Today, I will continue to discuss the technical skills required for embedded development.Embedded development requires “hardware-software collaboration,” which means that one must not only be proficient in software programming but also in hardware development. Even if one does not study hardware, they should be able to handle the Linux system aspects (files, networks, and various API interfaces).👇🏻1. Hardware TechnologyEmbedded development is inseparable from hardware, so mastering hardware technology is fundamental. Hardware technology includes circuit design, embedded processors, memory, interface technology, etc.
1. Circuit Design
Circuit design is the first step in embedded development, involving schematic design, PCB design, etc. It involves selecting processors, configuring memory and peripherals, etc. During the circuit design process, factors such as hardware performance, power consumption, and reliability must be considered;
2. Embedded Processors
Embedded processors are the core of embedded systems, responsible for the computation and control of the entire system. Currently, mainstream embedded processors in the market include ARM, x86, MIPS, etc. When selecting an embedded processor, it is necessary to choose the appropriate processor based on specific application requirements;
3. Memory
Memory is the device used in embedded systems to store data and programs, including ROM and RAM types. During the embedded development process, it is necessary to select the appropriate memory based on specific application requirements;
4. Interface Technology
Interface technology is the means by which embedded systems communicate with external devices, including serial ports, USB, Ethernet, etc. During the embedded development process, it is necessary to master the usage of various interface technologies;
2. Software Technology
Embedded development not only requires mastering hardware technology but also software technology. Software technology includes operating systems, programming languages, development tools, etc.
1. Operating Systems
The operating system is the core software of embedded systems, responsible for resource management and task scheduling. Currently, mainstream embedded operating systems in the market include FreeRTOS, uC/OS-II, Linux, etc. When selecting an embedded operating system, it is necessary to choose the appropriate operating system based on specific application requirements;
2. Programming Languages
Programming languages are the tools used to write programs in embedded development, including C, C++, JAVA, assembly language, etc. During the embedded development process, it is necessary to select the appropriate programming language based on specific application requirements;
3. Development Tools
Development tools are used in embedded development to write, debug, and download programs, including compilers, debuggers, downloaders, etc. During the embedded development process, it is necessary to master the usage of various development tools;
3. Other Technologies
In addition to hardware and software technologies, embedded development also requires mastering other technologies, such as driver development, real-time operating systems, network communication, etc.
1. Driver Development
Driver development is the technology used to develop hardware device drivers in embedded development, serving as a bridge for communication between embedded systems and hardware devices. During the driver development process, it is necessary to master the working principles and communication protocols of hardware devices;
2. Real-Time Operating Systems
A real-time operating system is one that can complete tasks within a specified time, widely used in embedded systems. In real-time operating systems, it is necessary to master task scheduling, interrupt handling, memory management, and other technologies for developing and debugging embedded systems;
3. Network Communication
Network communication is the technology for communication between embedded systems and external networks, widely used in smart homes, industrial control, etc. In network communication, it is necessary to master network protocols, network programming, and other technologies. Common communication protocols include UART, SPI, I2C, and CAN, used for data transmission and communication between devices;
4. Microcontroller and Processor Architecture
Understanding different types of microcontrollers and processors, such as ARM, AVR, and 8051, as well as their characteristics, architecture, and performance;
5. Edge Computing Frameworks
Used for data processing and analysis at the edge of devices, reducing data transmission volume and latency;
6. Wireless Protocols
Such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc., used for wireless communication and data transmission between devices;
7. AI Algorithm Deployment
Applying artificial intelligence algorithms to embedded devices for intelligent control and decision-making;
8. RISC-V Custom Development
RISC-V is an open-source processor architecture suitable for custom development, enhancing system flexibility and efficiency;
9. Robotic Motion Control
In robotics and other automation devices, embedded technology is used to control the motion and behavior of robots;
Next, we will discuss the widely used programming languages in embedded technology and career directions, such as C, C++, and microcontroller development, along with the technologies and development directions involved. Students in related majors such as Internet of Things Engineering and Electronic Information Engineering will cover these two areas of knowledge.
-
About Microcontroller Development
From smartwatches to bank terminals, microcontroller development is indispensable, as it is widely used in various electronic products in daily life. From familiar wearable devices, Bluetooth headsets, to smartwatches, small toys, and even smart rice cookers, water heaters, and thermometers, all rely on the magic of microcontroller development. Unlike complex development requiring an operating system,microcontroller development focuses more on implementing functions in a bare-metal environment, making it easier to get started. For example, various functional developments on the STM32 board. STM32 development is just the entry-level of microcontroller development.
-
Linux Application Development
Embedded Linux application development focuses on software-level design, without involving hardware control. It is mainly developed based onQT and C++ programming languages. For example, it is applied in search engines, recommendation systems, advertising systems, autonomous driving, smart vehicle development, machine vision algorithm optimization, audio and video development: video conferencing, multimedia players, security monitoring, Qt client development, financial quantification, high-frequency trading in financial securities, game server development, game engine development, chip development, operator computing power, industrial software development, military software development, blockchain, etc. Compared to microcontroller development, it has a certain level of difficulty,and the entry threshold and salary are often better than those of microcontroller development..
-
C Language Development
Embedded C language development is known for itsefficiency, hardware-level operation capability, cross-platform compatibility, rich library functions, and extensive community support. Its low-level operability and directness allow programmers to better control hardware resources and operate at the lower levels. The compilers and debugging tools for C language are also relatively mature, providing convenience for developers. Therefore, C language is widely used in embedded system development. For example,C language is often used to develop smart home devices, such as smart lighting control systems, smart sockets, etc. It is also widely used in automotive electronic control systems, including in-vehicle electronics, engine control systems, in-vehicle entertainment systems, etc. It is also commonly used in medical devices, such as ECG monitors, blood pressure monitors, etc. Compared to microcontroller development, it shares a certain level of difficulty, butthe entry threshold and salary are often better than those of microcontroller development..
With the advent of the Internet of Things era, the connection between embedded devices and the Internet will become closer. Embedded systems, as dedicated computer systems embedded in devices or systems, combine with the Internet of Things through various communication technologies to connect physical devices to the Internet for information exchange and communication, providing strong momentum for the development of smart devices and smart systems.
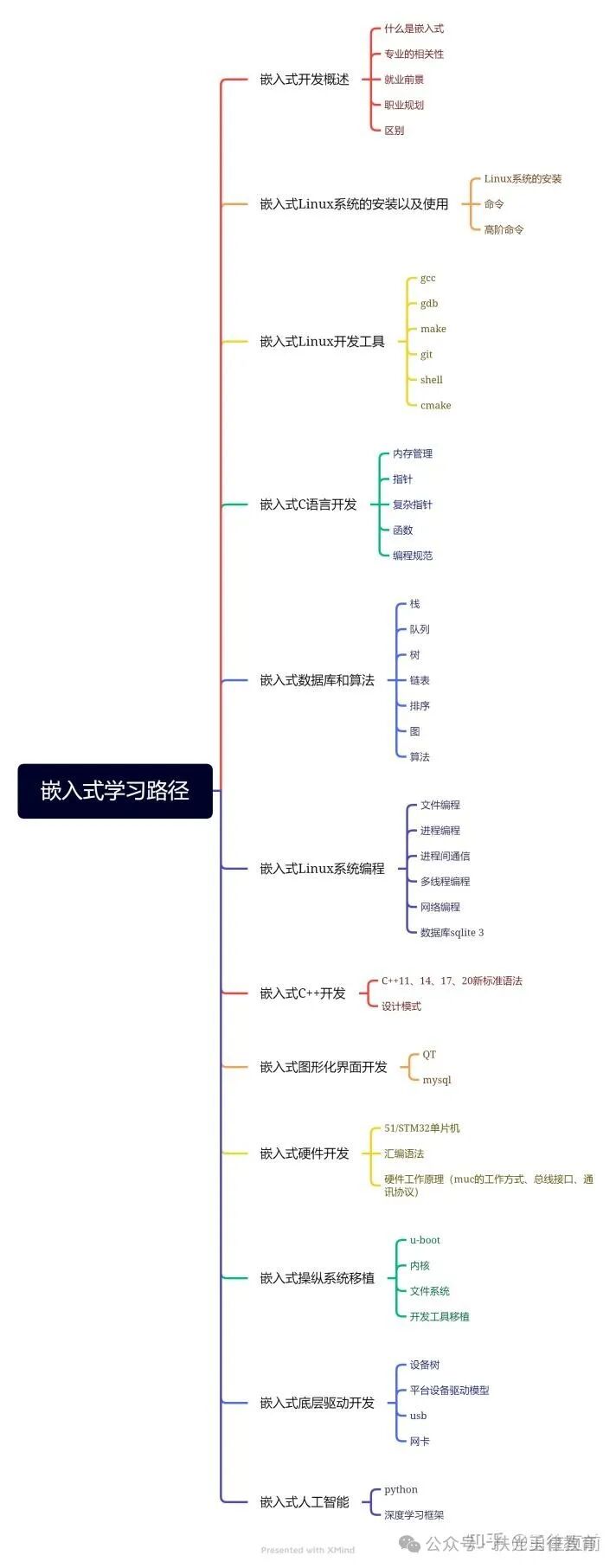
Finally, here is a reference roadmap for embedded learning.This roadmap can help everyone formulate a suitable learning plan based on their situation.