Click the blue text to follow us

Unveiling the
Mysteries of C Language
Bravery


Why learn C language?
– The “mother tongue” of programming: the foundation for low-level development of operating systems, databases, and embedded systems
– A “hard currency” in employment: essential skills for technical positions in major companies like Tencent and Huawei, with an average monthly salary exceeding 15K+
– A tool for logical training: cultivates structured thinking, making it easier to advance to languages like Python/Java
PART.01
Basic Syntax: Building the “Skeleton” of Programming

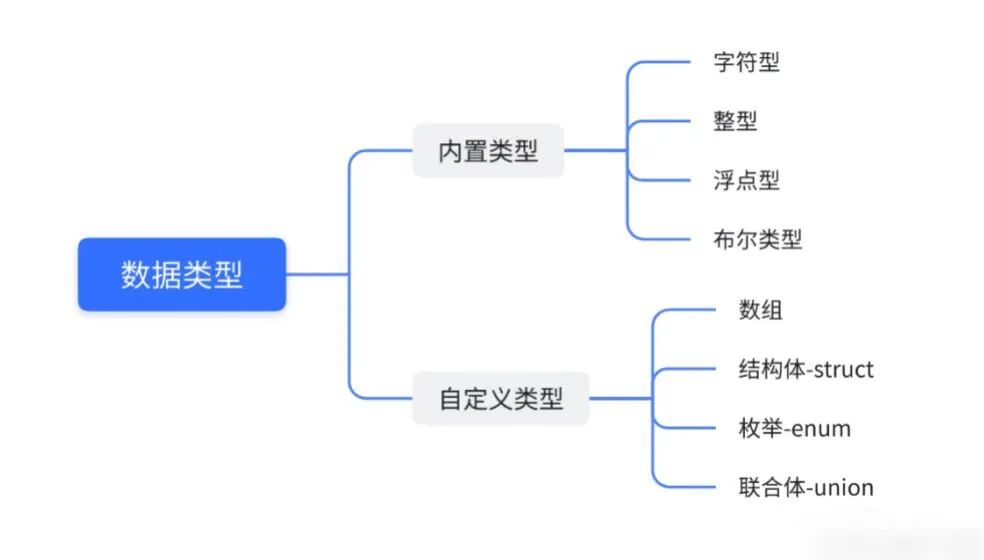
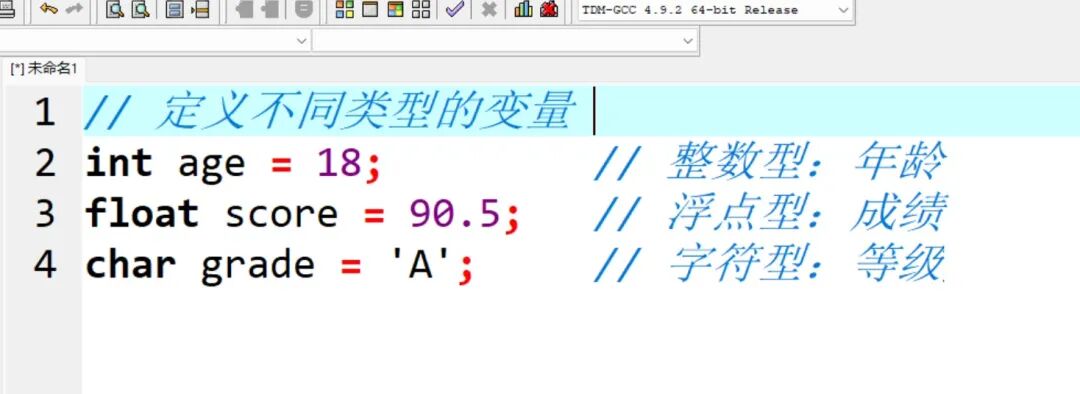
– Variables and Data Types (int/float/char)
– Operators and Expressions (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division/logical judgments)
– Control Flow (if-else loops/for/while statements)

Key Points 💡
Variables must be “defined before use”; data types determine memory allocation rules.
PART.02
Operators and Expressions

Arithmetic operations and logical judgments
Code example:
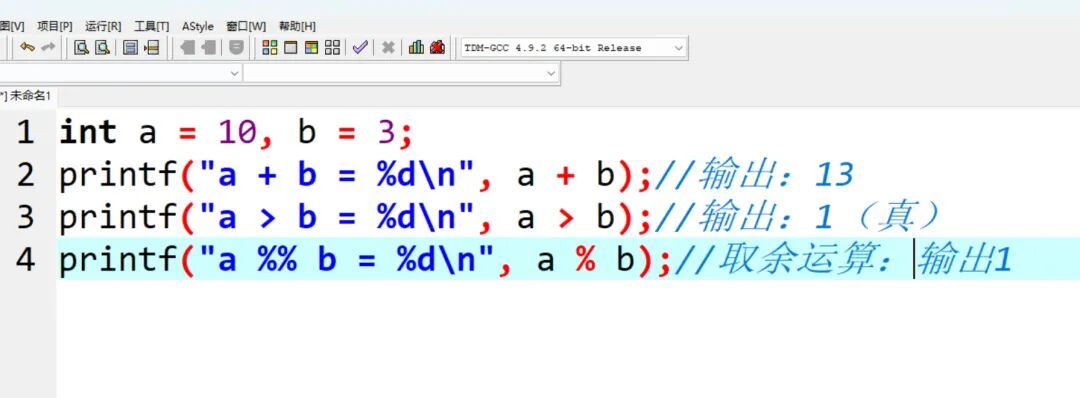
int a = 10, b = 3;
printf(“a + b = %d\n”, a + b); // Output: 13
printf(“a > b = %d\n”, a > b); // Output: 1 (true)
printf(“a %% b = %d\n”, a % b); // Modulus operation: Output 1
Note!!!
% is the modulus operator, applicable only to integers; logical result 1 means true, 0 means false.

PART.03

Control Flow: if-else and Loops

Example 1: Grade Level Judgment (if-else)
Code example:
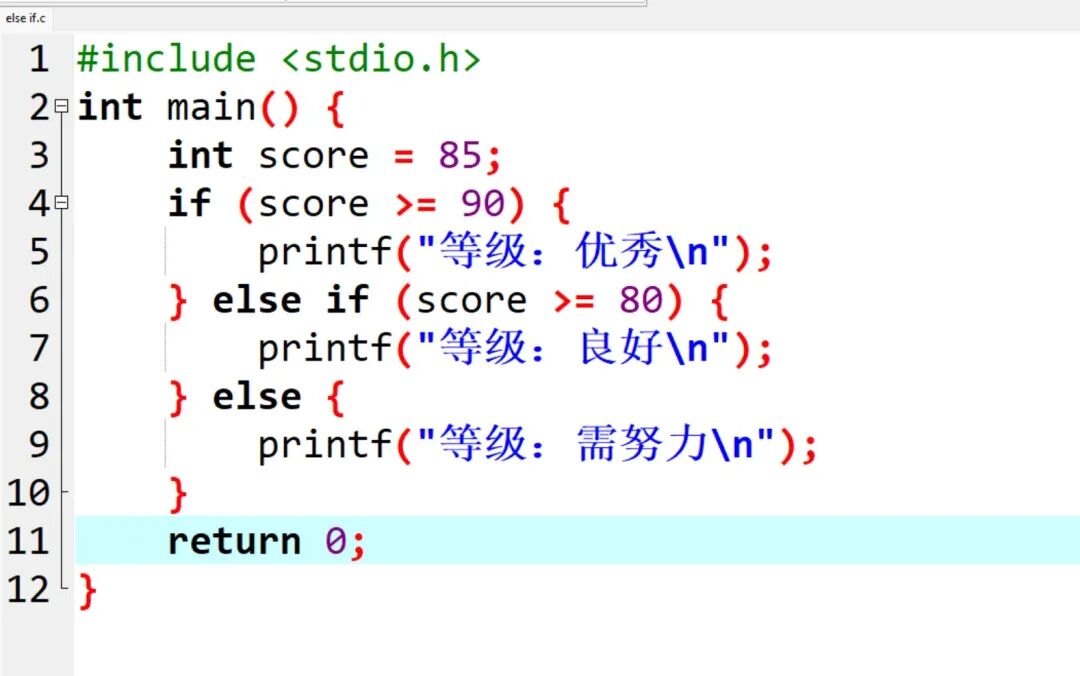
int score = 85;
if (score >= 90) {
printf(“Grade: Excellent\n”);
} else if (score >= 80) {
printf(“Grade: Good\n”);
} else {
printf(“Grade: Needs Improvement\n”);
}
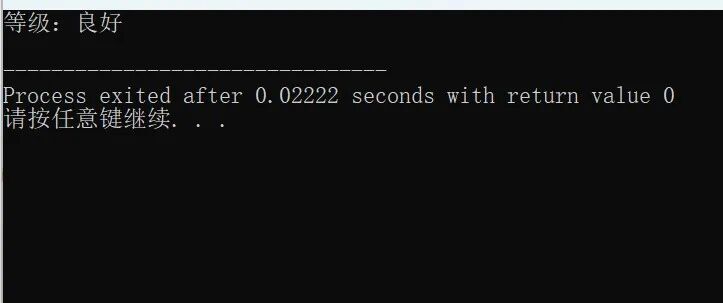
Output: Good
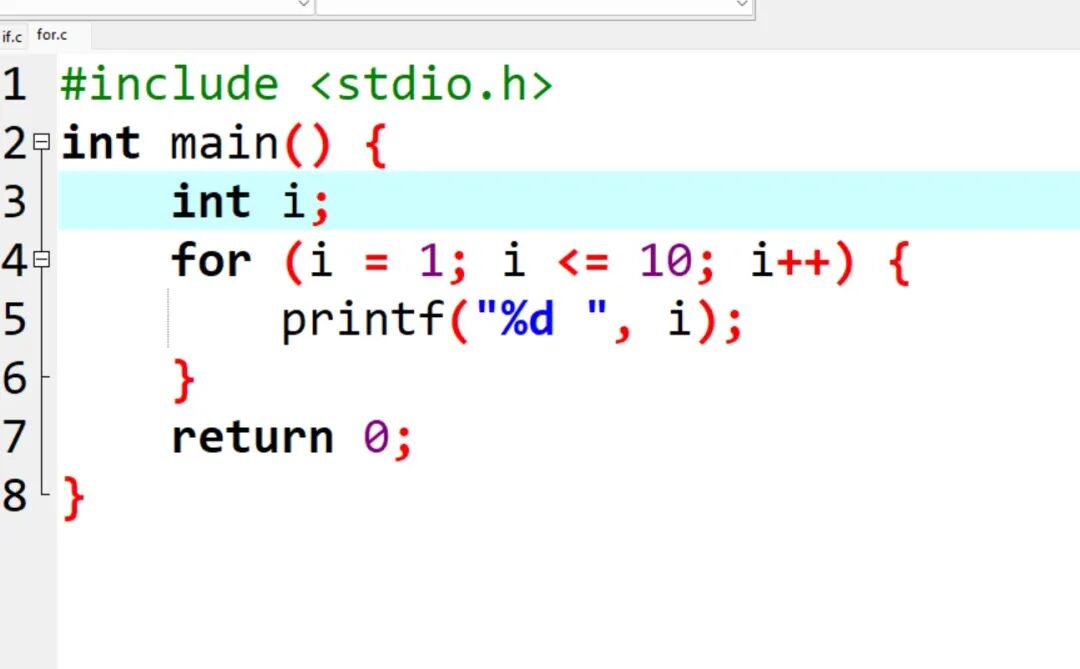
Example 2: Print numbers 1-10 (for loop)
Code example:
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
printf(“%d “, i);
}
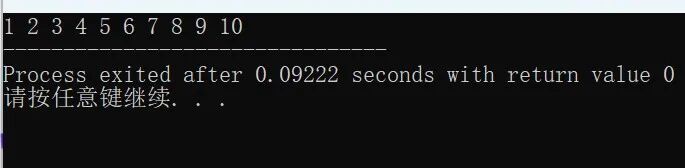
Output: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Tip ✨
The loop variable i can be understood as a “counter”; the condition i <= 10 controls the number of iterations.


C language is the first key to unlock the world of programming. Behind seemingly complex code lies a dual bloom of logic and creativity. Whether you want to enter a technical position or cultivate foundational programming thinking, start taking action now; the next programming expert could be you!

-end-
Illustration and text by Zhu Jinhao
Layout by Zhu Jinhao
Initial review by Zhu Junhao
Final review by Luo Jianguo
Zhuang Yishan
Final approval by Huang Sheng
