🔥 When you see the output of <span><span>ip a</span></span>, are you confused by the mysterious parameters like <span><span>LOOPBACK</span></span>, <span><span>fq_codel</span></span>, and <span><span>metric 100</span></span>? 🔥 This article uses real terminal output examples to analyze the meaning of each parameter line by line and reveals how to diagnose network issues using them!🚀 At the end of the article, we include 【Tuning Tips】, a must-read!
1. Full Display of Output Examples
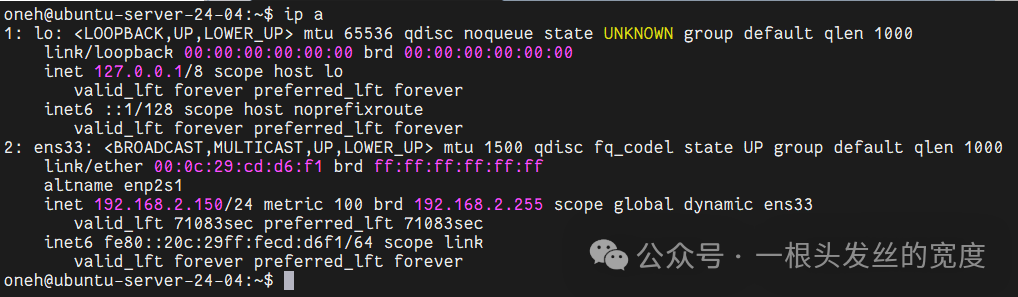
oneh@ubuntu-server-24-04:~$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:cd:d6:f1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp2s1
inet 192.168.2.150/24 metric 100 brd 192.168.2.255 scope global dynamic ens33
valid_lft 75842sec preferred_lft 75842sec
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fecd:d6f1/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2. Line-by-Line Breakdown: In-Depth Parameter Analysis
1. Loopback Interface <span>lo</span> Detailed Explanation
-
<span>LOOPBACK</span>: Identifies the loopback interface (used only for internal communication on the local machine). -
<span>mtu 65536</span>: Maximum Transmission Unit (a very large value, suitable for high-speed local communication). -
<span>qdisc noqueue</span>: No queue scheduling (no queuing, direct mode). -
<span>state UNKNOWN</span>: Special state identifier for the loopback interface (normal phenomenon).
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
<span>scope host</span>: Accessible only from the local machine, cannot be connected from external networks.<span>valid_lft forever</span>: IP address is permanently valid (static configuration).
2. Physical Network Card <span>ens33</span> Detailed Explanation
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
Interface Identity:
<span>2</span>: Interface number (a unique ID assigned by the system).<span>ens33</span>: Interface name (physical network cards commonly use<span>ethX</span>, virtual network cards are generally<span>ensXX</span>or<span>vethX</span>).
Status Tags: Vital Signs of the Network
<span>BROADCAST</span>: Supports broadcast communication (a typical Ethernet feature).<span>MULTICAST</span>: Supports multicast (e.g., video conferencing, cluster communication).<span>UP</span>: Software layer is enabled (<span>ip link set ens33 down</span>can disable it).<span>LOWER_UP</span>: Physical layer is connected (cable is plugged in/WIFI signal is normal).
Performance Triad: MTU, Queue, and Scheduler
-
<span>mtu 1500</span>: Maximum Transmission Unit. For example, the maximum size of a parcel. The default for LAN is<span>1500</span>, VPN/virtual machines can set<span>1450</span>to avoid fragmentation. Reference modification command:<span>sudo ip link set ens33 mtu 1450</span> -
<span>qdisc fq_codel</span>: Fair queue algorithm (automatically optimizes network latency and throughput).<span>mq(Multi-Queue)</span>: Multi-queue mode, suitable for multi-core CPUs. -
<span>state UP</span>: Interface is enabled (software layer activated). -
<span>qlen 1000</span>: Send queue length. It affects performance; if the value is too small, packets may be lost under high traffic (queue overflow); if the value is too large, latency increases (queuing time becomes longer).
link/ether 00:0c:29:cd:d6:f1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp2s1
<span>link/ether</span>: MAC address of the network card (hardware unique identifier).<span>altname enp2s1</span>: Alternate name of the interface (compatible with different naming conventions).
inet 192.168.2.150/24 metric 100 brd 192.168.2.255 scope global dynamic ens33
<span>metric 100</span>: Routing priority (the smaller the value, the higher the priority).<span>scope global</span>: Accessible from external networks (e.g., public IP).<span>dynamic</span>: IP is dynamically assigned by DHCP (<span>valid_lft 75842sec</span>indicates the remaining lease time).
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fecd:d6f1/64 scope link
<span>fe80::</span>: IPv6 link-local address (valid only within the same local area network).<span>scope link</span>: Cannot communicate across routers.
3. Key Parameter State Changes
1. Interface State Combinations
| Status Tag | Meaning | Typical Scenario |
|---|---|---|
<span>UP + LOWER_UP</span> |
Interface is enabled and physical link is normal | Normal network connection state |
<span>UP</span> (without <span>LOWER_UP</span>) |
Software layer is enabled but physical link is disconnected | Cable not plugged in/WIFI not connected |
<span>DOWN</span> |
Interface is manually disabled | Network is actively turned off |
2. <span>valid_lft</span> and IP Lifecycle
-
<span>dynamic</span>Type of IP:valid_lft 75842sec # Remaining about 21 hours - DHCP lease will automatically renew before expiration.
-
<span>static</span>Type of IP:valid_lft forever # Permanently valid
4. Practical Tuning Tips
1. Optimize Network Latency (<span>qdisc</span>)
# Enable fair queue algorithm (default optimized)
sudo tc qdisc replace dev ens33 root fq_codel
# View current queue configuration
sudo tc -s qdisc show dev ens33
2. Adjust Routing Priority (<span>metric</span>)
# Modify interface routing priority (the smaller the value, the higher the priority)
sudo ip route modify default via 192.168.2.1 metric 50 dev ens33
3. Temporarily Increase Queue Length (<span>qlen</span>)
# To cope with high traffic scenarios (prevent packet loss)
sudo ip link set dev ens33 txqueuelen 2000
4. High-Concurrency Web Server
sudo ip link set ens33 txqueuelen 200 # Increase send queue
sudo ethtool -L ens33 combined 4 # Enable 4 transmission queues
sudo ip link set ens33 mtu 9000 # Enable jumbo frames, requires switch support
# Create load balancing group
sudo ip link set ens33 group lb
sudo ip link set ens34 group lb
# Batch configuration
sudo ip link set group lb mtu9000 txqueuelen 2000
5. Quick Troubleshooting Scripts
1. Check Physical Link Status
ip a | grep -A2 "ens33" | grep "LOWER_UP"
# Output → Cable is connected; no output → Physical link issue
2. View Remaining DHCP Lease Time
journalctl -u NetworkManager | grep "DHCPv4 address"
# Example output: DHCPv4 address 192.168.2.150/24 ... expires in 75842 seconds
3. Verify IPv6 Connectivity
ping6 fe80::20c:29ff:fecd:d6f1%ens33
# Other devices in the same local area network can respond
Further Learning
- Advanced Commands:
<span><span>ip route</span></span>(routing table),<span><span>ip neigh</span></span>(ARP table) - Permanent Configuration Modifications: Edit for Ubuntu systems
<span><span>/etc/netplan/</span></span><code><span>, for CentOS systems edit</span><code><span><span>/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/</span></span><code>
Core Parameter Quick Reference Table
| Parameter | Function | Key Command |
|---|---|---|
<span>mtu</span> |
Controls packet size | <span>ip link set ens33 mtu 9000</span> |
<span>qdisc</span> |
Controls network queue scheduling algorithm | <span>tc qdisc show</span> |
<span>metric</span> |
Routing priority decision | <span>ip route show</span> |
<span>valid_lft</span> |
Determines if IP is dynamically assigned | <span>journalctl -u NetworkManager</span> |
<span>LOWER_UP</span> |
Diagnoses physical link issues | <span>ip a | grep LOWER_UP</span> |
Open your Linux terminal, type “ip a”, and refer to this article to analyze your network configuration! If you encounter any issues, feel free to leave a comment for discussion! 👇
Previous Reviews: Download links for open-source operating systems (Red Hat series) – CentOS, Rocky, Alma, openEuler, please bookmark for future use. Step-by-step installation of Ubuntu 24.04 Server version.
Please open in the WeChat client