01
About the Three Musketeers of Linux
-
grep: Filters keyword information data. Mainly used to search for data within text.
-
sed: Edits text data and modifies the original file content.
-
awk: Filters and extracts data from files, and can format the output.
-
awk can also present the processed data in a more visually appealing way.
02
What is sed
-
sed software itself
-
Commands provided by sed for processing
-
Source data provided to sed
sed Syntax Format
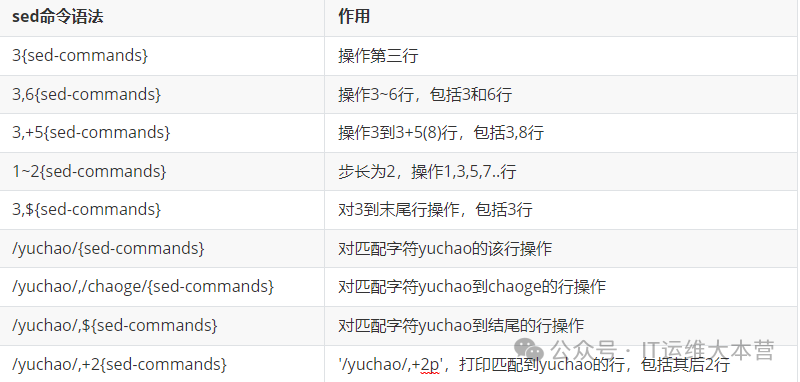
sed [options] [sed built-in command character] [input file]Explanation:
- Note that there must be at least one space between the sed software, options, sed command, and input file.
- To avoid confusion, the text refers to sed as the sed software. sed-commands (sed commands) are some built-in command options of the sed software, distinguished from the previous options.
- sed-commands can be a single sed command or a combination of multiple sed commands.
- input-file (input file) is optional; sed can also get input from standard input or a pipe.
Syntax
sed replace character data
s replace instruction
#data before replacement (regex)#data after replacement#
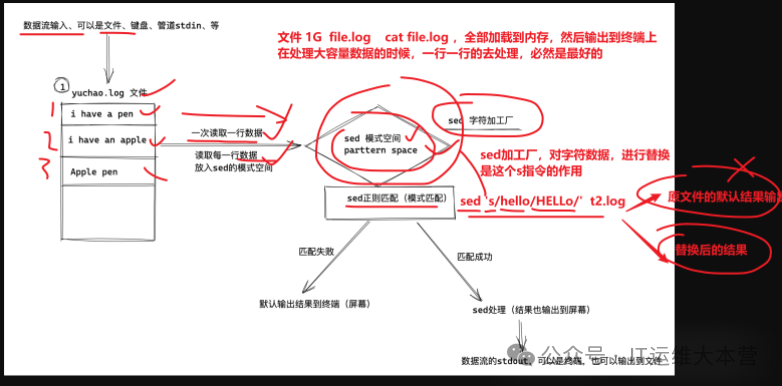
sed 's#data before replacement#data after replacement#' file.txtsed Command Execution Process
Overview process:
sed software reads a line from a file or pipe, processes one line, outputs one line; then reads another line, processes it, and outputs it....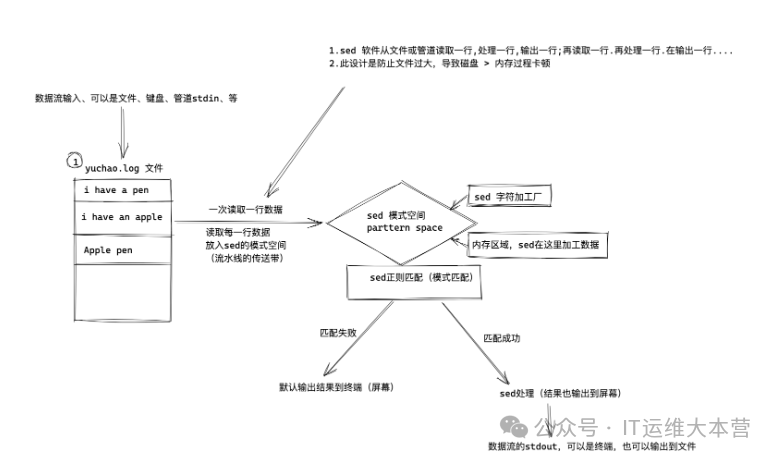
sed Parameters
sed modifies data in the pattern space by default
(Simply put, sed reads a line of text data, modifies it in memory, and the result is not written back to the file by default; it is only modified in memory and printed for you to see the result)
To write the modified result back to the file,
you need to use the parameter function.
-i Write the result processed by sed to the file, and do not print it to the terminal.
sed -i 's#data before replacement#data after replacement#' file.txtoptions[options]
Explanation
-n Cancel the default output of sed software, often used with the sed command p.
-e A single command statement can execute multiple sed commands.
-f The option can be followed by the filename of the sed script.
-r Use extended regular expressions; by default, sed only recognizes basic regular expressions.
-i Directly modify the file content instead of outputting to the terminal. If the -i option is not used, sed only modifies the data in memory and does not affect the file on disk.sed Commands
sed provides many functional commands
Insert data at a specific line
Replace character data
sed-commands[sed commands]
Explanation
a Append, add one or more lines of text after the specified line.
c Replace the specified line.
d Delete the specified line.
D Delete part of the content in the pattern space until a newline character is encountered, related to multi-line mode.
i Insert, add one or more lines of text before the specified line.
h Copy the content of the pattern space to the hold space.
H Append the content of the pattern space to the hold space.
g Copy the content of the hold space to the pattern space.
G Append the content of the hold space to the pattern space.
x Swap the content of the pattern space and the hold space.
l Print invisible characters.
n Clear the pattern space and read the next line of data, appending it to the pattern space.
N Do not clear the pattern space, read the next line of data, and append it to the pattern space.
p Print the content of the pattern space, usually p is used with the -n option.
P (uppercase) Print the content of the pattern space until a newline character is encountered, ending the operation.
q Exit sed.
r Read data from the specified file.
s Replace, s#old#new#g==> here g is the substitute flag for the s command, note the distinction from the g command.
w Save, save the content of the pattern space to a file.
y Convert characters based on corresponding positions.
:label Define a label t. If the previous command executes successfully, jump to the label t to continue executing subsequent commands; otherwise, continue the normal execution flow.sed Matching Text Range
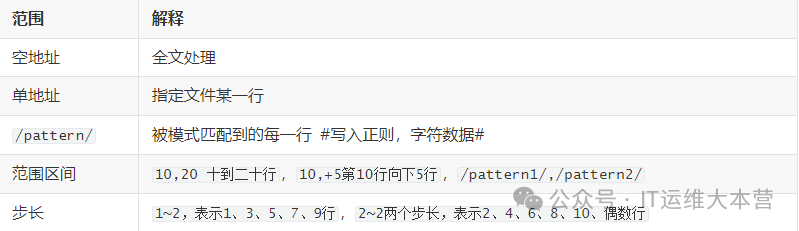
sed Modifying Characters and Canceling Default Output
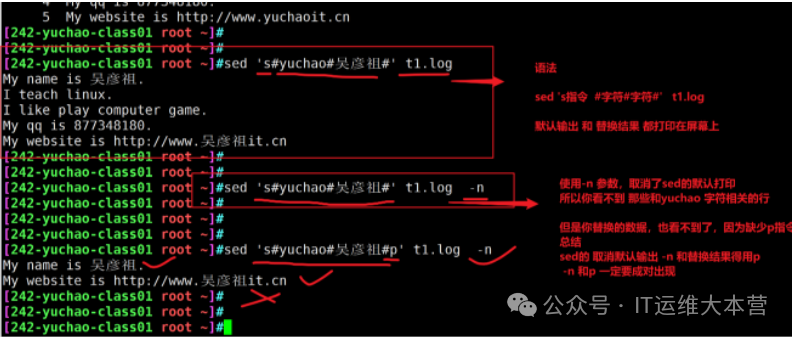
sed CRUD (Practice) During practice, do not use the -i parameter to modify the source file, just observe the replacement results.
sed Add Character Command
"a": Append text to the specified line, remember that the full spelling of a is append, meaning to add. Add one or more lines of text.
3a means to append data below the third line.
"i": Insert text before the specified line, remember that the full spelling of i is insert, meaning to insert. Add one or more lines of text.
3i means to insert data above the third line.Single Line Add Command
Line
sed 'line number sed command your character data to add' Insert data after the second line in the source file, 'Today is another beautiful day.'[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed '2 a "今天又是美好的一天" ' t1.log
My name is yuchao.
I teach linux.
"今天又是美好的一天"
I like play computer game.
My qq is 877348180.
My website is http://www.yuchaoit.cnInsert data before the second line
sed '2 i 今天雾霾比较大' t1.logsed Multi-line Addition
Data to be added contains newlines.
cat to Achieve Multi-line Text Append
cat >>my.log<<EOF
你好
我好
他也好
EOFecho Append Multi-line Data
Usage is as follows
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#echo -e "hello\nworld\n你好\n我也好" > hello.log
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#cat hello.log
hello
world
你好
我也好sed Append Multi-line Text
Both cat and echo can only append content to the end of the file.
However, sed processes text line by line, allowing you to specify which line to process, meaning you can insert character data at a specified line.
Use \n to add multi-line data.
Add two lines of data to the beginning of t1.log
加油
奥力给
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed -i '1 i 加油\n奥力给' t1.log
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#cat -n t1.log
1 加油
2 奥力给
3 My name is yuchao.
4 I teach linux.
5 I like play computer game.
6 My qq is 877348180.
7 My website is http://www.yuchaoit.cnPractice sed to Append Configuration File Information (Single Line)
1. Practice modifying the nginx configuration file, inserting new data listen 81; at line 39.
Only modify and see the modification result on the terminal, but do not modify the file.
sed '39 i listen 81;' /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
sed -i '39 i listen 81;' /etc/nginx/nginx.confModify sshd_config in Practice For example, when optimizing system initialization, we need to modify the sshd server settings and add the following multi-line configuration.
Port 25515 # Change port
PermitRootLogin no # Do not allow root login
PerminEmptyPasswords no # Do not allow empty passwords
UseDNS no # Do not perform hostname resolution, speed up ssh connection
GSSAPIAuthentication no # Do not perform hostname resolution, speed up ssh connectionBackup the Source File Before Modification
Source file /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Backup, add ori suffix
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config{,.ori}sed Write Multi-line Configuration Add These Configurations at the Beginning
sed -i '1 i Port 25515\nPermitRootLogin no\nPerminEmptyPasswords no\nUseDNS no\nGSSAPIAuthentication no' /etc/ssh/sshd_configsed Delete Character Data
d Delete the specified line
d command means delete, delete means delete.
sed processes all text by default; if no range is specified, sed will delete all text line data.sed Delete the Second Line of Data
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed '2 d' t1.logsed Delete Lines 1 to 4
sed '1,4d' t1.logAbout sed Handling File Line Range Syntax
Delete the third line of data
sed '3 d' t1.log
Delete lines 3 to 6 of the file
sed '3,6 d' t1.log
Delete starting from the third line, down 2 lines
sed '3,+2 d' t1.log
Delete odd lines 1,3,5,7,9
sed '1~2 d' t1.log
Delete even lines 2,4,6,8
sed '2~2 d' t1.log
Keep the first three lines
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed -e '4,$ d' t1.log
Find the line containing game and delete it
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed '/game/ d' t1.log
Delete from the line containing game to the end
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed '/game/,$ d' t1.log
Delete all lines containing game and the next line
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed '/game/,+1 d' t1.log
Print Line Range Practice
sed provides the print command p
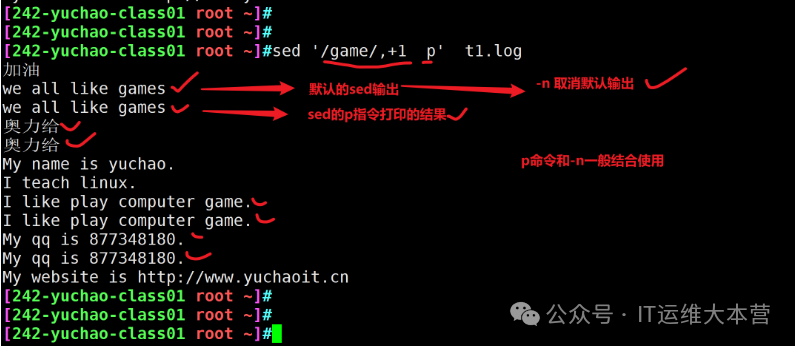
sed Delete Command Practice
Metadata
[yuchao-linux01 root ~]#cat chaoge.log
My name is yuchao.
I teach linux.
I like play computer game.
My qq is 877348180.
My website is http://www.yuchaoit.cnDelete All Lines in the File
sed does not specify a line number, by default matches all lines, executing d to delete command
sed 'line number d command' file
sed 'd' fileDelete the Second Line of the File
sed '2 d' fileDelete Lines 1 to 3
sed '1,3 d'Delete Lines 1, 2, and 4
The syntax is to separate multiple commands with semicolons for multiple deletions.
sed '1 d;2 d;4d;' t1.logDelete Lines Containing game
sed '/game/d' t1.logDelete Lines Containing game and http
sed '/game/d;http/d' t1.logDelete Lines Starting with My
sed '/^My/d' t1.logsed Ignore Case Commandsed provides the uppercase I command to ignore case.
sed '/^My/ld' t1.logDelete Lines Ending with .
sed '/.$/d' t1.logDelete Lines from the Second Line to the Line Containing qq
sed '2,7d' t1.log
sed '2,/qq/d' t1.logDelete Lines 2 and 5
sed '2d;5d' t1.logDelete Lines 2 to 5
sed '2,5d' t1.logDelete Lines from 3 to the End
sed '3,$d' t1.logDelete Even Lines (Step)
seq 1 10 | sed '2~2d'Delete Odd Lines (Step)
seq 1 10 | sed '1~2 d'Exclamation Mark Negation
!d The command of sed to ignore case
Delete All Lines Except Those Containing yuchao
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed '/yuchao/!d' t1.log
My name is yuchao.
My website is http://www.yuchaoit.cnDelete All Lines Except Those Starting with My
sed '/^My/!d' t1.logsed Modify Data
Replace Entire Line Command (c)
c Replace the selected line with new text.
Replace line 11 with new data, "Woke up, feeling refreshed."
Syntax
sed '11 c 睡醒了,精神很饱满' t1.logReplace the Second Line of the File with “I love linux, python!”
Replace the entire line
sed '2c I love linux, python!' t1.logReplace Characters (s Command)
Explanation of the sed replacement command
This delimiter is commonly in the following forms:
sed 's/old_string/new_string/'
sed 's#old_string#new_string/'
sed 's@old_string@new_string/'
It is strongly recommended to use #
sed 's#old_string#new_string#'
Replace once
sed 's/replaced character/replacement character/' file
Global replacement, global replacement
sed 's/replaced character/replacement character/g' file
s replaces the first matching character in each line
s/old_string/new_string/
sed 's#i#I#' t1.log
g global replacement, every matching character in each line is replaced
s/old_string/new_string/
sed 's#i#I#g' t1.log
sed 's/i/I/g' t1.log
-i option, parameter, directly modify the file
sed by default modifies the data in the pattern space in memory and does not modify the source file. Using -i will modify the source file and the data on disk.Test Data
My name is yuchao. you can call me yuchao.
I teach linux.
I like play computer game.
My qq is 877348180.
My website is http://www.yuchaoit.cn , and another website is https://www.yuchao.top/Replace character yuchao with 老于 Replace once
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed 's#yuchao#老于#' t1.log
My name is 老于. you can call me yuchao.
I teach linux.
I like play computer game.
My qq is 877348180.
My website is http://www.老于it.cn , and another website is https://www.yuchao.top/Replace Multiple Times, Global Replacement
sed 's#yuchao#老于#g' t1.log Replace the Third Line’s computer with linux
sed ‘3 s#computer#linux#g’ t1.log
All My to His Specify my beginning
Note that sed provides the command to ignore case, uppercase I
Note the case
Without the case-ignoring command
sed 's#^My#His#' t1.log
Add the case-ignoring command
sed 's#my#His#Ig' t1.lognew_name="彭于晏"
Note the role of single quotes and double quotes in variable parsing
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed "s#yuchao#$new_name#g" t1.logsed Group Replacement
Do not forget the extended regex -r parameter
Syntax:
sed software also provides the grouping function with \(\)
Use \1 to reference the data of the first bracket
\2 to reference the data of the second bracket
sed can remember up to 9 groups
() \1 to reference group data backwardExtract the word welcome
echo 'I am teacher yuchao,welcome my linux course' | sed -r 's/^.*,(.*)m.*/\1/g'
welcomeGroup Extraction of IP
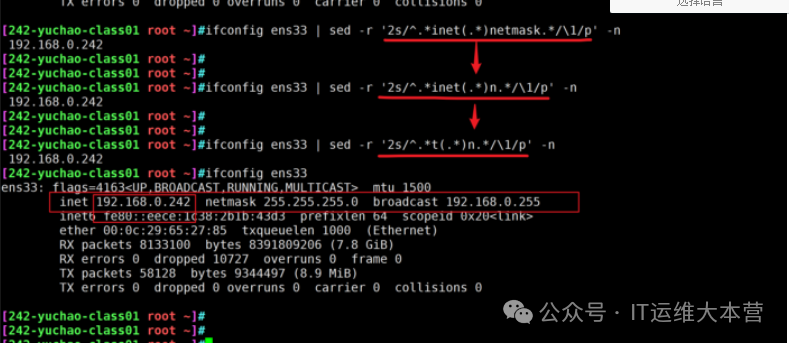
\s represents a single space
Head and tail removal method
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#ifconfig ens33 | sed -e '2s/^.*inet//' -e '2s/netmask.*//p' -n
192.168.0.242
Group Extraction Method
sed Query
sed print command p prints the data processed by sed regex
And sed prints the pattern space by default, which can be canceled with -n
Text, 10 data > sed reads line by line, edits > prints
Fixed usage, as long as p is used to print some data, it is necessary to use -n to cancel the default print, the purpose is to only see the data you want to print.
Print the Second Line
sed '2 p' t1.logPrint the First Three Lines
sed '1,3p' t1.log -nOnly Display the Line Containing the QQ Number
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed -r '/[0-9]{9}/p' t1.log -n
My qq is 877348180. my num is 1555555555.Find the Lines Containing http and linux
-e Multiple Edits
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed -e '/http/p' -e '/linux/p' t1.log -n
I teach linux.
My website is http://www.yuchaoit.cn , and another website is https://www.yuchao.top/
[242-yuchao-class01 root ~]#sed '/http/p;/linux/p' -n t1.log
I teach linux.
My website is http://www.yuchaoit.cn , and another website is https://www.yuchao.top/
sed Other Commands
w Command
The function is to write the results of sed operations to a specified file.
sed '/pattern/w new_file' old_file
Must find the line containing computer, write the data to game2.log file
sed '/computer/w game2.log' t1.log -nReplace all yuchao in the file with 老于, write new data to yu.log
sed 's#yuchao#老于#g' t1.log -n-e Option
-e option is used to connect multiple sed commands Extract information from lines 1, 2, and 4
Syntax
sed -e 'sed command' -e 'sed command' -e 'sed command'
sed -e '1p' -e '2p' -e '4p' t1.log -n; Semicolon
Semicolon is also used to execute multiple commands, just like basic Linux commands support this syntax.
Extract information from lines 1, 2, and 4 separately
sed '1p;2p;4p' t1.log -n sed -e '1p' -e '2p' -e '4p' t1.log -n