
“To achieve the ideal of “autonomous driving”, major automakers and suppliers are currently developing “Advanced Driver Assistance Systems” (ADAS). As ADAS continues to improve, vehicles are gradually transitioning from NHTSA Level 0 to Level 4, achieving full automation.”
ADAS (Advanced Driving Assistant System) is an advanced driving assistance system with over a dozen functions developed so far.
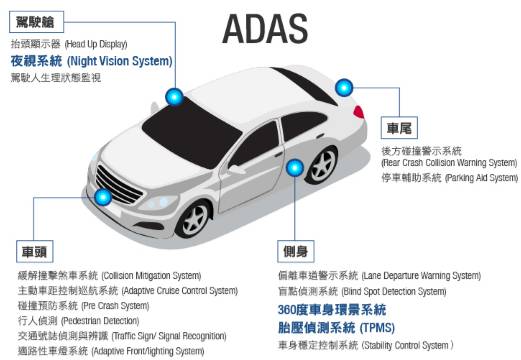
Based on functionality, it can be categorized as follows:
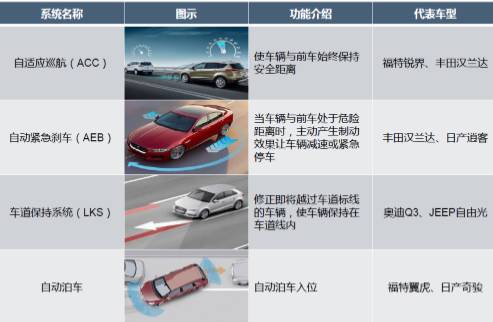
1. Active Control ADAS: ACC/AEB/LKS, etc.
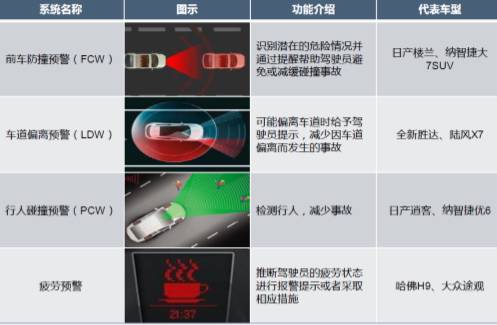
2. Warning ADAS: FCW/LDW/PCW, etc.
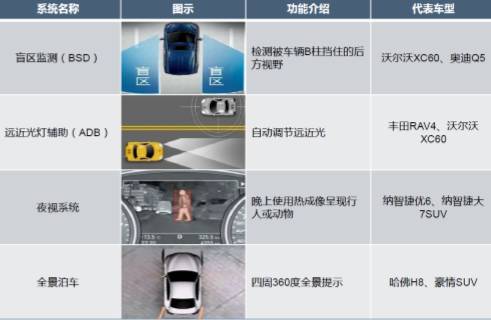
3. Other Assistance ADAS: BSD/ADB/Parking Assistance, etc.
Let’s take a look at how each function is implemented.
1: Adaptive Cruise Control System (ACC)
The Adaptive Cruise Control System is an intelligent automatic control system developed based on the existing cruise control technology. During vehicle operation, the distance sensor (radar) installed at the front of the vehicle continuously scans the road ahead while the wheel speed sensor collects speed signals. When the distance to the vehicle ahead is too short, the ACC control unit can coordinate with the anti-lock braking system and engine control system to appropriately brake the wheels and reduce engine output to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead.

2: Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB)
AEB is an active safety technology for vehicles, primarily consisting of three modules. The core of the distance measurement module includes microwave radar, laser radar, and video systems, which provide safe, accurate, and real-time images and road condition information ahead.
The AEB system uses radar to measure the distance to the vehicle or obstacle ahead, then compares this distance with the alert distance and safe distance using a data analysis module. If it is less than the alert distance, an alert is issued; if it is less than the safe distance, the AEB system activates automatically to brake the vehicle, ensuring safety during travel.
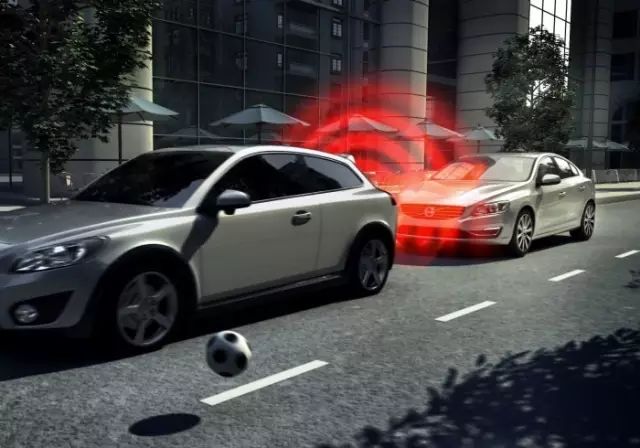

3: Adaptive Front Lights (AFL)
This technology can be installed in vehicles to change the direction of headlights based on the shape of the road. Some intelligent headlight control systems can also adjust the intensity of the headlights according to vehicle speed and road conditions.
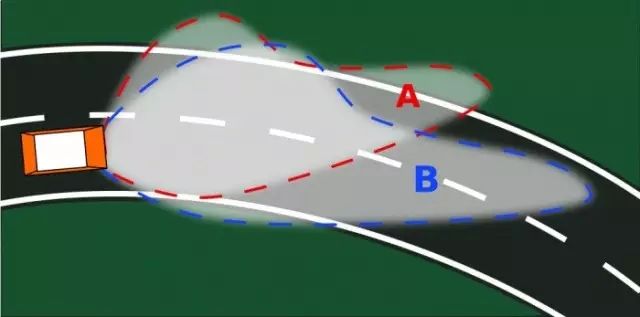
4: Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM)
The blind spot detection system uses collision avoidance radars, Doppler radars, infrared radars, and blind spot detectors arranged around the vehicle. Controlled by a computer, it provides necessary information to the driver about the vehicle’s surroundings through sound and light (flashing lights on the side mirrors) in hazardous situations such as overtaking, reversing, lane changing, fog, or rain, and can automatically take measures to effectively prevent accidents.
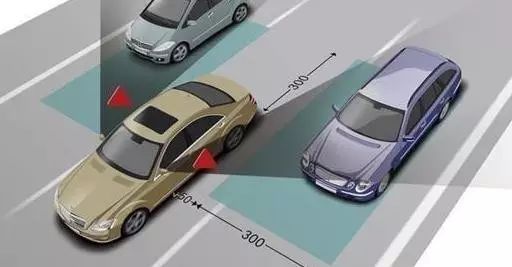
5: Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS)
This system uses sensors to detect the driver’s attention. If the driver looks ahead and a crisis situation is detected, the system will alert with flashing lights and loud sounds. If the driver does not respond, the vehicle will automatically brake.

6: Forward Collision Warning (FCW)
FCW can monitor the distance, position, and relative speed between the vehicle and the vehicle ahead at all times using radar systems and cameras. When a potential collision danger exists, it warns the driver. The FCW system itself does not take any braking measures to avoid collisions or control the vehicle.
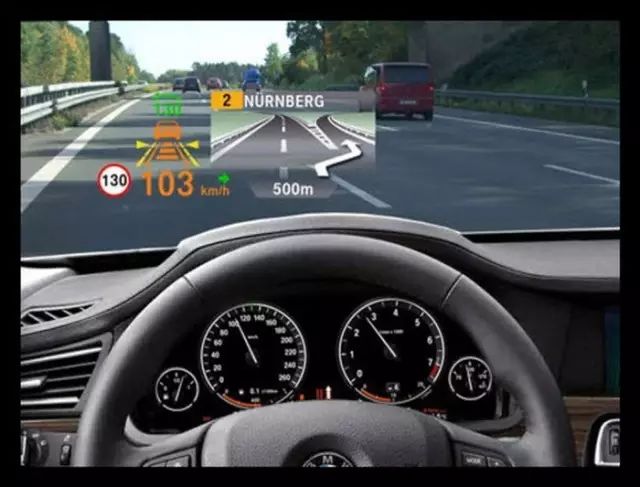
7: Heads-Up Display (HUD)
This technology projects important information (such as speed) from the vehicle’s instruments onto the windshield during driving, helping inexperienced drivers control their speed and avoid speeding violations in many speed-restricted areas. More importantly, it allows the driver to read information instantly without shifting their gaze, keeping them alert and maintaining optimal observation conditions.
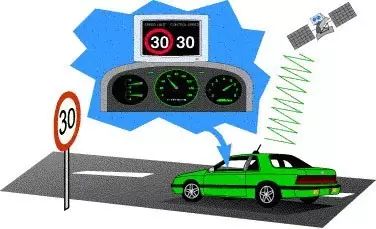
8: Intelligent Speed Adaptation (ISA)
The Intelligent Speed Adaptation system can recognize traffic signs and control the throttle based on the maximum speed limit information read, ensuring that the driver operates within the legal speed limit and effectively avoids speeding in an unconscious manner.
9: Lane Departure Warning (LDW)
The Lane Departure Warning system mainly consists of a HUD, cameras, controllers, and sensors. When the lane departure system is activated, the cameras (usually installed on the side of the vehicle or in the rearview mirror) continuously collect lane marking lines and obtain the vehicle’s position parameters within the current lane through image processing. When the vehicle is detected to be deviating from the lane, the sensors will promptly collect vehicle data and the driver’s operational status, and then the controller will issue an alert signal. The entire process takes about 0.5 seconds, providing the driver with more reaction time. If the driver activates the turn signal to change lanes normally, the lane departure warning system will not issue any alerts.
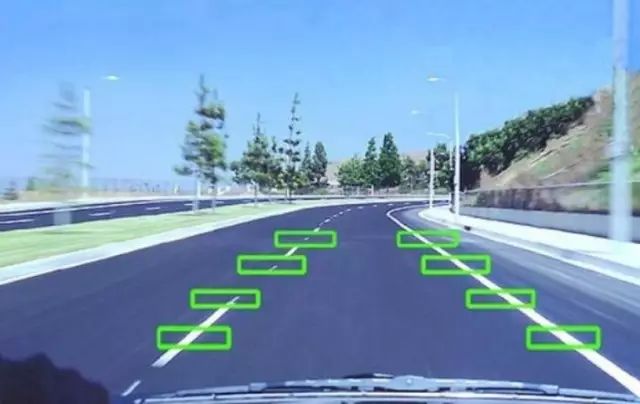
10: Night Vision System (NVS)
The Night Vision System uses infrared technology to make darkness visible as if it were daylight, allowing the driver to see further and more clearly at night. The night vision system consists of two parts: one part is the infrared camera, and the other part is the light display system on the windshield.

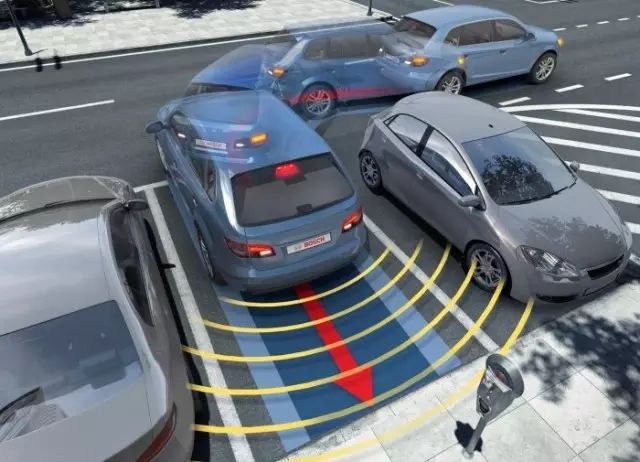
11: Parking Assistance (PA)
The Parking Assistance system detects parking spaces using cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared sensors installed on the vehicle, drawing parking maps and dynamically planning parking paths in real-time to guide or directly control the steering wheel into the parking position.

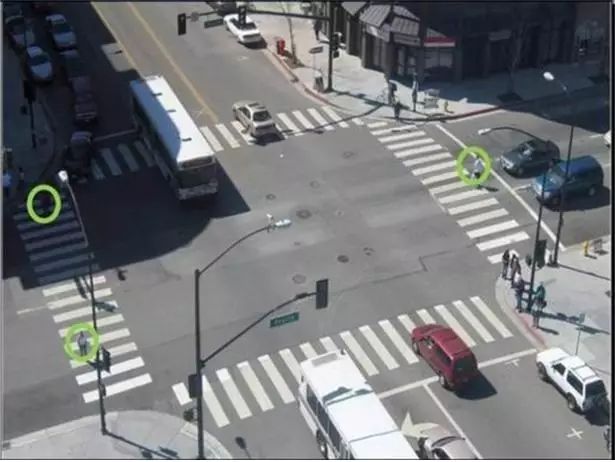
12: Pedestrian Detection System (PDS)
During vehicle operation, cameras and laser radars can detect pedestrians in all directions, adjusting speed in a timely manner within a safe distance.

13: Road Sign Recognition (RSR)
This technology enables vehicles to automatically recognize traffic signals or signs, such as speed limits or stop signs.

14: Surround View Cameras (SVC)
The Surround View Cameras system consists of four ultra-wide-angle fisheye cameras installed around the vehicle, capturing images from all sides. Through image processing, distortion correction, angle transformation, image stitching, and enhancement, it ultimately forms a seamless 360-degree top view around the vehicle. While displaying the panoramic view, it can also show any single view along with reference lines to accurately locate the position and distance of obstacles.

In addition, Mobileye has released a collision warning system that includes six ADAS features.
1: Distance Monitoring and Warning HMW

2: Forward Collision Warning FCW

3: Lane Departure Warning LDW
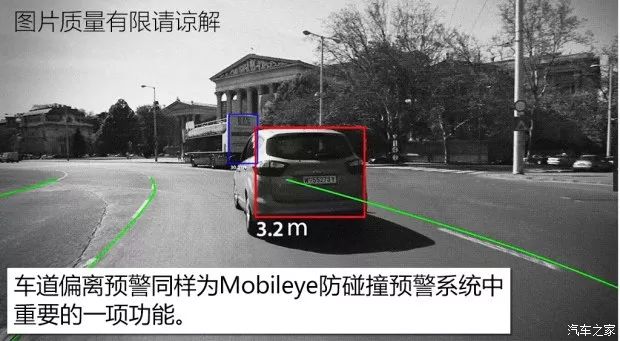
4: Intelligent High Beam Control IHC

5: Speed Limit Warning SLI

6: Pedestrian and Bicycle Warning PCW

Recommended Reading
▼




▎This article is republished from Robot 2025 and Auto Home.

