What is the difference between gateways and routers? They are both network communication devices that serve the purpose of information transmission, and they seem quite similar, but there are indeed some differences.
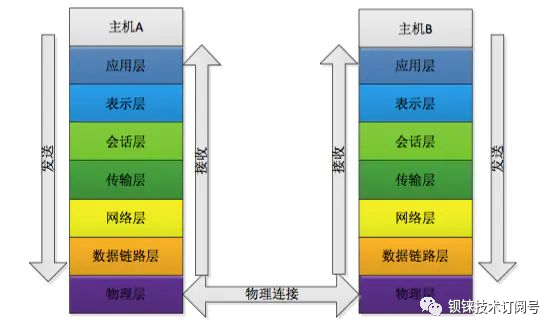
A gateway, also known as an inter-network connector or protocol converter, implements network interconnection above the network layer. It is the most complex network interconnection device, used solely for interconnecting networks with different high-level protocols. Gateways can be used for both wide area network and local area network interconnections. A gateway acts as a conversion system or device that facilitates communication between two systems that may use different communication protocols, data formats, or even completely different architectures. Unlike a bridge that merely transmits information, a gateway repackages the received information to meet the needs of the destination system. A router, on the other hand, is relatively simpler.
Differences Between Gateways and Routers: Essential Differences
Their positions in network transmission are not the same; the gateway operates at the application layer. This device is primarily used to connect different devices and facilitate communication. How does communication occur? It cannot happen directly; it must go through the gateway to transmit data according to various protocols.
A router belongs to the network layer and determines the network location of devices. It typically sends data in packets. In the router’s sub-interface, it plays a role in segmenting broadcast domains, so after using a switch to create VLANs, a three-layer routing must be performed on the router.
Differences Between Gateways and Routers: Usage Differences
A router can be called a gateway, but a gateway is not necessarily a router. A gateway can be a router, switch, or PC. Communication within the same subnet does not require the intervention of a gateway; however, if two hosts on different networks want to connect, a gateway must be used. After the data packet is sent to the gateway device, it is forwarded or processed by the gateway. A router can be considered a narrow gateway used to segment broadcast domains. Currently, routers in the market are generally divided into two categories: single-protocol routers and multi-protocol routers. Routers can convert data formats, making them essential devices for interconnecting networks with different protocols.
Differences Between Gateways and Routers: Functional Differences
Gateways can be categorized into transport gateways and application gateways, serving the role of conversion, essentially acting as an IP address connecting one network to another. The functions of a router mainly include connecting different networks and facilitating information transmission, as well as providing local area network services. Based on usage, they can be divided into access, enterprise-level, backbone-level, multi-WAN, and 4G wireless types.
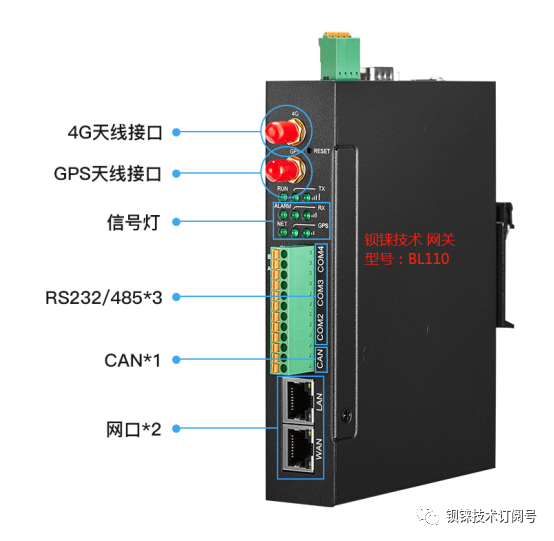
Taking the Bailey-Reilly technology products as an example:
The Bailey-Reilly intelligent gateway generally only supports traditional Ethernet or serial communication, while industrial 4G routers include 3G, 4G, WiFi, and other methods. Both gateways and routers support data transparent transmission.

In summary
The differences between gateways and routers are as described above; overall, their distinctions are not significant, and there exists a close relationship between gateways and routers.