Today, let’s talk about the differences between Modbus and TCP.
These two protocols have both differences and close connections. Their combination not only enables remote network communication based on the Modbus/TCP/IP protocol but also promotes the use of Modbus in its corresponding fields.
The Modbus protocol is mainly used in electrical automation and process control, typically employing RS-232 or RS-485 communication interfaces. Its drawback is the short transmission distance and slow speed, which limits its application. The TCP/IP protocol is primarily used in the Internet or intranet, and its advantages include long transmission distances, high speed, and a wide range of applications.
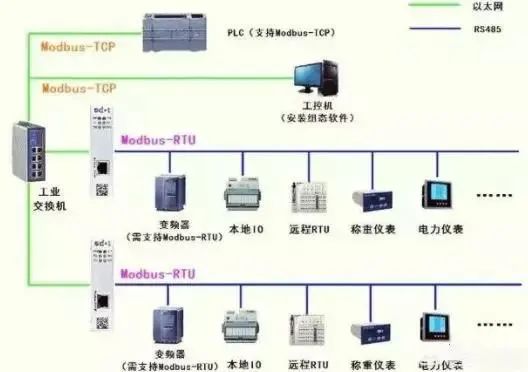
There are two communication modes for Modbus: ASCII and RTU. Although there are two modes, only one can be used at a time; mixed usage is not allowed.
TCP/IP Protocol
In simple terms, this protocol is a complete set of network protocols over a physical network. The role of TCP is to provide transport layer services, while the role of IP is to provide network layer services. The core components of the TCP/IP protocol are the transport layer protocols (TCP/UDP), network layer protocols (IP), and physical interface layer.
As mentioned above, there are two modes of the Modbus protocol:
Modbus-RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) and Modbus-ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange), as shown below:
1. Base: RTU is eight-bit binary, ASCII is hexadecimal.
2. Byte length: RTU has 11 bits, ASCII has 10 bits.
3. Bit information: RTU has a start bit, eight data bits, sends LSB first, one parity bit, and one stop bit, exactly meeting RTU’s byte length of 11 bits. ASCII has a start bit, seven data bits, sends LSB first, one parity bit, and one stop bit, exactly meeting ASCII’s byte length of 10 bits.
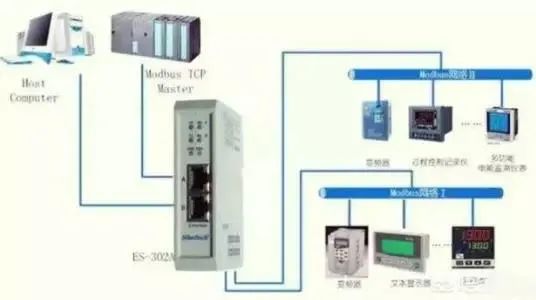
Note: Content sourced from the internet, infringement will be deleted!