1. Introduction to IPI Interrupts
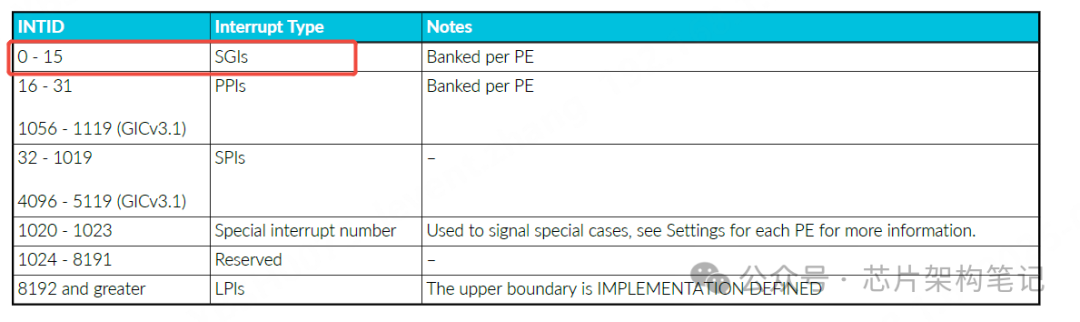
IPI interrupts, or Inter-Processor Interrupts, are essentially the SGI interrupts (Software Generated Interrupts) defined in the ARM GIC architecture. In the GICv3 architecture, there are a total of 16 SGI interrupts (excluding extensions), with interrupt numbers ranging from 0 to 15, as shown in the figure below.
Inter-Processor Interrupts are signals sent from one CPU core (PE) to a target CPU core (target PE) in the system to prompt the target CPU to perform specific operations. The basic flow of an IPI interrupt is as follows: PE triggers -> GICR -> GICD -> target GICR -> target CPU interface -> target PE.
Triggering IPI Interrupts: PE triggers by writing to system registers ICC_SGI0R_EL1, ICC_SGI1R_EL1, or ICC_ASGI1R_EL1.
There are two routing modes for IPI interrupts (set via ICC_SGI0R_EL1.IRM/ ICC_SGI1R_EL1.IRM):
-
If the IRM bit is 1, the SGI will be broadcast to all PE in the system (except the PE that generated the SGI).
-
If the IRM bit is 0, the SGI will be sent to specific PE, designated by Aff3.Aff2.Aff1. (This can include the PE that generated the SGI).
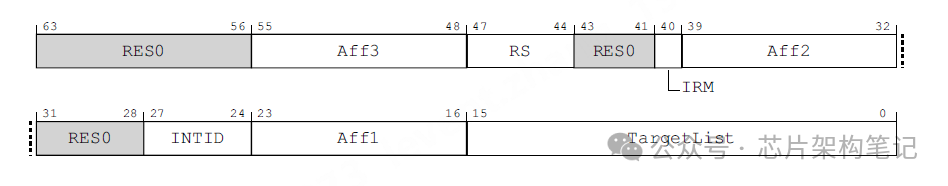 Registers ICC_SGI0R_EL1/ICC_SGI1R_EL1
Registers ICC_SGI0R_EL1/ICC_SGI1R_EL1
2. Types of IPI Interrupts in Linux
In the Linux kernel code, 8 types of IPI interrupts are defined by default (SGI0 – SGI7), as follows (linux/arch/arm64/kernel/smp.c):
enum ipi_msg_type { IPI_RESCHEDULE, IPI_CALL_FUNC, IPI_CPU_STOP, IPI_CPU_CRASH_STOP, IPI_TIMER, IPI_IRQ_WORK, IPI_WAKEUP, NR_IPI};
-
IPI_RESCHEDULE
enum ipi_msg_type { IPI_RESCHEDULE, IPI_CALL_FUNC, IPI_CPU_STOP, IPI_CPU_CRASH_STOP, IPI_TIMER, IPI_IRQ_WORK, IPI_WAKEUP, NR_IPI};IPI_RESCHEDULE
Interrupt 0, re-schedules the process scheduler_ipi().
Typically, the TIF_NEED_RESCHED flag is set for the process (indicating that the process needs to be scheduled). If the process is not on the current CPU, the IPI_RESCHEDULE interrupt is triggered for the target CPU via the smp_send_reschedule interface, and the target CPU eventually enters handle_IPI’s scheduler_ipi.
-
IPI_CALL_FUNC
IPI_CALL_FUNC
Interrupt 1, calls generic_smp_call_function_interrupt(), executing a callback function on a remote CPU.
When a function needs to be called on a specific CPU (not the current CPU), the IPI_CALL_FUNC interrupt is triggered, commonly using the smp_call_function interface to trigger the target CPU’s IPI_CALL_FUNC soft interrupt.
-
IPI_CPU_STOP
IPI_CPU_STOP
Interrupt 2, calls local_cpu_stop() to stop the current CPU and enter a low-power state (wfi/wfe).
When one CPU wants to stop other CPUs, it sends this IPI. The main interfaces are machine_halt, machine_power_off, and machine_restart. These interfaces will call smp_send_stop to trigger the IPI_CPU_STOP interrupt, and the target CPU will call local_cpu_stop() upon receiving the interrupt, as follows:
static void local_cpu_stop(void) { set_cpu_online(smp_processor_id(), false);/* Bring the current CPU offline */ local_daif_mask(); /* Set the DAIF state bits of pstate to 1, disabling system debugging (D), system error SError (A), IRQ interrupts (I), and FIQ interrupts (F) for this CPU */ sdei_mask_local_cpu(); cpu_park_loop(); /* Enter low-power standby state using wfe and wfi instructions */ }
-
IPI_CPU_CRASH_STOP
IPI_CPU_CRASH_STOP
Interrupt 3, calls ipi_cpu_crash_stop(), stopping the processor.
When a system crash occurs, the crashing CPU sends this interrupt to other CPUs. In systems with KEXEC enabled, the following response is made: register information is saved and passed to the second kernel. KEXEC is commonly used to quickly enter the second kernel without rebooting during a system crash. The purpose of the second kernel is to save the current DDR memory image for later analysis of the system crash issue using crash tools.
-
IPI_TIMER :
IPI_TIMER :
Interrupt 4, calls tick_receive_broadcast(), broadcasting clock events.
When a CPU calls tick_broadcast(const struct cpumask *mask), it triggers the IPI_TIMER interrupt to send a timer broadcast interrupt to the specified CPUs (as designated by the mask), and the target CPU executes the tick_receive_broadcast() function in response.
-
IPI_IRQ_WORK :
IPI_IRQ_WORK :
Interrupt 5, calls irq_work_run(), executing a callback function in the interrupt context.
-
IPI_WAKEUP :
IPI_WAKEUP :
Interrupt 6, calls acpi_parking_protocol_valid(cpu), waking up the CPU. When a CPU core receives this IPI interrupt, it wakes up from the parked state (low-power state of wfi/wfe).
-
NR_IPI :
NR_IPI :
Interrupt 7, not used.
3. IPI Interrupt Source Code
The function responsible for handling IPI interrupts ishandle_IPI, with the source code as follows:
<arch/arm64/kernel/smp.c> void handle_IPI(int ipinr, struct pt_regs *regs) { unsigned int cpu = smp_processor_id(); /* Get the current CPU id */ struct pt_regs *old_regs = set_irq_regs(regs); /* pt_regs structure contains the current register information */ if ((unsigned)ipinr < NR_IPI) { /* The current valid IPI interrupts are 7 */ trace_ipi_entry_rcuidle(ipi_types[ipinr]); /* ftrace records entry into IPI interrupt for debugging */ __inc_irq_stat(cpu, ipi_irqs[ipinr]); /* Count different types of IPI interrupts for each CPU */ } switch (ipinr) { case IPI_RESCHEDULE: scheduler_ipi(); /* Trigger re-scheduling */ break; case IPI_CALL_FUNC: irq_enter(); generic_smp_call_function_interrupt(); /* Execute all function callbacks for this CPU */ irq_exit(); break; case IPI_CPU_STOP: irq_enter(); local_cpu_stop(); /* Stop this CPU and enter low-power state */ irq_exit(); break; case IPI_CPU_CRASH_STOP: if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_KEXEC_CORE)) { /* If KEXEC is configured, the system panic will enter the second kernel */ irq_enter(); ipi_cpu_crash_stop(cpu, regs); unreachable(); } break; #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_CLOCKEVENTS_BROADCAST case IPI_TIMER: irq_enter(); tick_receive_broadcast(); /* Receive timer broadcast and execute timer interrupt callback */ irq_exit(); break; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_WORK case IPI_IRQ_WORK: irq_enter(); irq_work_run(); /* Execute irq_work for this CPU */ irq_exit(); break; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_ACPI_PARKING_PROTOCOL case IPI_WAKEUP: /* Wake up this CPU from low-power state */ WARN_ONCE(!acpi_parking_protocol_valid(cpu), "CPU%u: Wake-up IPI outside the ACPI parking protocol\n", cpu); break; #endif default: pr_crit("CPU%u: Unknown IPI message 0x%x\n", cpu, ipinr); break; } if ((unsigned)ipinr < NR_IPI) trace_ipi_exit_rcuidle(ipi_types[ipinr]); set_irq_regs(old_regs); }