“Learning Kubernetes from Scratch“
Deployment (Deploy)
To better address the issue of service orchestration, Kubernetes introduced the Deployment controller starting from version 1.2. It is worth mentioning that this controller does not directly manage Pods but instead manages ReplicaSets to indirectly manage Pods. In other words, the Deployment manages ReplicaSets, and ReplicaSets manage Pods, making Deployment more powerful than ReplicaSet.
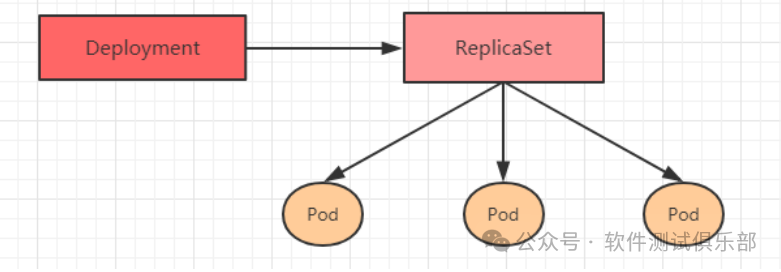
The Deployment is essentially a two-layer controller. First, the Deployment describes the version of the application through the number of ReplicaSets. Then, the Deployment ensures the number of Pod replicas through the attributes of the ReplicaSet (such as the value of replicas).
The main functions of Deployment include the following:
1. Supports all functions of ReplicaSet
2. Supports stopping and resuming releases
3. Supports rolling updates and version rollbacks
Resource manifest file for Deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1 # Version
kind: Deployment # Type
metadata: # Metadata
name: # Deployment Name
namespace: # Namespace
labels: # Labels
controller: deploy
spec: # Specification
replicas: 3 # Number of replicas
revisionHistoryLimit: 3 # Retain historical versions, default is 10
paused: false # Pause deployment, default is false
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600 # Deployment timeout (s), default is 600
strategy: # Strategy
type: RollingUpdate # Rolling update strategy
rollingUpdate: # Rolling update
maxSurge: 30% # Maximum additional replicas allowed, can be a percentage or an integer
maxUnavailable: 30% # Maximum number of Pods that can be unavailable, can be a percentage or an integer
selector: # Selector, specifies which Pods this controller manages
matchLabels: # Labels matching rules
app: nginx-pod
matchExpressions: # Expressions matching rules
- {key: app, operator: In, values: [nginx-pod]}
template: # Template, when the number of replicas is insufficient, Pods will be created based on this template
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.20.2-alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 80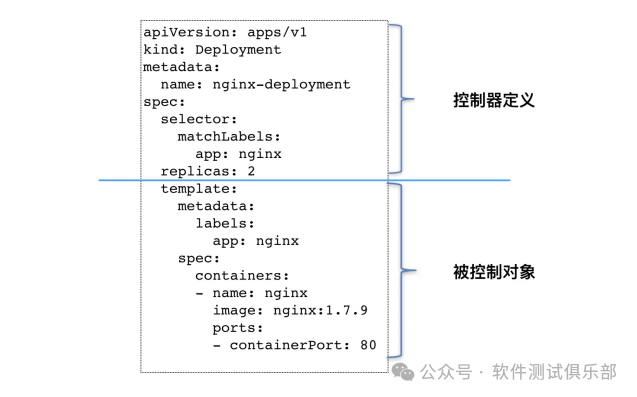
Creation:
# Create pc-deployment.yaml
cat > pc-deployment.yaml < EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pc-deployment
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1-alpine
EOF# Create deployment
# kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml
# View deployment
# READY Expected number of Pod replicas
# UP-TO-DATE Number of latest version Pods
# AVAILABLE Number of currently available Pods
kubectl get deploy pc-deployment -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 8s
# View rs
# After creating the Deployment object, a ReplicaSet with 3 Pod replicas will be created immediately, with a name composed of the Deployment name and a random string
kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 3 3 3 16s
# View pod
# The name of the pod has a 5-digit random string appended to the name of the rs
kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-5fjrd 1/1 Running 0 23s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fhcb7 1/1 Running 0 23s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fxqdp 1/1 Running 0 23sScaling:
# Change the number of replicas to 5
kubectl scale deploy pc-deployment --replicas=5 -n dev
# View deployment
kubectl get deploy pc-deployment -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
pc-deployment 5/5 5 5 98s
# View pod
kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-5fjrd 1/1 Running 0 109s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-ccmhz 1/1 Running 0 19s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-dfq2m 1/1 Running 0 19s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fhcb7 1/1 Running 0 109s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fxqdp 1/1 Running 0 109s
# Edit the number of replicas in the deployment, modify spec:replicas: 3
kubectl edit deploy pc-deployment -n dev
# View pod
kubectl get deploy pc-deployment -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 2m26s
kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-5fjrd 1/1 Running 0 2m35s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fhcb7 1/1 Running 0 2m35s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fxqdp 1/1 Running 0 2m35sImage Update:
The deployment supports two update strategies:Recreate and RollingUpdate (default), which can be specified through strategy to indicate the type of strategy, supporting two properties:
strategy: Specifies the strategy for replacing old Pods with new Pods, supporting two properties:
type: Specifies the type of strategy, supporting two strategies
Recreate: All existing Pods will be killed before creating new Pods
RollingUpdate: Rolling update, which kills some and starts some, during the update process, there are two versions of Pods
rollingUpdate: Effective when type is RollingUpdate, used to set parameters for RollingUpdate, supporting two properties:
maxUnavailable: Specifies the maximum number of unavailable Pods during the upgrade process, default is 25%
maxSurge: Specifies the maximum number of Pods that can exceed the expected number during the upgrade process, default is 25%Recreate Update:
Edit pc-deployment.yaml, add update strategy under the spec node
spec:
strategy: # Strategy
type: Recreate # Recreate updatecat > pc-deployment.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pc-deployment
namespace: dev
spec:
strategy:
type: Recreate
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1-alpine
EOFCreate deploy for verification:
# Update pc-deployment's yaml file
kubectl apply -f pc-deployment.yaml
# View deployment version
kubectl get deploy pc-deployment -n dev -o wide
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 3m39s nginx nginx:1.17.1-alpine app=nginx-pod
# Observe the upgrade process, then open a new shell to execute the update, all pods start updating simultaneously
kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-5fjrd 1/1 Running 0 3m56s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fhcb7 1/1 Running 0 3m56s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fxqdp 1/1 Running 0 3m56s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fxqdp 1/1 Terminating 0 4m21s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-5fjrd 1/1 Terminating 0 4m21s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-fhcb7 1/1 Terminating 0 4m21s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-68zms 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-7mxpv 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-nkdn2 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-68zms 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-7mxpv 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-nkdn2 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-7mxpv 1/1 Running 0 1
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-nkdn2 1/1 Running 0 20
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-68zms 1/1 Running 0 36s
# Change image
kubectl set image deployment pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.2-alpine -n devRolling Update:
Edit pc-deployment.yaml, add update strategy under the spec node
spec:
strategy: # Strategy
type: RollingUpdate # Rolling update strategy
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 25%cat > pc-deployment.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pc-deployment
namespace: dev
spec:
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 25%
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1-alpine
EOF# Update pc-deployment's yaml file
kubectl apply -f pc-deployment.yaml
# View deployment version
kubectl get deploy pc-deployment -n dev -o wide
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 11m nginx nginx:1.17.1-alpine app=nginx-pod
# Observe the upgrade process, then open a new shell to execute the update
kubectl get pods -n dev -w
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-9xvnj 1/1 Running 0 49s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-mkqhj 1/1 Running 0 48s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-n7fj v 1/1 Running 0 51s
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-vkv8k 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-vkv8k 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-vkv8k 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-vkv8k 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-vkv8k 1/1 Running 0 20s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-mkqhj 1/1 Terminating 0 3m2s
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-ss7pk 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-ss7pk 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-ss7pk 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-ss7pk 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-mkqhj 0/1 Terminating 0 3m3s
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5-ss7pk 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
# Change image
kubectl set image deployment pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.3-alpine -n devRolling update process:
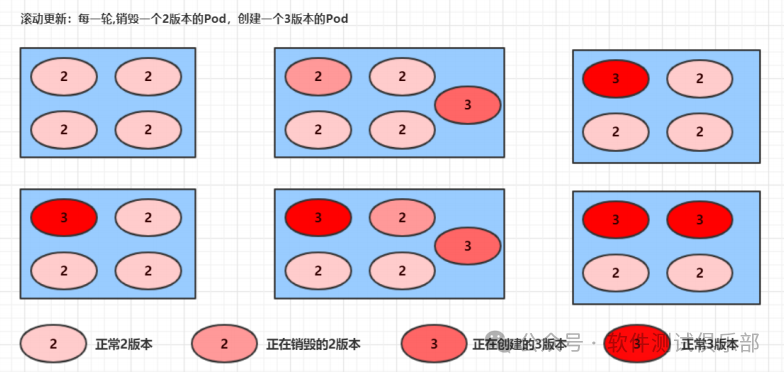
Changes in rs during image update
# View rs, the original rs still exists, but the number of pods has become 0, and then a new rs is generated with 3 pods
# This is actually the secret behind the deployment's ability to perform version rollbacks, which will be explained in detail later
kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5 3 3 3 2m20s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 0 0 0 14m
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 0 0 0 10mVersion Rollback:
The deployment supports various functions such as pausing, resuming, and rolling back during the version upgrade process.
kubectl rollout: Version upgrade related functions, supporting the following options:
1. status Displays the current upgrade status
2. history Displays the upgrade history
3. pause Pauses the version upgrade process
4. resume Resumes the already paused version upgrade process
5. restart Restarts the version upgrade process
6. undo Rolls back to the previous version (can use –to-revision to roll back to a specified version)
# Delete deployment
kubectl delete -f pc-deployment.yaml
# Edit pc-deployment.yaml
cat > pc-deployment.yaml < EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pc-deployment
namespace: dev
spec:
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 25%
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1-alpine
EOF# Create deployment, --record records the deployment operation process
# kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record
# View deploy, rs, pod
kubectl get deploy,rs,pod -n dev
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 25s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 3 3 3 25s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-g95pv 1/1 Running 0 25s
pod/pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-ghhlx 1/1 Running 0 25s
pod/pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-twgw8 1/1 Running 0 25s
# Open 2 new shells to observe the process, the update will create a new rs, and the pods under the old rs will be 0
kubectl get rs -n dev -w
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 3 3 3 3m13s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 1 0 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 1 0 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 1 1 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 1 1 1 2
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 2 3 3 4m21s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 2 1 1 2
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 2 3 3 4m21s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 2 1 1 2
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 2 2 2 4m21s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 2 2 1 2
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 2 2 2 4
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 1 2 2 4m23s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 3 2 2 4
# Open 2 new shells to observe the process, the updated pods will be under the new rs
kubectl get pods -n dev -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-g95pv 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-ghhlx 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-twgw8 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-p79xr 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-p79xr 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-p79xr 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-p79xr 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-p79xr 1/1 Running 0 2
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-twgw8 1/1 Terminating 0 4m21s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-l5qpv 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-l5qpv 0/1 Pending 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-l5qpv 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-l5qpv 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475-ghhlx 0/1 Terminating 0 4m24s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd-l5qpv 1/1 Running 0 1
# Change image
kubectl set image deploy pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.2-alpine -n dev
# -record indicates that this command is recorded in the operation history
kubectl set image deploy pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.2-alpine -n dev --record# View rs, the rs has been updated along with the deployment, the old rs is used for version rollback
kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 0 0 0 7m20s
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 3 3 3 3m1s# View the status of the current upgrade version
kubectl rollout status deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment "pc-deployment" successfully rolled out
# View upgrade history
kubectl rollout history deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
# Again, change image
kubectl set image deploy pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.3-alpine -n dev
# -record indicates that this command is recorded in the operation history
kubectl set image deploy pc-deployment nginx=nginx:1.17.3-alpine -n dev --record
# Again, view upgrade history
kubectl rollout history deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
# It can be seen that there are three version records, indicating that two upgrades have been completed
# View deployment version
kubectl get deploy -n dev -o wide
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 18m nginx nginx:1.17.3-alpine app=nginx-pod
# Version rollback
# Here directly use --to-revision=1 to roll back to version 1, if this option is omitted, it will roll back to the previous version, which is version 2
kubectl rollout undo deployment pc-deployment --to-revision=1 -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment rolled back
# View shows that the nginx image version has returned to the first version
kubectl get deploy -n dev -o wide
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
pc-deployment 3/3 3 3 18m nginx nginx:1.17.1-alpine app=nginx-pod
# View rs, find that there are 3 pods running in the first rs, while the pods in the updated two versions of rs are 0
# The reason why deployment can achieve version rollback is that it records the historical rs
# Once you want to roll back to a certain version, you just need to reduce the current version pod count to 0, and then increase the pod count of the rollback version to the target count
kubectl get rs -n dev
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
pc-deployment-545fbd7bb5 0 0 0 3m4s
pc-deployment-7d9bdf9475 3 3 3 19m
pc-deployment-9d4dbb5bd 0 0 0 14m
# Again, view upgrade history, find that version 1 is gone, because it has now rolled back to version 4 which is version 1
kubectl rollout history deploy pc-deployment -n dev
deployment.apps/pc-deployment REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true
kubectl create -f pc-deployment.yaml --record=true