In the previous article, we discussed the differences between Modbus and RS-485, which belong to different layers. If we use a language analogy, then Modbus determines which “language” to use, while RS-485 and RS-232 determine the method of communication, such as face-to-face or telephone communication. In this article, we will discuss the differences between RS-485 and RS-232. Both belong to the physical layer and are hardware interface standards, defining the electrical and mechanical characteristics of physical connections between devices..
RS-485 is commonly used, so during electrical design, we studied its differences with RS-232. Although RS-232 is less commonly used by individuals, many power devices have this interface. Therefore, this article will explore their similarities and differences.
1. Similarities between RS-232 and RS-485
When discussing similarities, an unavoidable term is “serial communication.” In communication and computer science, serial communication is a general concept that refers to all serial communication protocols, such as RS-232, RS-422, RS-485, USB, etc. Serial communication refers to a method of communication that transmits data bit by bit using only one receiving line and one sending line. Although serial communication is slower than parallel communication, which transmits data by bytes, serial ports (hereafter referred to as serial ports) can achieve data transmission using only two wires.
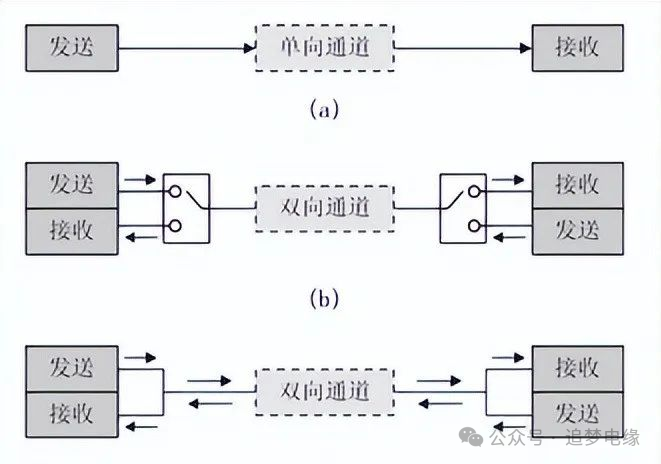
Serial communication modes include simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex, where simplex mode only supports data transmission in one direction. Half-duplex mode allows data to be transmitted in both directions, but only one direction at a time. Full-duplex mode supports simultaneous data transmission in both directions, achieving true bidirectional communication.
2. Now let’s discuss the differences
1. Differences in physical interfaces:

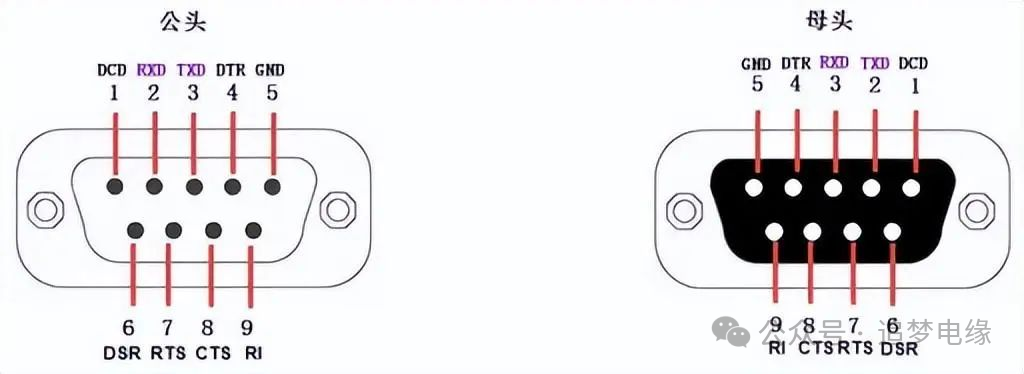
From the image above, the differences in their physical interfaces are evident. RS-485 interface is well-known, so let’s discuss the RS-232 interface. RS-232 typically uses a DB9 connector. Since the receive and transmit signals (RXD and TXD) between two communication devices should be cross-connected, the wiring of the DB9 female connector at the modem end is generally opposite to that of the male connector. In addition, there is also the DB25 connector, which has 25 pins, with different pins defining different signal functions. The details of the DB9 male and female connectors and pin assignments are shown in the images and tables below.
2. Differences in transmission methods
We previously discussed half-duplex and simplex: Full-duplex RS-422 is not commonly encountered, so we won’t discuss it. RS-485 is half-duplex communication, while RS-232 is simplex communication. That is, RS-485 uses differential signaling for data transmission, transmitting data through two signal lines, with the signal recognized by comparing the voltage difference between the two lines. One of the biggest advantages of RS-485 is that it supports multipoint communication, allowing multiple devices to be connected.
RS-232 uses single-ended signaling for data transmission, transmitting data through one signal line and a ground line. It only supports point-to-point communication and cannot meet the needs of multiple devices communicating simultaneously. However, due to its simplicity and ease of use, both hardware and software implementations are relatively easy, and the cost is low, making it the preferred choice in early computer and peripheral communications.
3. Differences in transmission distance and rate
RS-485 logic 1 is represented by a voltage difference of + (2 – 6) V between the two wires, while logic 0 is represented by a voltage difference of – (2 – 6) V. This differential transmission method has strong anti-interference capabilities, effectively canceling out external noise interference, allowing RS-485’s transmission distance to be greatly increased, with a maximum of 1200 meters. In terms of transmission rate, it can reach up to 10 Mbps, but the rate decreases with increasing distance.
RS-232 has a higher voltage standard, with logic 1 corresponding to a voltage range of -3V to -15V, and logic 0 corresponding to a voltage range of +3V to +15V. This larger voltage signal fluctuation enhances its anti-interference capability to some extent, but also limits its transmission distance, usually not exceeding 15 meters, and it is also prone to damage the interface circuit chips. In terms of transmission rate, RS-232 generally ranges from 19.2 kbps to 1 Mbps.
Well, the above introduction is quite comprehensive for us in the power industry!