Overview of Embedded Systems
An embedded system is a dedicated computer system that is application-centric and based on computer technology, capable of adapting to various applications, integrating configurable and customizable hardware and software.Characteristics of Embedded Systems1. Strong specificity: Software and hardware are closely integrated.2. Strong real-time performance: Requires timely responses within a specified time frame.3. Strong hardware-software dependency4. Dedicated processors5. Integration of multiple technologies6. System transparency7. Limited system resources: Storage capacity, number of I/O devices, and processing power of the processor are relatively limited.Components of Embedded Systems (5 Core Functional Components)1. Sensors: Convert physical parameters into electrical signals for processing.2. Processing Unit (PE): Receives digital data from input interfaces, processes the data, and decides to execute a certain output function.3. Actuators: Receive electrical signals and perform physical actions.4. Input Interface: Converts electrical signals into a digital form that can be processed by a computer.5. Output Interface: Processes the binary data output from the real-time computer and converts it into the signal format required by actuators or other output devices.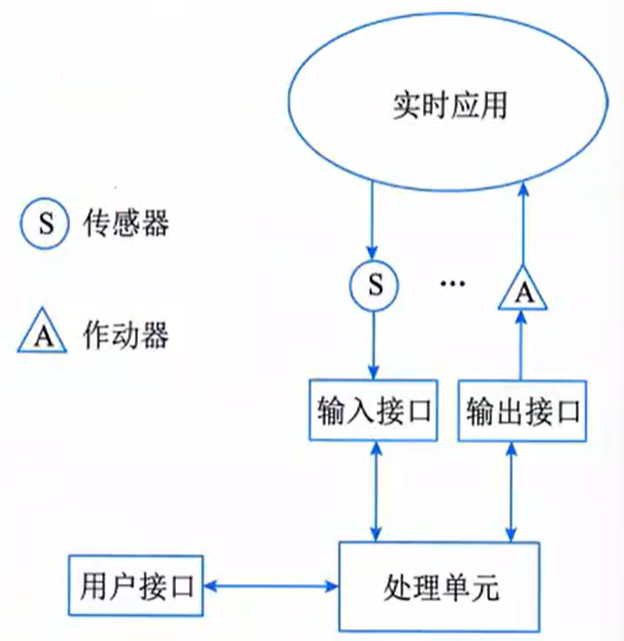 Architecture of Embedded Systems
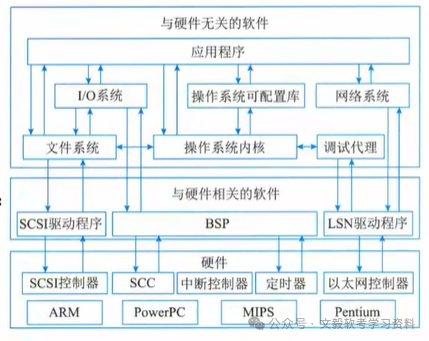
Architecture of Embedded Systems
- Hardware Layer: Includes embedded microprocessors, memory, general device interfaces, and I/O interfaces.
- Middle Layer: Hardware Abstraction Layer/Board Support Package (BSP), separates the upper software from the lower hardware, making the system’s lower-level drivers hardware-independent. This layer generally includes initialization of related lower-level hardware, input/output operations, and configuration functions for hardware devices.
- System Software Layer: Composed of Real-Time Operating System (RTOS), file systems, graphical user interfaces (GUI), embedded databases, network systems, and general component modules.
- Functional Layer: Composed of programs developed to perform specific tasks running on the operating system.

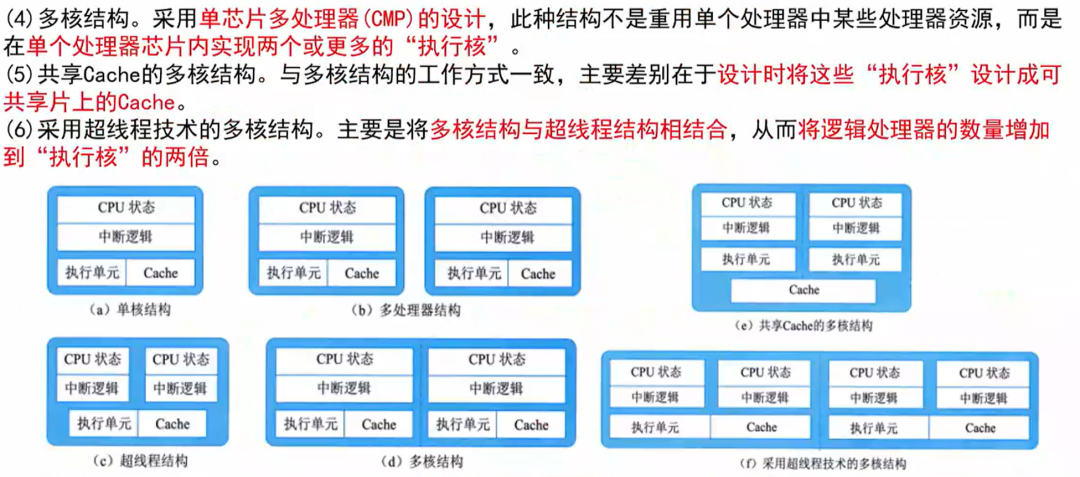 Typical Architectures of Embedded Systems
Typical Architectures of Embedded Systems
1. Hierarchical Model Architecture
There is a dependency relationship between high-level abstract concepts and lower-level more concrete concepts.
2. Recursive Model Architecture
Top-down: Identify structural objects starting from the system level.
Bottom-up: Focus on the construction of domains, first identifying key classes and relationships within the domain.
Principles and Characteristics of Embedded System Software Architecture
Overall structure, hierarchical structure, client/server structure, object-oriented structure.
The following diagram is an architecture diagram of an overall structure, based on a structured programming design method.

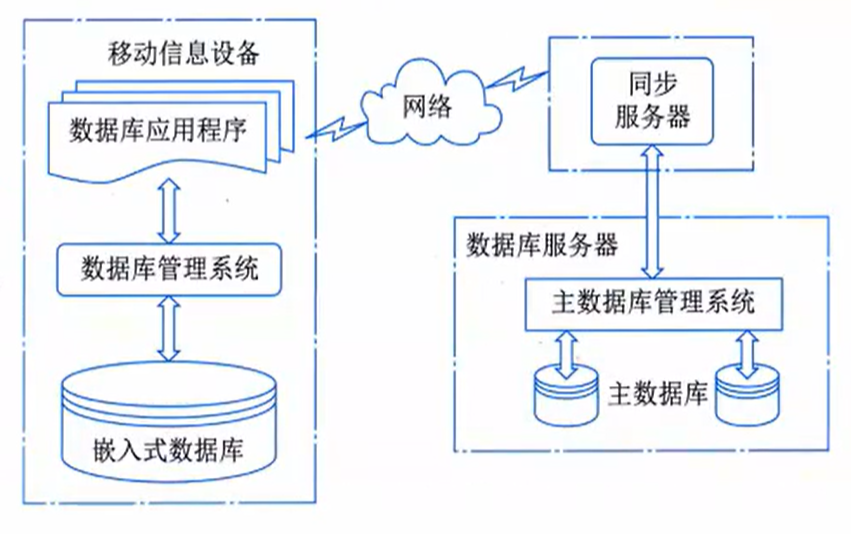
Embedded Database Systems
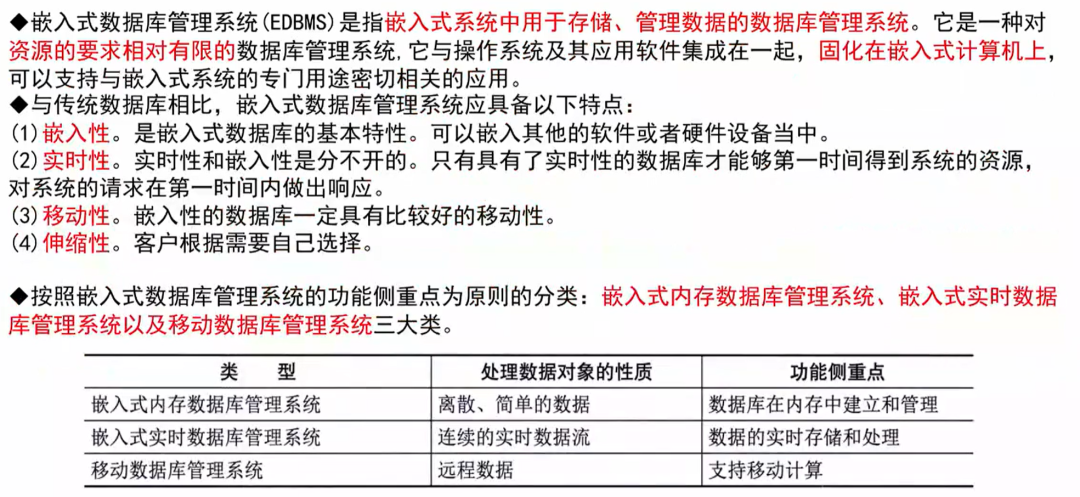 A complete EDBMS consists of the following parts
A complete EDBMS consists of the following parts
1. Embedded Database
2. Synchronization Server
3. Database Server
4. Connection Network
Embedded Operating Systems
 For different hardware platforms, operating systems are usually built on an abstraction layer. This abstraction layer is located between the underlying hardware and the kernel, providing various portable macro definition interfaces for the kernel. When porting between different platforms, only the macro definitions need to be modified.The structure of hardware abstraction is divided into three levels
For different hardware platforms, operating systems are usually built on an abstraction layer. This abstraction layer is located between the underlying hardware and the kernel, providing various portable macro definition interfaces for the kernel. When porting between different platforms, only the macro definitions need to be modified.The structure of hardware abstraction is divided into three levels
1. System Structure Abstraction Layer: Abstracts the characteristics of the CPU core.
2. Processor Variant Abstraction Layer: Abstracts the characteristics of CPU variants.
3. Platform Abstraction Layer: Abstracts the characteristics of different platforms.




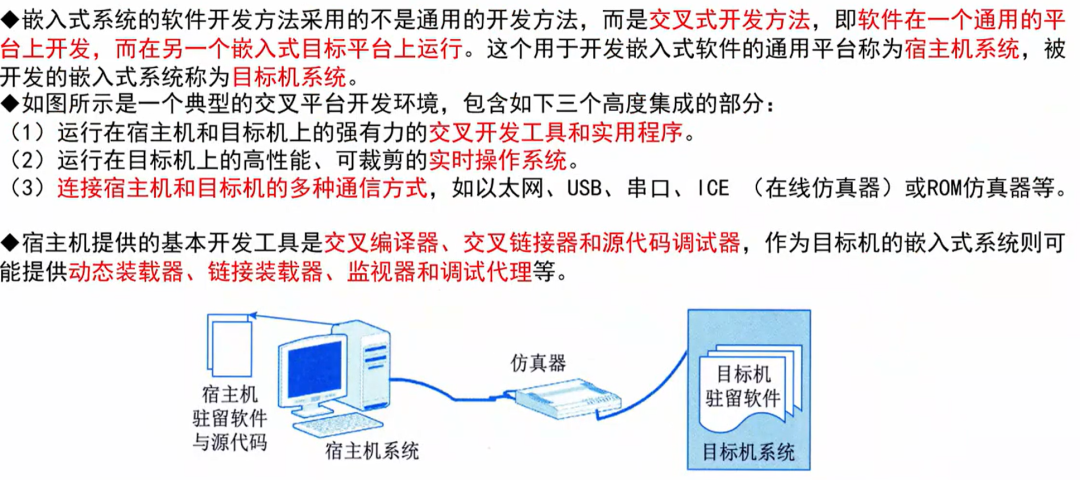
Embedded System Development
 Embedded System Software Architecture Design Methods
Embedded System Software Architecture Design Methods
1. Typically adopts a top-down design approach, based on architectural software design (ABSD)
2. Attribute-driven software design (ADD) takes a set of quality attribute scenarios as input, using the understanding of the relationship between quality attribute implementation and architectural design to design software.
3. Real-time system design method (DARTS) mainly decomposes real-time systems into multiple concurrent tasks and defines the interfaces between these tasks.
Embedded System Rapid Object-Oriented Process (ROOPES)
Half-spiral lifecycle model combines the waterfall model and spiral model, appropriately tailored to fit different projects. The half-spiral model requires creating a series of prototypes, with different parts of the prototypes developed independently by different teams, then integrated and tested together.
Wireless Internet Service Engineering Process (WISEP)
Dedicated domain process model for wireless internet services.


Embedded System Verification
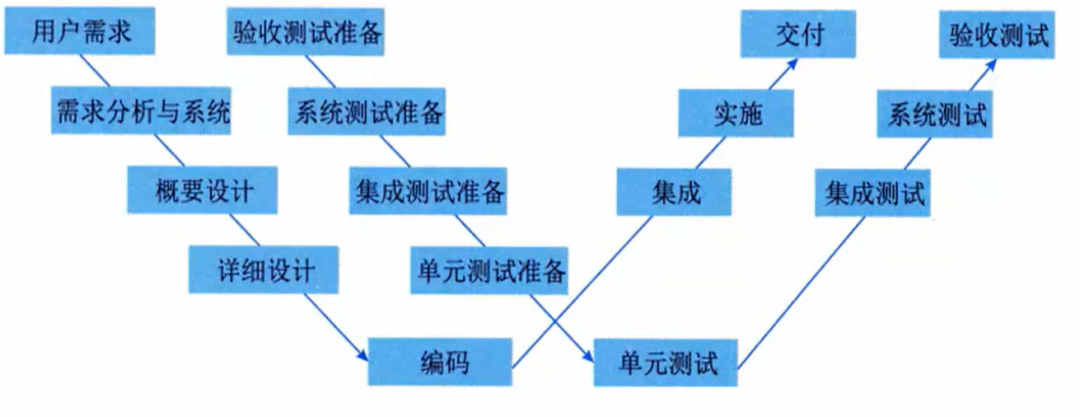

White-box testing: Confirms the internal logic, data, and program structure of components.
Black-box testing: Confirms the external functionality, behavior, and interfaces of components.