Click the blue text to follow us
1. Overview of EtherCAT
1. Features
① Open Technology
EtherCAT, short for EtherNet Control Automation Technology, is a real-time Ethernet technology proposed by Beckhoff Automation in Germany. EtherCAT is an open but not open-source technology, meaning you can use this technology freely, but you need to obtain relevant authorization from Beckhoff for the development of related devices.
② Speed

Compared to traditional fieldbus systems, EtherCAT has significantly improved data transmission rates, with options for 10Mbit/s or 100Mbit/s, and even reaching up to 1000Mbit/s with the supplementary EtherCAT G technology. Additionally, EtherCAT transmits based on standard Ethernet frames, with a single frame data capacity of up to 1486 Bytes. This gives EtherCAT unparalleled advantages in terms of data transmission volume.
③ Topology Flexibility
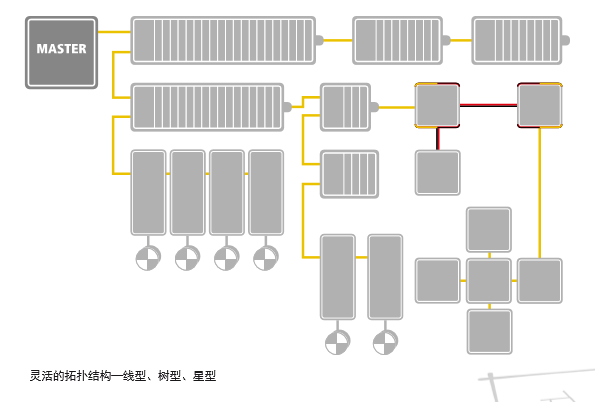
EtherCAT supports almost all topologies: star, linear, tree, daisy chain, etc., and supports various communication media such as cables and optical fibers, as well as hot-swappable features, ensuring flexibility in device connections. Furthermore, EtherCAT has virtually no device capacity limits, with a maximum of 65,535 slave devices, allowing EtherCAT data to reach each slave directly through the topology of the devices without the need for switches.
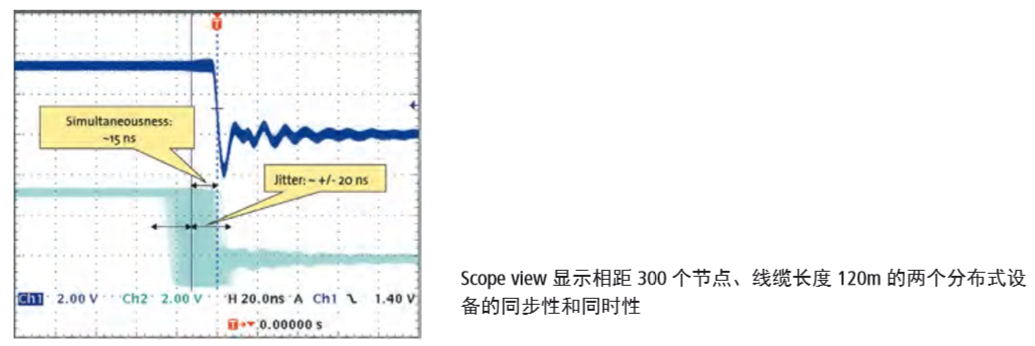
④ Precision of Synchronization
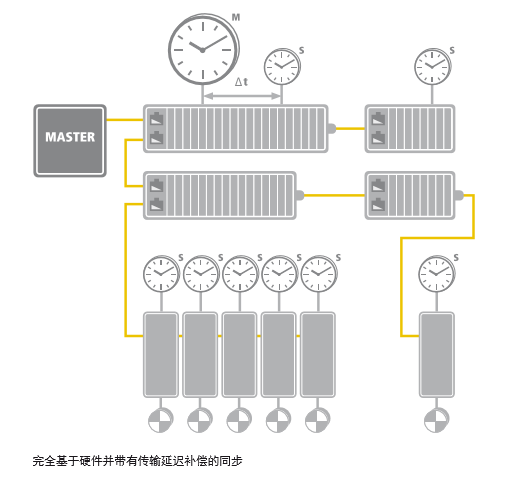
For applications requiring high data synchronization, such as coordinated motion of multiple servo axes, EtherCAT can use distributed clocks (DC) to synchronize nodes and employs a fully hardware-based time calibration mechanism, resulting in a system jitter time of less than 1us, making it fully applicable for such applications. As shown in the figure below, the signal time jitter among 300 EtherCAT nodes is only 20ns:
⑤ High Availability
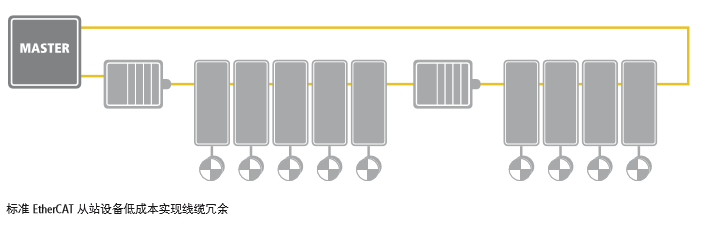
EtherCAT can achieve cable redundancy through simple measures. By connecting the last node in the network to the Ethernet port in the master device, the linear topology can be expanded into a ring redundancy topology. When cable damage or node failure occurs, additional software detection in the master stack will detect this and immediately switch to the redundant line, with no need for the nodes to change or even be aware that network communication is running on the redundant line.
2. ISO/OSI Reference Model
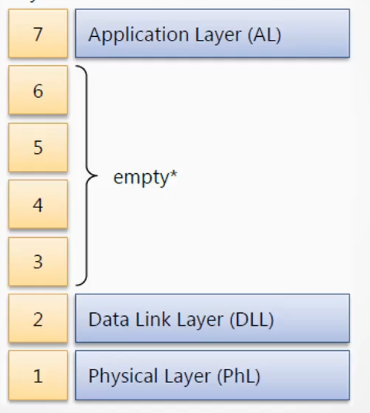
EtherCAT only uses three layers of protocols: physical layer, link layer, and application layer, which is similar to most traditional fieldbuses, but compared to other real-time Ethernet protocols such as PROFINET and EtherNet/IP, its protocol stack is more streamlined. This is one of the important reasons why EtherCAT protocol’s real-time performance is superior to other real-time Ethernet protocols.
3. EtherCAT Master-Slave Architecture
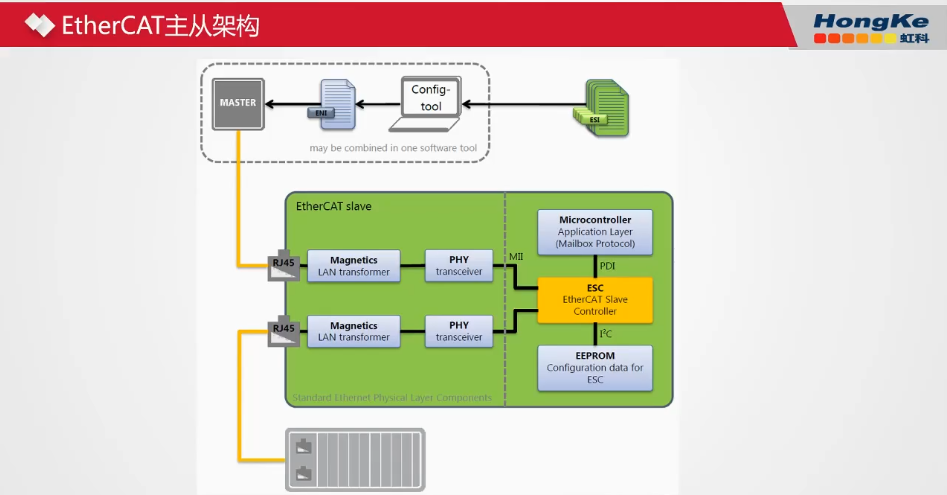
The EtherCAT network adopts a master-slave architecture, where network configuration is done on a PC host, requiring the use of relevant EMI (EtherCAT Master Information Files) and ESI (EtherCAT Slave Information Files) files. After configuration through dedicated software (usually integrated into the master configuration software), an ENI (EtherCAT Network Information Files) file is generated and downloaded to the master, which then identifies the entire network based on this file.
The internal composition of the EtherCAT slave device in the figure represents the process of implementing the EtherCAT protocol OSI model: RJ45 network port and PHY physical layer chip for the physical layer protocol; ESC for the link layer protocol, usually implemented using Beckhoff’s official ET1100 chip; and MCU for the application layer protocol, where manufacturers need to write program code according to the respective protocol or directly use protocol stack code.
4. Message Frame Transmission Method
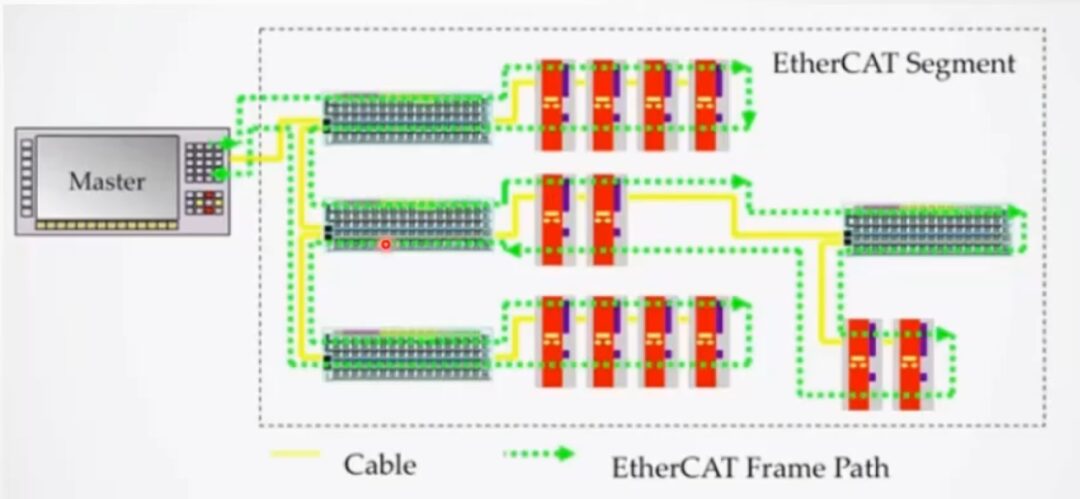
EtherCAT message frames can only be sent by the master. During a communication cycle, the master sends Ethernet data frames to each slave. When the data frame reaches the slave, each slave extracts the corresponding data from the data frame based on addressing and writes the feedback data back into the data frame. Once the data frame reaches the last slave, it returns and goes back to the master through the first slave. This transmission method allows data communication to be completed within a cycle and improves bandwidth utilization, with a maximum effective data utilization rate of over 90%. (This transmission method is somewhat similar to a circular subway in real life, where passengers get off at their destination, and passengers at each station will board accordingly.)
Exhibition Invitation
From October 12-15, 2020, the South China International Industrial Fair will be grandly held at the Shenzhen International Convention and Exhibition Center (New Hall). Our professional technical engineers are exhibiting the latest industrial communication and industrial IoT solutions at Booth A107 in Hall 10 (near Gate 2 of Hall 10), and you are welcome to visit!

About Hongke Industrial Communication
Hongke is a high-tech company with over 10 years of experience in the field of industrial automation, particularly in the industrial bus communication industry. The Hongke Industrial Communication Division collaborates deeply with world-renowned industrial communication experts such as PEAK-System, Hilscher, Kunbus, SYS TEC, Koenig-Pa, Port, Copa-data, TenAsys, SoC-e, RELYUM, etc., providing top-level industrial bus protocol hardware and software solutions, including protocols such as CAN, CANopen, EtherCAT, PROFIBUS, PROFINET, EtherNET/IP, and TSN. Product types include code, software, chips, boards, modules, etc. Hongke Industrial Communication is customer-oriented and technology-driven, providing the most suitable products and the most satisfactory services for domestic enterprises. Especially in the context of Industry 4.0, Hongke Industrial Communication keeps pace with the times and has launched TSN (Time-Sensitive Networking) solutions, which will play a connecting role like a highway in promoting the trend of the Internet of Things.