

-
The growth rate of manufacturing has significantly declined, with a series of contradictions such as overcapacity, supply-demand imbalance, and slow conversion of new and old driving forces; the original growth model based on quantity, scale, and speed can no longer meet, grasp, or lead the new normal of economic development.
-
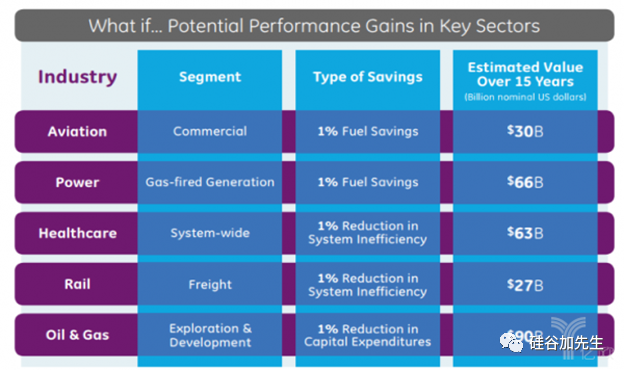
Currently, China’s manufacturing is “large but not strong”: in recent years, the added value rate of China’s manufacturing industry is about 20%, far below the level of 35% in industrialized countries. The industrial internet will promote the transformation and upgrading of manufacturing, enhancing the overall added value of the manufacturing sector.
-
At this stage, the labor population is continuously decreasing, and labor costs are rising: although the average annual salary of manufacturing in China has increased 98 times compared to 597 yuan in 1978, in some regions labor costs are approaching those of industrial robots. The competitive advantage gained by the manufacturing industry in its early stages due to labor cost advantages has gradually weakened.




