
Author: Zhao Xiaofei
IoT Think Tank Original
Please indicate the source and origin when reprinting
Introduction
Satellite-based NB-IoT networks and privately built NB-IoT networks are both aimed at expanding the ways of connecting IoT devices, achieving the goal of “connecting the unconnected”, and broadening the scope of 5G connectivity to cover as many scenarios as possible.

The author previously mentioned in the preface of the “2020 National IoT Panorama Report” that IoT communication technology is expanding its connectivity range to connect the unconnected. In recent years, NB-IoT, as a communication technology specifically for IoT, has not only been deployed by mainstream operators but has also been continuously expanding its deployment forms, aiming to cover most low-power, large-connection, long-range IoT scenarios with appropriate connectivity solutions.
Satellite-Based NB-IoT
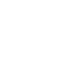
A new direction for NB-IoT is to develop towards space-based IoT, which provides a globally ubiquitous NB-IoT network through satellites, enabling IoT connectivity regardless of whether one is at sea or in deep mountains.
The startup Skylo Technologies provides ubiquitous connectivity services for global IoT users, with a highlight being the planned launch of a satellite-based global NB-IoT network in the summer of 2020, aimed at servicing mobile devices primarily in agriculture, transportation, maritime, and emergency sectors. Skylo was founded in 2017 and secured $13 million in Series A funding from three institutions by the end of that year, one of which is a venture capital firm by former Google CEO Eric Schmidt; recently, the company received $103 million in Series B funding led by SoftBank.
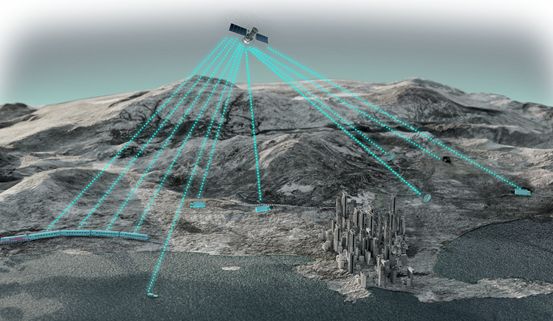
Skylo’s satellite-based NB-IoT network connects Skylo’s gateways deployed on Earth via geosynchronous communication satellites. The network operates in frequency bands defined by 3GPP, in addition to specialized synchronous satellite communication business frequency bands. This is a two-way communication network, where the gateway not only sends data back to the satellite but also, due to proprietary antenna technology, the satellite can feed data back to the gateway without additional equipment. The gateways are 8×8 inch boxes typically installed on fishing boats, train cars, and other equipment, acting as transceivers that collect local sensor data and transmit it to the cloud platform via the satellite network.
Currently, there are many satellite communication solutions, but satellite communication generally comes with high costs, whereas this NB-IoT network is relatively low-cost. According to the CEO of Skylo, the connection cost of this network saves 95% compared to existing satellite communication solutions. Specifically, the connection fee for this network is about $1 per user per month, and the hardware cost for the gateway is under $100. Skylo’s satellite NB-IoT network initially provides services in India, with its first customer being Indian Railways, which will install Skylo’s gateways in its train cars to use Skylo’s NB-IoT network.
According to data released by GSMA, as of January 2020, there are already 92 commercial NB-IoT networks worldwide. While mainstream operators globally deploy NB-IoT networks, satellite-based NB-IoT networks are fulfilling the mission of “connecting the unconnected”, supplementing cellular networks on one hand, and competing with them to some extent on the other.
In fact, Skylo is not the only vendor providing satellite NB-IoT; another American IoT company, Ligado Networks, has announced plans to build a satellite network using NB-IoT standards in the 1500MHz-1700MHz band; a Luxembourg-based company named OQ Technology has already tested software-defined radio (SDR) based NB-IoT wireless access on some commercial satellites. Additionally, we have seen many startups launch low-cost low-earth orbit satellite IoT solutions in recent years, and several private satellite companies in China are also promoting satellite IoT advancements, though no satellite-based NB-IoT networks have emerged in China yet.
Private NB-IoT Networks
According to GSMA, as of January, there are 92 commercial NB-IoT networks, all provided by mainstream operators as public IoT networks in their regions. With the maturation of NB-IoT, private NB-IoT networks have begun to emerge, providing safer and more reliable support for key industries.
In June 2019, a company named Puloli based in California, USA, announced the launch of the first private NB-IoT network, which uses the 700MHz spectrum and is deployed in northern Florida, covering most of the population in that area, aimed at providing deployment for a utility company in that region. For the private network, Puloli has explored a network-as-a-service (NaaS) business model, responsible for network design, deployment, and operation. In addition to network services, this private NB-IoT network uses NB-IoT modules based on Sequans Monarch chips from Pycom, which support the 700MHz band.
As it is a private network, Puloli has customized the frequency band specifically, using 1MHz for downlink and another 1MHz for uplink within the 700MHz band. However, since the 700MHz band has already been purchased by 21 infrastructure entities, including power, gas, water, oil, and railway companies, spectrum deployment is the most challenging aspect of establishing a private network. Puloli has collaborated with a spectrum consulting firm named Select Spectrum, which provides planning, consulting, and data analysis services for the buying and selling of radio frequency spectrum, to finalize the spectrum customization plan.

Deploying private networks is not a new phenomenon. Throughout various historical stages of mobile communication development, many key industries and enterprises have built or commissioned the construction of their own private networks based on their business needs, ensuring physical isolation from the public networks provided by operators to guarantee security. Therefore, while mainstream operators are actively deploying public NB-IoT networks, the emergence of NB-IoT private networks is a normal phenomenon.
However, from the current development situation, NB-IoT private networks have not formed a large-scale deployment trend. In fact, as early as June 2016, when the NB-IoT standard was frozen, Huawei launched the eLTE-IoT private network solution based on NB-IoT, which was described as follows by Huawei’s enterprise network official WeChat:
The eLTE-IoT solution is designed for the unlicensed IoT market for enterprises, providing low-power, medium-to-long-range wireless technology based on Sub-GHz unlicensed spectrum. Targeting typical M2M application scenarios that require low data rates, large numbers of terminals, and wide coverage, eLTE-IoT can open up vast IoT markets for government and enterprise customers, such as smart cities, electricity, and gas/water manufacturers. The eLTE-IoT chip will completely reuse the 3GPP NB-IoT chip, and the participants in the eLTE-IoT industry chain are also players in the 3GPP NB-IoT ecosystem.
Since the NB-IoT ecosystem can be reused, as the NB-IoT industry develops, the private network industry chain will also be ready. However, in addition to the industry chain, aspects such as demand and business models also need to be ready. In recent years, only a few industries like electricity have seen applications of NB-IoT private networks.
In the context of the rapid development of 5G, NB-IoT has been included in the candidate standards for 5G mMTC. Previously, many countries and industries around the world have been exploring the development of 5G private networks, and many countries have begun allocating spectrum for enterprises to build 5G private networks, forming a typical form of 5G empowering industries. Enterprises building their own 5G private networks are largely used for communication between things, connecting various IoT devices within companies, where the low-power, large-connection part will be supported by NB-IoT. From this perspective, future NB-IoT private networks will be presented more through 5G private networks.
Whether it is the satellite-based NB-IoT network or the privately built NB-IoT network, both aim to expand the ways of connecting IoT, achieving the goal of “connecting the unconnected” and broadening the scope of 5G connectivity to cover all scenarios as much as possible.
Selected Previous Articles
What Went Wrong with Those “Industry 4.0” Projects That Failed Now?
Who Will Handle the 30% IoT Connections That NB-IoT and 5G Cannot Support?

Research Report on IoT Applications Based on Blockchain| Attached
Download

A Cartoon Explains: What Can the Recently Popular NB-IoT Do Besides WiFi and Bluetooth?

2019 China IoT Industry Panorama Report|
Welcoming the Implementation of IoT Technology Solutions


