Linux Directory Management Commands1. Displaying the Path (pwd) 1. Command Function The pwd command is used to display the absolute path of the current working directory. 2. Command Format The format of the pwd command is:pwd.3. Command Examples Example 1: Log in as the root user and display the home directory of the root user. The code and result are as follows: Execute the command “cd ~” to switch to the user’s home directory, then execute the “pwd” command to check the current path, confirming that the home directory of the root user is /root.Example 2: Switch to the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory and display the current directory path. The code and result are as follows:
Execute the command “cd ~” to switch to the user’s home directory, then execute the “pwd” command to check the current path, confirming that the home directory of the root user is /root.Example 2: Switch to the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory and display the current directory path. The code and result are as follows: Execute the command “cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts” to switch to the specified directory, then execute the “pwd” command to find that the switched path is /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts.2. Switching Directories (cd)1. Command Function The cd command is used to switch the current working directory to a specified directory.2. Command Format The format of the cd command is:cd directory_name/special_symbol.3. Special Symbol Explanation The special symbols that can be used with the cd command and their meanings are shown in the table.
Execute the command “cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts” to switch to the specified directory, then execute the “pwd” command to find that the switched path is /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts.2. Switching Directories (cd)1. Command Function The cd command is used to switch the current working directory to a specified directory.2. Command Format The format of the cd command is:cd directory_name/special_symbol.3. Special Symbol Explanation The special symbols that can be used with the cd command and their meanings are shown in the table.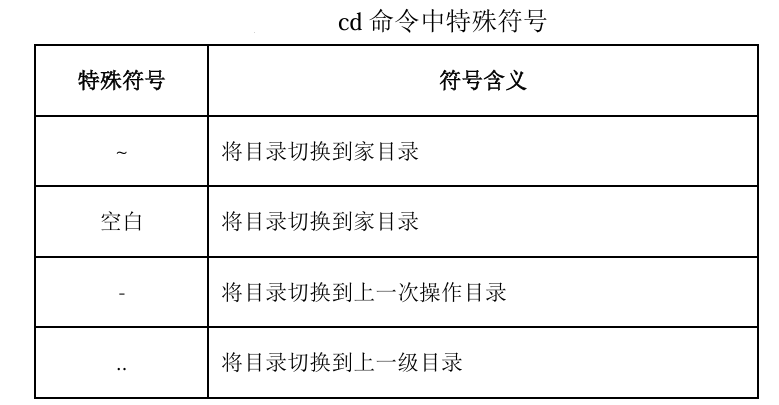 4. Command Examples Example 1: Use absolute path to switch from the current directory to the /usr/share/doc directory. The code and result are as follows:
4. Command Examples Example 1: Use absolute path to switch from the current directory to the /usr/share/doc directory. The code and result are as follows: You can switch directories using the absolute path, for example, execute the command “cd /usr/share/doc” to switch from the current directory to the /usr/share/doc directory.Example 2: Use relative path to switch from the current directory to the /usr/share/man directory. The code and result are as follows:
You can switch directories using the absolute path, for example, execute the command “cd /usr/share/doc” to switch from the current directory to the /usr/share/doc directory.Example 2: Use relative path to switch from the current directory to the /usr/share/man directory. The code and result are as follows: You can switch directories using the relative path. The current directory is /usr/share/doc, and both /usr/share/man and /usr/share/doc are under the /usr/share directory. Execute the command “cd ../man” to switch to the /usr/share/man directory, where “..” indicates the parent directory of the current directory /usr/share/doc, which is /usr/share.Example 3: Switch back to the /usr/share/doc directory from the current directory. The code and result are as follows:
You can switch directories using the relative path. The current directory is /usr/share/doc, and both /usr/share/man and /usr/share/doc are under the /usr/share directory. Execute the command “cd ../man” to switch to the /usr/share/man directory, where “..” indicates the parent directory of the current directory /usr/share/doc, which is /usr/share.Example 3: Switch back to the /usr/share/doc directory from the current directory. The code and result are as follows: When performing file directory operations, it is common to switch back and forth between directories. If you want to switch to the directory you just operated on, you need to input the path of the directory whether using absolute or relative paths. In such cases, you can use the special symbol “-“. For example, to switch back to the previously operated /usr/share/doc directory, you can simply execute the command “cd -” to complete the directory switch.Example 4: Switch from the current directory to the /usr/share directory. The code and result are as follows:
When performing file directory operations, it is common to switch back and forth between directories. If you want to switch to the directory you just operated on, you need to input the path of the directory whether using absolute or relative paths. In such cases, you can use the special symbol “-“. For example, to switch back to the previously operated /usr/share/doc directory, you can simply execute the command “cd -” to complete the directory switch.Example 4: Switch from the current directory to the /usr/share directory. The code and result are as follows: When performing file directory operations, returning to the parent directory is also a common occurrence. Although you can switch to the parent directory using the absolute path, the directory path can be long and prone to input errors. In such cases, you can use the special symbol “..”. For example, to switch from the /usr/share/doc directory to the /usr/share directory, you can simply execute the command “cd ..” to complete the directory switch.
When performing file directory operations, returning to the parent directory is also a common occurrence. Although you can switch to the parent directory using the absolute path, the directory path can be long and prone to input errors. In such cases, you can use the special symbol “..”. For example, to switch from the /usr/share/doc directory to the /usr/share directory, you can simply execute the command “cd ..” to complete the directory switch.
-END-