Skip to content

Introduction: As more and more IoT devices connect, they generate massive amounts of data. However, sending all this data to the cloud for processing may be counterproductive. Edge computing pushes data processing closer to the source (sensor devices) instead of sending it to a centralized cloud located thousands of miles away.
 In recent years, low-cost computing, reliable sensors, and good connectivity have contributed to the commercial application of IoT. With IoT, we can connect sensor objects to the internet, exchange data, and monitor their interactions. According to surveys, businesses worldwide are rapidly adopting IoT solutions. However, given the number of IoT devices and the explosive growth of data generated, sending all information to the cloud is feasible but requires better alternatives. Edge computing fills this gap well and addresses this massive data impact. By analyzing data at the source, edge computing can reduce the pressure on data centers and latency, ensuring that business operates more efficiently.
In recent years, low-cost computing, reliable sensors, and good connectivity have contributed to the commercial application of IoT. With IoT, we can connect sensor objects to the internet, exchange data, and monitor their interactions. According to surveys, businesses worldwide are rapidly adopting IoT solutions. However, given the number of IoT devices and the explosive growth of data generated, sending all information to the cloud is feasible but requires better alternatives. Edge computing fills this gap well and addresses this massive data impact. By analyzing data at the source, edge computing can reduce the pressure on data centers and latency, ensuring that business operates more efficiently.
 What is IoT IoT is a system composed of interconnected physical, digital, mechanical, and computing devices or embedded unique identifiers, allowing them to interact with each other over the internet. These devices cover all areas from ordinary items to complex tools. IoT devices are equipped with “smart” sensors. These sensors collect information, generating vast amounts of data. IoT gateways act as routers, sending data to the cloud via multiple data protocols such as HTTP and MQTT. Once the data reaches the cloud, analytical tools process the data and extract important information, which is then sent back to end users via APIs.
What is IoT IoT is a system composed of interconnected physical, digital, mechanical, and computing devices or embedded unique identifiers, allowing them to interact with each other over the internet. These devices cover all areas from ordinary items to complex tools. IoT devices are equipped with “smart” sensors. These sensors collect information, generating vast amounts of data. IoT gateways act as routers, sending data to the cloud via multiple data protocols such as HTTP and MQTT. Once the data reaches the cloud, analytical tools process the data and extract important information, which is then sent back to end users via APIs.
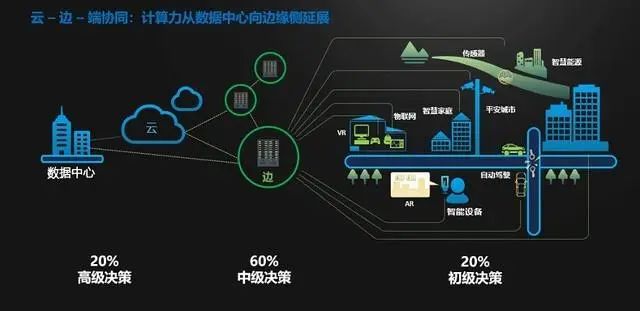 What is Edge Computing In fact, the growing popularity of IoT is a powerful driver for edge computing. As more IoT devices connect, they generate vast amounts of data. However, sending all this data to the cloud for processing may be counterproductive. First, the cost of sending all data to the cloud can be daunting. Second, sending such large amounts of data to the cloud can lead to latency and bandwidth issues. Edge computing pushes data processing closer to the source (sensor devices) instead of sending it to a centralized cloud located thousands of miles away. This is particularly necessary when data is time-sensitive and decisions must be made instantly. Edge devices perform advanced analytics on the available information at the network edge, providing organizations with much-needed predictions and solutions in real-time. Similarities Between IoT and Edge Computing IoT and edge computing have certain similarities. Essentially, both technologies are used to capture data in a distributed computing environment. Using sensors to capture data and generating large amounts of data, both are revolutionary technologies that are transforming the way we use data.
What is Edge Computing In fact, the growing popularity of IoT is a powerful driver for edge computing. As more IoT devices connect, they generate vast amounts of data. However, sending all this data to the cloud for processing may be counterproductive. First, the cost of sending all data to the cloud can be daunting. Second, sending such large amounts of data to the cloud can lead to latency and bandwidth issues. Edge computing pushes data processing closer to the source (sensor devices) instead of sending it to a centralized cloud located thousands of miles away. This is particularly necessary when data is time-sensitive and decisions must be made instantly. Edge devices perform advanced analytics on the available information at the network edge, providing organizations with much-needed predictions and solutions in real-time. Similarities Between IoT and Edge Computing IoT and edge computing have certain similarities. Essentially, both technologies are used to capture data in a distributed computing environment. Using sensors to capture data and generating large amounts of data, both are revolutionary technologies that are transforming the way we use data.
 Differences Between IoT and Edge Computing While IoT and edge computing have similarities, they are not the same. Here are the distinctions between the two technologies: ● In edge computing, data processing is done locally, while in IoT devices, data is sent to the cloud for analysis. This is one of the most significant differences between IoT and edge devices. ● IoT devices must be connected to the internet to function properly. In edge devices, this functionality is optional. ● Each IoT device can only perform specific functions, while a single edge device can handle multiple functions. IoT devices have minimal data processing needs, making them best suited for simple tasks. In contrast, edge devices run complex operating systems, allowing them to support a range of data processing capabilities. IoT Use Cases Automotive IoT Automotive IoT includes equipping vehicles with sensors, gadgets, and internet access for real-time predictive maintenance and ensuring safety. Through IoT, vehicle owners can monitor the health of their vehicles and receive updates on maintenance and care. Smart Homes Smart homes are currently one of the most popular IoT applications. In smart homes, everyday devices connect to the smart home system, allowing us to monitor and control devices even from afar.
Differences Between IoT and Edge Computing While IoT and edge computing have similarities, they are not the same. Here are the distinctions between the two technologies: ● In edge computing, data processing is done locally, while in IoT devices, data is sent to the cloud for analysis. This is one of the most significant differences between IoT and edge devices. ● IoT devices must be connected to the internet to function properly. In edge devices, this functionality is optional. ● Each IoT device can only perform specific functions, while a single edge device can handle multiple functions. IoT devices have minimal data processing needs, making them best suited for simple tasks. In contrast, edge devices run complex operating systems, allowing them to support a range of data processing capabilities. IoT Use Cases Automotive IoT Automotive IoT includes equipping vehicles with sensors, gadgets, and internet access for real-time predictive maintenance and ensuring safety. Through IoT, vehicle owners can monitor the health of their vehicles and receive updates on maintenance and care. Smart Homes Smart homes are currently one of the most popular IoT applications. In smart homes, everyday devices connect to the smart home system, allowing us to monitor and control devices even from afar.
 Smart Cities Smart cities rely on a large-scale IoT ecosystem equipped with applications and sensors to collect data. Analyzing data at the source will help cities improve services and enhance operational efficiency. Industrial IoT Industrial IoT includes devices used in factories and other industrial sectors. These devices connect to an internal monitoring system that tracks KPIs and ensures everything runs smoothly. Edge Computing Use Cases Edge computing enables manufacturers to collect real-time information about manufacturing processes and make quicker decisions. By deploying sensors throughout the factory, manufacturers can gain insights into the health of machines, allowing them to identify production issues before they occur. Autonomous vehicles are one of the best examples of edge computing. Vehicles must analyze data in real-time while driving; otherwise, they are useless. Edge devices study data in real-time and provide immediate results to assist vehicle navigation. Edge computing is having a revolutionary impact on the healthcare industry. With instant data processing, hospitals can provide better patient care, even beyond the hospital’s walls. For example, wearable medical devices support remote monitoring of chronic patients and notify caregivers when patients exhibit erroneous readings or abnormal behavior. Other uses include training staff with augmented and virtual reality technologies, remotely managing mobile medical devices, and enabling robot-assisted surgeries. Future Trends of IoT and Edge Computing More and more businesses are using edge computing and IoT to enhance efficiency and unlock business value. Here are some trends in IoT and edge computing expected to dominate in 2022. Greater Growth Ahead In 2021, the edge computing market size was $36.5 billion. This figure is expected to grow to $87.3 billion by 2026. The massive growth in numbers can be attributed to businesses achieving rapid growth through the use of IoT and edge devices. 5G Progress The success of IoT devices depends on their speed of connection to the cloud or other devices. As 5G is touted to be much faster than 4G, businesses are expected to leverage its speed to develop new use cases. Additionally, consumers will benefit from 5G as these networks can handle many devices without failure. Increased Focus on Security Edge computing centers are also susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Distributed attacks, software injection, and router attacks are some ways edge devices may be threatened. As edge computing begins to handle more sensitive information, they must adopt secure access service edge frameworks. This model includes zero-trust network access, firewall as a service, and cloud access security brokers that ensure secure access regardless of location. Stakeholders Will Adopt AI As the volume of data generated by IoT devices continues to grow, it is vital to derive actionable insights from it. Artificial intelligence helps networks think intelligently. Therefore, devices can learn from past activities and predict future behaviors without human intervention.
Smart Cities Smart cities rely on a large-scale IoT ecosystem equipped with applications and sensors to collect data. Analyzing data at the source will help cities improve services and enhance operational efficiency. Industrial IoT Industrial IoT includes devices used in factories and other industrial sectors. These devices connect to an internal monitoring system that tracks KPIs and ensures everything runs smoothly. Edge Computing Use Cases Edge computing enables manufacturers to collect real-time information about manufacturing processes and make quicker decisions. By deploying sensors throughout the factory, manufacturers can gain insights into the health of machines, allowing them to identify production issues before they occur. Autonomous vehicles are one of the best examples of edge computing. Vehicles must analyze data in real-time while driving; otherwise, they are useless. Edge devices study data in real-time and provide immediate results to assist vehicle navigation. Edge computing is having a revolutionary impact on the healthcare industry. With instant data processing, hospitals can provide better patient care, even beyond the hospital’s walls. For example, wearable medical devices support remote monitoring of chronic patients and notify caregivers when patients exhibit erroneous readings or abnormal behavior. Other uses include training staff with augmented and virtual reality technologies, remotely managing mobile medical devices, and enabling robot-assisted surgeries. Future Trends of IoT and Edge Computing More and more businesses are using edge computing and IoT to enhance efficiency and unlock business value. Here are some trends in IoT and edge computing expected to dominate in 2022. Greater Growth Ahead In 2021, the edge computing market size was $36.5 billion. This figure is expected to grow to $87.3 billion by 2026. The massive growth in numbers can be attributed to businesses achieving rapid growth through the use of IoT and edge devices. 5G Progress The success of IoT devices depends on their speed of connection to the cloud or other devices. As 5G is touted to be much faster than 4G, businesses are expected to leverage its speed to develop new use cases. Additionally, consumers will benefit from 5G as these networks can handle many devices without failure. Increased Focus on Security Edge computing centers are also susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Distributed attacks, software injection, and router attacks are some ways edge devices may be threatened. As edge computing begins to handle more sensitive information, they must adopt secure access service edge frameworks. This model includes zero-trust network access, firewall as a service, and cloud access security brokers that ensure secure access regardless of location. Stakeholders Will Adopt AI As the volume of data generated by IoT devices continues to grow, it is vital to derive actionable insights from it. Artificial intelligence helps networks think intelligently. Therefore, devices can learn from past activities and predict future behaviors without human intervention.




 What is IoT IoT is a system composed of interconnected physical, digital, mechanical, and computing devices or embedded unique identifiers, allowing them to interact with each other over the internet. These devices cover all areas from ordinary items to complex tools. IoT devices are equipped with “smart” sensors. These sensors collect information, generating vast amounts of data. IoT gateways act as routers, sending data to the cloud via multiple data protocols such as HTTP and MQTT. Once the data reaches the cloud, analytical tools process the data and extract important information, which is then sent back to end users via APIs.
What is IoT IoT is a system composed of interconnected physical, digital, mechanical, and computing devices or embedded unique identifiers, allowing them to interact with each other over the internet. These devices cover all areas from ordinary items to complex tools. IoT devices are equipped with “smart” sensors. These sensors collect information, generating vast amounts of data. IoT gateways act as routers, sending data to the cloud via multiple data protocols such as HTTP and MQTT. Once the data reaches the cloud, analytical tools process the data and extract important information, which is then sent back to end users via APIs. What is Edge Computing In fact, the growing popularity of IoT is a powerful driver for edge computing. As more IoT devices connect, they generate vast amounts of data. However, sending all this data to the cloud for processing may be counterproductive. First, the cost of sending all data to the cloud can be daunting. Second, sending such large amounts of data to the cloud can lead to latency and bandwidth issues. Edge computing pushes data processing closer to the source (sensor devices) instead of sending it to a centralized cloud located thousands of miles away. This is particularly necessary when data is time-sensitive and decisions must be made instantly. Edge devices perform advanced analytics on the available information at the network edge, providing organizations with much-needed predictions and solutions in real-time. Similarities Between IoT and Edge Computing IoT and edge computing have certain similarities. Essentially, both technologies are used to capture data in a distributed computing environment. Using sensors to capture data and generating large amounts of data, both are revolutionary technologies that are transforming the way we use data.
What is Edge Computing In fact, the growing popularity of IoT is a powerful driver for edge computing. As more IoT devices connect, they generate vast amounts of data. However, sending all this data to the cloud for processing may be counterproductive. First, the cost of sending all data to the cloud can be daunting. Second, sending such large amounts of data to the cloud can lead to latency and bandwidth issues. Edge computing pushes data processing closer to the source (sensor devices) instead of sending it to a centralized cloud located thousands of miles away. This is particularly necessary when data is time-sensitive and decisions must be made instantly. Edge devices perform advanced analytics on the available information at the network edge, providing organizations with much-needed predictions and solutions in real-time. Similarities Between IoT and Edge Computing IoT and edge computing have certain similarities. Essentially, both technologies are used to capture data in a distributed computing environment. Using sensors to capture data and generating large amounts of data, both are revolutionary technologies that are transforming the way we use data. Differences Between IoT and Edge Computing While IoT and edge computing have similarities, they are not the same. Here are the distinctions between the two technologies: ● In edge computing, data processing is done locally, while in IoT devices, data is sent to the cloud for analysis. This is one of the most significant differences between IoT and edge devices. ● IoT devices must be connected to the internet to function properly. In edge devices, this functionality is optional. ● Each IoT device can only perform specific functions, while a single edge device can handle multiple functions. IoT devices have minimal data processing needs, making them best suited for simple tasks. In contrast, edge devices run complex operating systems, allowing them to support a range of data processing capabilities. IoT Use Cases Automotive IoT Automotive IoT includes equipping vehicles with sensors, gadgets, and internet access for real-time predictive maintenance and ensuring safety. Through IoT, vehicle owners can monitor the health of their vehicles and receive updates on maintenance and care. Smart Homes Smart homes are currently one of the most popular IoT applications. In smart homes, everyday devices connect to the smart home system, allowing us to monitor and control devices even from afar.
Differences Between IoT and Edge Computing While IoT and edge computing have similarities, they are not the same. Here are the distinctions between the two technologies: ● In edge computing, data processing is done locally, while in IoT devices, data is sent to the cloud for analysis. This is one of the most significant differences between IoT and edge devices. ● IoT devices must be connected to the internet to function properly. In edge devices, this functionality is optional. ● Each IoT device can only perform specific functions, while a single edge device can handle multiple functions. IoT devices have minimal data processing needs, making them best suited for simple tasks. In contrast, edge devices run complex operating systems, allowing them to support a range of data processing capabilities. IoT Use Cases Automotive IoT Automotive IoT includes equipping vehicles with sensors, gadgets, and internet access for real-time predictive maintenance and ensuring safety. Through IoT, vehicle owners can monitor the health of their vehicles and receive updates on maintenance and care. Smart Homes Smart homes are currently one of the most popular IoT applications. In smart homes, everyday devices connect to the smart home system, allowing us to monitor and control devices even from afar. Smart Cities Smart cities rely on a large-scale IoT ecosystem equipped with applications and sensors to collect data. Analyzing data at the source will help cities improve services and enhance operational efficiency. Industrial IoT Industrial IoT includes devices used in factories and other industrial sectors. These devices connect to an internal monitoring system that tracks KPIs and ensures everything runs smoothly. Edge Computing Use Cases Edge computing enables manufacturers to collect real-time information about manufacturing processes and make quicker decisions. By deploying sensors throughout the factory, manufacturers can gain insights into the health of machines, allowing them to identify production issues before they occur. Autonomous vehicles are one of the best examples of edge computing. Vehicles must analyze data in real-time while driving; otherwise, they are useless. Edge devices study data in real-time and provide immediate results to assist vehicle navigation. Edge computing is having a revolutionary impact on the healthcare industry. With instant data processing, hospitals can provide better patient care, even beyond the hospital’s walls. For example, wearable medical devices support remote monitoring of chronic patients and notify caregivers when patients exhibit erroneous readings or abnormal behavior. Other uses include training staff with augmented and virtual reality technologies, remotely managing mobile medical devices, and enabling robot-assisted surgeries. Future Trends of IoT and Edge Computing More and more businesses are using edge computing and IoT to enhance efficiency and unlock business value. Here are some trends in IoT and edge computing expected to dominate in 2022. Greater Growth Ahead In 2021, the edge computing market size was $36.5 billion. This figure is expected to grow to $87.3 billion by 2026. The massive growth in numbers can be attributed to businesses achieving rapid growth through the use of IoT and edge devices. 5G Progress The success of IoT devices depends on their speed of connection to the cloud or other devices. As 5G is touted to be much faster than 4G, businesses are expected to leverage its speed to develop new use cases. Additionally, consumers will benefit from 5G as these networks can handle many devices without failure. Increased Focus on Security Edge computing centers are also susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Distributed attacks, software injection, and router attacks are some ways edge devices may be threatened. As edge computing begins to handle more sensitive information, they must adopt secure access service edge frameworks. This model includes zero-trust network access, firewall as a service, and cloud access security brokers that ensure secure access regardless of location. Stakeholders Will Adopt AI As the volume of data generated by IoT devices continues to grow, it is vital to derive actionable insights from it. Artificial intelligence helps networks think intelligently. Therefore, devices can learn from past activities and predict future behaviors without human intervention.
Smart Cities Smart cities rely on a large-scale IoT ecosystem equipped with applications and sensors to collect data. Analyzing data at the source will help cities improve services and enhance operational efficiency. Industrial IoT Industrial IoT includes devices used in factories and other industrial sectors. These devices connect to an internal monitoring system that tracks KPIs and ensures everything runs smoothly. Edge Computing Use Cases Edge computing enables manufacturers to collect real-time information about manufacturing processes and make quicker decisions. By deploying sensors throughout the factory, manufacturers can gain insights into the health of machines, allowing them to identify production issues before they occur. Autonomous vehicles are one of the best examples of edge computing. Vehicles must analyze data in real-time while driving; otherwise, they are useless. Edge devices study data in real-time and provide immediate results to assist vehicle navigation. Edge computing is having a revolutionary impact on the healthcare industry. With instant data processing, hospitals can provide better patient care, even beyond the hospital’s walls. For example, wearable medical devices support remote monitoring of chronic patients and notify caregivers when patients exhibit erroneous readings or abnormal behavior. Other uses include training staff with augmented and virtual reality technologies, remotely managing mobile medical devices, and enabling robot-assisted surgeries. Future Trends of IoT and Edge Computing More and more businesses are using edge computing and IoT to enhance efficiency and unlock business value. Here are some trends in IoT and edge computing expected to dominate in 2022. Greater Growth Ahead In 2021, the edge computing market size was $36.5 billion. This figure is expected to grow to $87.3 billion by 2026. The massive growth in numbers can be attributed to businesses achieving rapid growth through the use of IoT and edge devices. 5G Progress The success of IoT devices depends on their speed of connection to the cloud or other devices. As 5G is touted to be much faster than 4G, businesses are expected to leverage its speed to develop new use cases. Additionally, consumers will benefit from 5G as these networks can handle many devices without failure. Increased Focus on Security Edge computing centers are also susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Distributed attacks, software injection, and router attacks are some ways edge devices may be threatened. As edge computing begins to handle more sensitive information, they must adopt secure access service edge frameworks. This model includes zero-trust network access, firewall as a service, and cloud access security brokers that ensure secure access regardless of location. Stakeholders Will Adopt AI As the volume of data generated by IoT devices continues to grow, it is vital to derive actionable insights from it. Artificial intelligence helps networks think intelligently. Therefore, devices can learn from past activities and predict future behaviors without human intervention.
