Introduction
Edge computing is a distributed open platform that integrates network, computing, storage, and application core capabilities to provide edge intelligence services near the source of objects or data. In simpler terms, edge computing analyzes the data collected from terminals directly on local devices or networks close to where the data is generated, eliminating the need to transmit the data to a cloud data processing center.
01
Why Do We Need Edge Computing?
The rapid development of Internet of Things (IoT) technology has enabled an increasing number of ordinary objects with independent functions to interconnect, realizing the Internet of Everything. Thanks to the characteristics of IoT, various industries are quickly utilizing IoT technology to achieve digital transformation, and more and more industry terminal devices are connected through the network.
However, as a vast and complex system, IoT has different application scenarios across various industries. According to third-party analysis agencies, by 2025, there will be over a hundred billion terminal devices connected to the network, and the terminal data volume will reach 300ZB. With such a massive data volume, traditional data processing methods require all data to be uploaded to cloud computing platforms for analysis, which presents significant challenges such as high network latency, massive device access, difficulties in processing large amounts of data, insufficient bandwidth, and excessive power consumption.
To address the high latency and lack of real-time data analysis capabilities associated with traditional data processing methods, edge computing technology has emerged. Edge computing technology provides edge intelligence services near the source of objects or data through the integration of network, computing, storage, and application core capabilities in a distributed open platform. In simpler terms, edge computing analyzes the data collected from terminals directly on local devices or networks close to where the data is generated, without the need to transmit the data to a cloud data processing center.
02
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
The concept of edge computing is relative to cloud computing, where the processing method of cloud computing involves uploading all data to a centralized cloud data center or server for processing. Any request that needs to access this information must be sent to the cloud for processing.
As a result, the disadvantages of cloud computing are becoming increasingly evident in the era of explosive growth in IoT data volumes:
-
Cloud computing cannot meet the explosive demand for massive data processing.
With the integration of the internet and various industries, especially after the widespread adoption of IoT technology, the demand for computing has surged, and traditional cloud computing architectures cannot meet such enormous computing requirements.
-
Cloud computing cannot meet the demand for real-time data processing.
In traditional cloud computing models, IoT data must first be transmitted to the cloud computing center after being collected by terminals, and then processed through cluster computing to return results, leading to longer response times. However, some emerging application scenarios, such as autonomous driving and smart mining, have extremely high requirements for response times, making reliance on cloud computing unrealistic.
The emergence of edge computing can help address these issues faced by cloud computing. As shown in the image below, the data generated by IoT terminal devices does not need to be transmitted to distant cloud data centers for processing but can be analyzed and processed directly at the network edge, making it more efficient and secure compared to cloud computing.
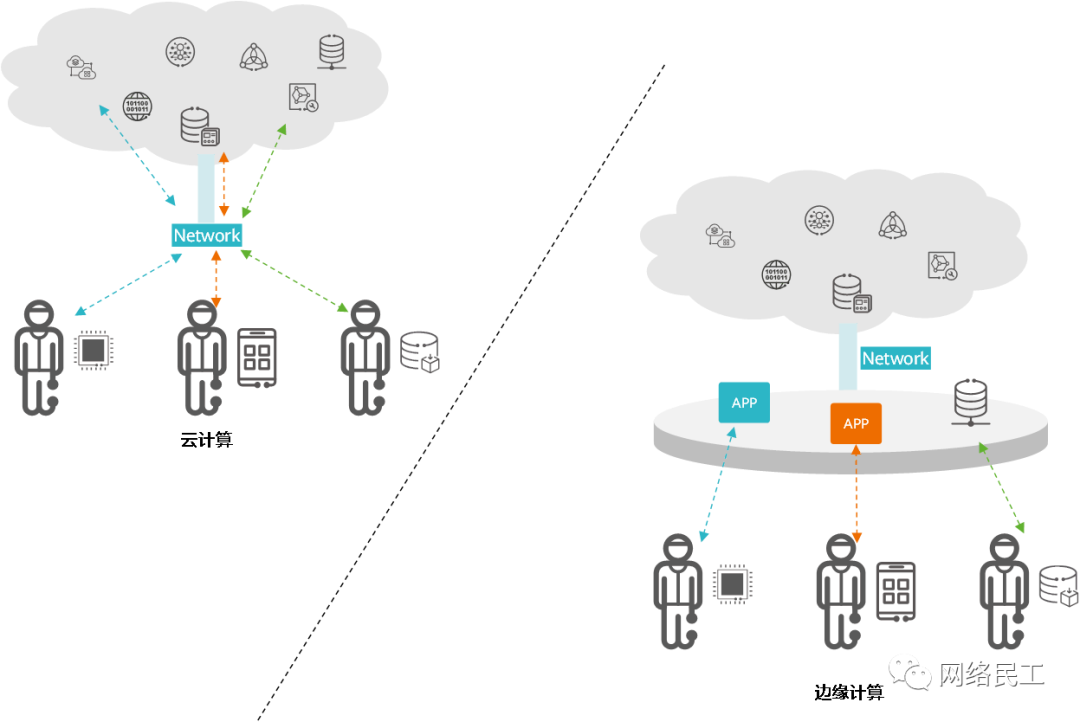
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
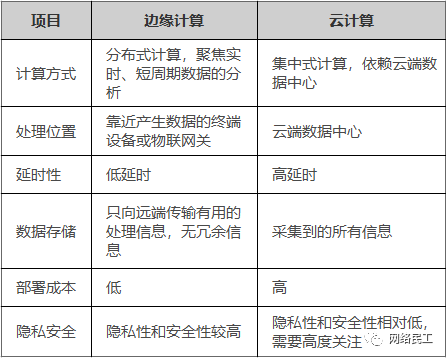
Table 1-1 Differences Between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
03
How Does Edge Computing Work?
The architecture of edge computing is shown in the image below, processing data as close to the terminal nodes as possible, distancing the data, applications, and computing capabilities from centralized cloud computing centers.
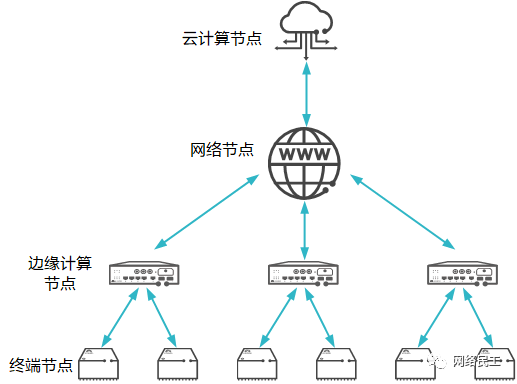
Edge Computing Architecture
-
Terminal Nodes:
Composed of various IoT devices (such as sensors, RFID tags, cameras, smartphones, etc.), primarily responsible for collecting raw data and reporting it. At the terminal layer, only the perception capabilities of various IoT devices are required, without needing computing capabilities.
-
Edge Computing Nodes:
Edge computing nodes achieve basic service responses by reasonably deploying and allocating the computing and storage capabilities of network edge nodes.
-
Network Nodes:
Responsible for uploading the useful data processed by edge computing nodes to cloud computing nodes for analysis and processing.
-
Cloud Computing Nodes:
The reported data from the edge computing layer will be permanently stored at cloud computing nodes, while analysis tasks that edge computing nodes cannot handle and tasks that require comprehensive global information processing still need to be completed at cloud computing nodes. In addition, cloud computing nodes can dynamically adjust the deployment strategies and algorithms of the edge computing layer based on network resource distribution.
04
Typical Applications of Edge Computing
Based on its ability to process data more in real-time and its characteristics of faster response times, edge computing is particularly suitable for application in the IoT field. By utilizing IoT gateways with edge computing capabilities to provide device management and control services close to the network edge, it addresses the “last mile” communication issue of IoT, ultimately achieving intelligent connections and efficient management of IoT devices.
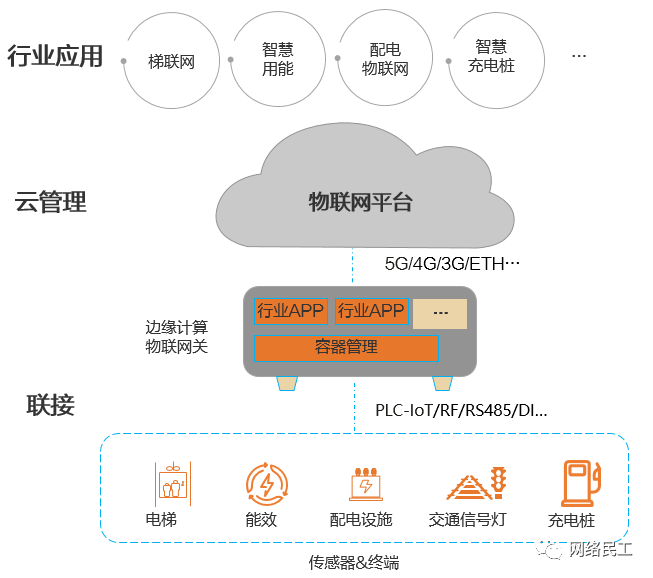
The IoT architecture for edge computing is shown in the image below, focusing on the industrial IoT field. It not only supports a variety of industrial protocols and IoT interfaces, adapting widely to different industry device connection scenarios, but also quickly meets the edge intelligent data processing needs of different industries through an open edge computing capability and cloud management architecture:
-
Connection:
Enables massive terminal devices to connect to the IoT network, primarily through various IoT interfaces supported by edge computing gateways (IP PLC/RF/RS485/RS232, etc.) connecting various sensors and terminals, achieving terminal device connectivity.
-
Cloud Management:
Utilizes IoT platforms and cloud computing technology to achieve unified cloud management of edge IoT devices (such as networks, devices, containers, and applications), while supporting flexible integration with other industry application systems in the northbound direction.
-
Industry Applications:
The IoT platform provides standard open interfaces for open integration with industry application systems from different partners, building broad industry adaptability and developing more tailored IoT industry applications that fit specific industry scenarios.