building health monitoring, and healthcare. With the rapid development of electronics, embedded microcontrollers, smart wireless sensors, networks, and communication technologies, it has become possible to achieve low-cost and low-power wireless sensor nodes.
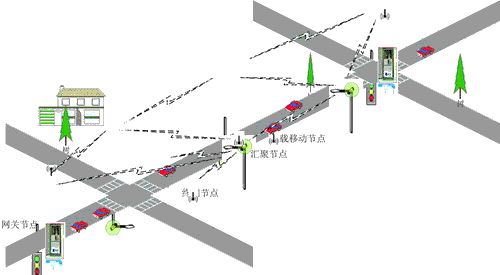
Wireless Sensor Networks
The sensor unit consists of sensors and analog-to-digital conversion modules, used to perceive and acquire information in the monitored area and convert it into digital signals; the processing unit consists of an embedded system, including processors, memory, etc., responsible for controlling and coordinating the work of various parts of the node, storing and processing the data collected by itself and the data sent from other nodes; the wireless communication unit consists of wireless communication modules, responsible for communicating with other sensor nodes, exchanging control information and transmitting collected data; the power supply unit usually uses micro batteries to provide the necessary energy for the normal operation of the sensor nodes.
2) Data Acquisition
Data acquisition (DAQ) refers to the automatic collection of non-electric or electric signal quantities from sensors and other devices under test, sending them to the host computer for analysis and processing. A data acquisition system combines measurement hardware and software products based on computers or other dedicated testing platforms to achieve flexible, user-defined measurement systems. Data acquisition is the process of automatically collecting information from sensors and other devices under test. The data acquisition system integrates signals, sensors, exciters, signal conditioning, data acquisition devices, and application software.

Data Acquisition Panel
The purpose of data acquisition is to measure physical phenomena such as voltage, current, temperature, pressure, or sound. PC-based data acquisition is achieved through the combination of modular hardware, application software, and computers. Although data acquisition systems have different definitions based on different application needs, the purpose of collecting, analyzing, and displaying information remains the same across all systems. Data acquisition systems integrate signals, sensors, exciters, signal conditioning, data acquisition devices, and application software.
3) Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnection of various objects through the internet. Simply put, it is an internet where everything is connected. The IoT connects smart objects through various information sensing devices and communication protocols, enabling information transmission and exchange through various communication networks to achieve decision-making and control. The IoT utilizes communication technologies to connect sensors, controllers, machines, people, and objects in new ways, forming a network that connects people and objects, and objects with each other, achieving informatization, remote management control, and intelligent networking.

Internet of Things
3 Introduction to Some Popular IoT Sensors
1) Temperature and Humidity Sensor
The DHT11 is a temperature and humidity sensor with calibrated digital signal output. Its accuracy is ±5% RH for humidity and ±2°C for temperature, with a humidity range of 20-90% RH and a temperature range of 0~50°C.

DHT11
2) Smoke Sensor
The MQ-2 smoke sensor can be used for gas leak monitoring devices in homes and factories, suitable for detecting liquefied gas, butane, propane, methane, alcohol, hydrogen, smoke, etc.

MQ-2 Smoke Sensor
3) Dust Sensor
This sensor has extremely low current consumption (maximum 20mA, typical 11mA) and can carry sensors up to 7VDC. It outputs an analog voltage proportional to the measured dust concentration, with a sensitivity of 0.5V/0.1mg/m3. It can detect the AQI value.
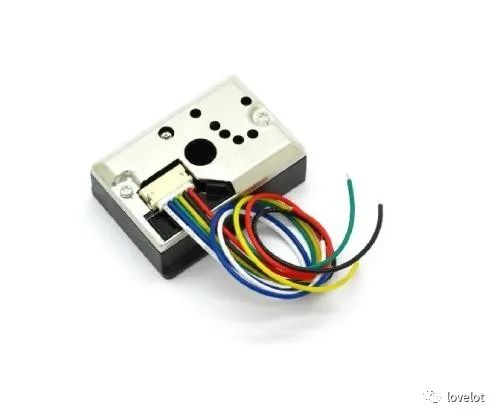

Dust Sensor
4) Infrared Emission and Reception Module
The infrared emission and reception module plays an important role in our daily lives. Many household appliances use this device, such as air conditioners, TVs, DVDs, etc., due to its wireless remote sensing capabilities, allowing for control over longer distances, making it very convenient to use.
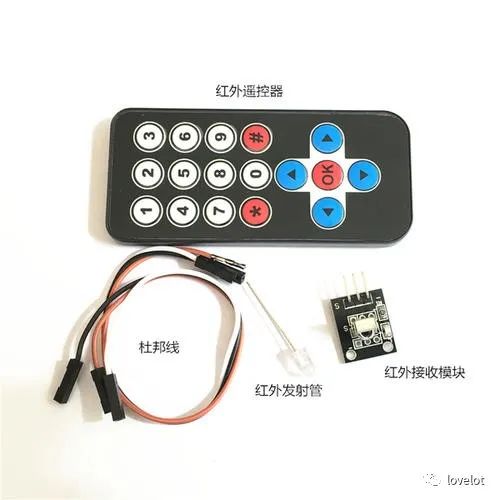

Infrared Emission and Reception Module
4 Sensor Application Examples
For example, uploading temperature and humidity data to the Lichuang IoT cloud platform:
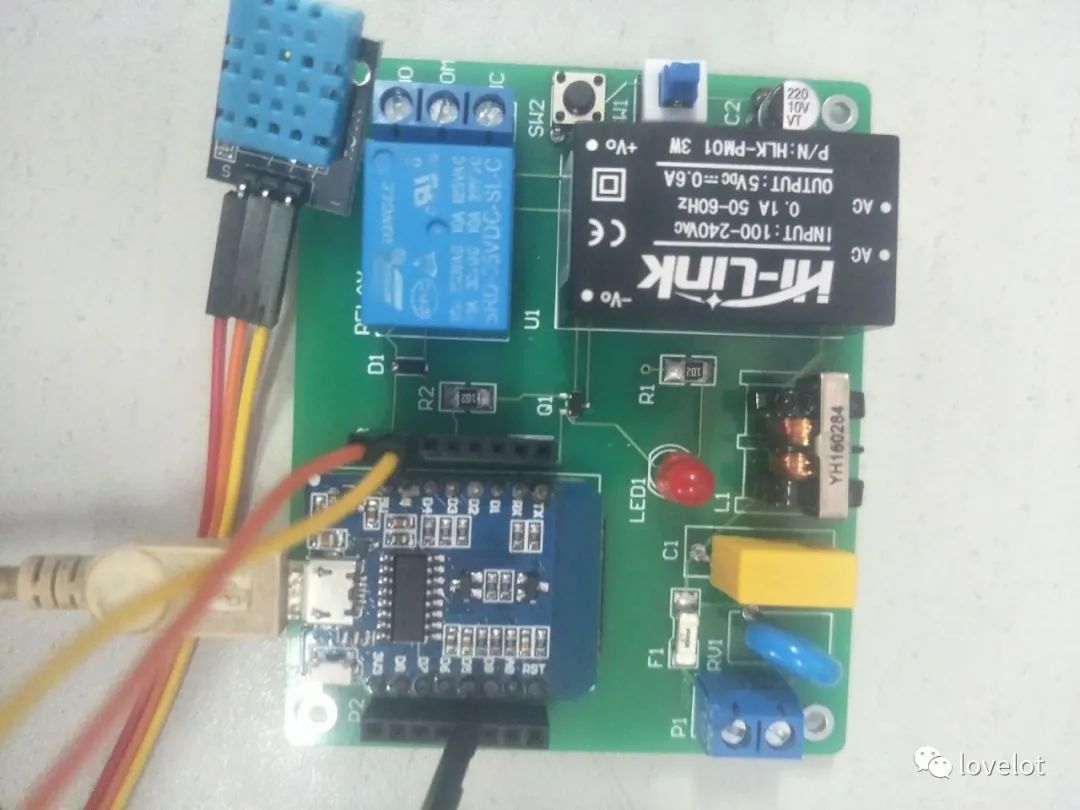
Temperature Experiment
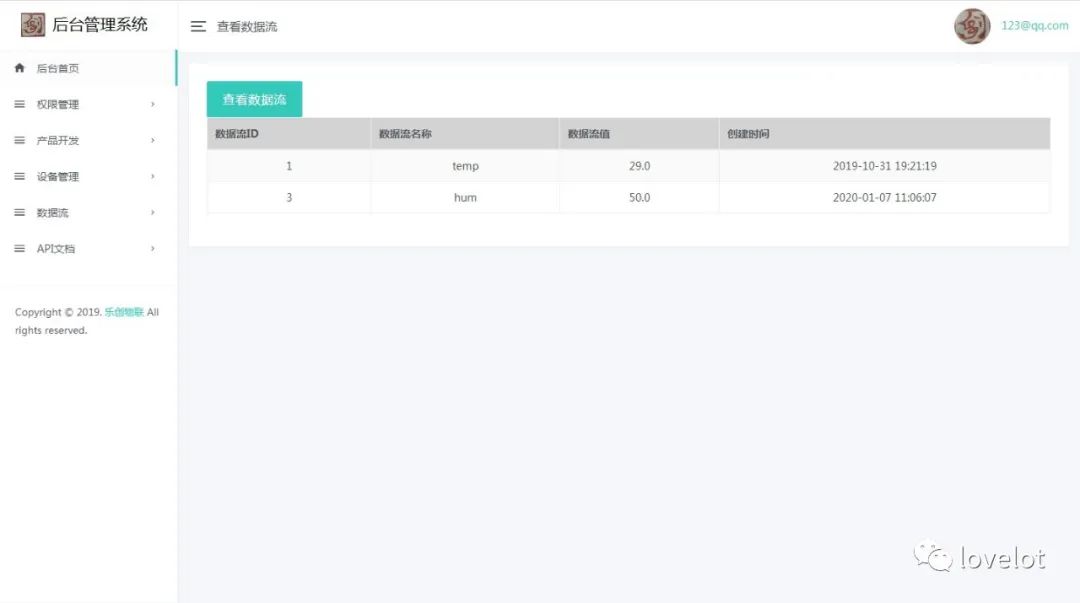
Lichuang IoT Cloud Platform
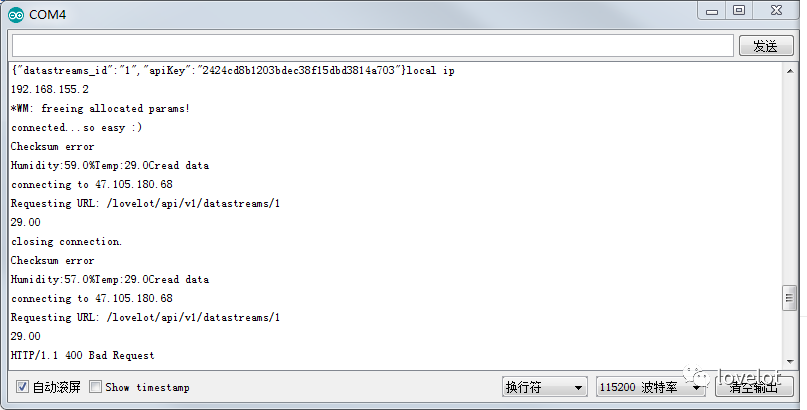
Serial Port Display
5 Conclusion
These are all verified through practice. I originally wanted to wait to open a column for these, but since it doesn’t make money, let’s make friends! Join me in getting started with IoT!