When there are issues with the CAN bus, it is often accompanied by various faults, such as abnormal dashboard displays, the vehicle not starting, or not being able to turn off after starting, etc. We will mainly introduce the eight common types of CAN bus faults and specific troubleshooting methods. Below is the main text.
The most common fault symptom is an abnormal display on the dashboard, as shown in the figure below.

During the inspection process, the specific fault symptoms should first be checked. Based on the fault symptoms and network structure diagram, a preliminary analysis can be made to identify possible causes, and then relevant diagnostic instruments should be used for diagnosis. Based on the diagnostic results, a relevant repair plan can be formulated to ensure clarity of the situation and clear objectives.
Next, locate the specific fault point and cause while using corresponding detection methods and measurement results to find the fault point, thereby completely eliminating the fault.
Since the CAN network uses multiple protocols, each control module’s port should have a standard voltage under normal conditions. Therefore, the voltage measurement method can be used to determine if there are issues such as short circuits to ground or power supply, or short circuits between phases.
To determine whether the CAN H or CAN L wire is damaged or whether the signal is normal, the voltage to ground (average voltage) can be measured. The measurement point is usually at the OBD diagnostic interface, as shown in the figure below.
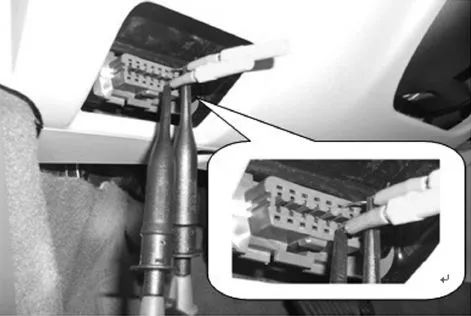
Pin 6 of the diagnostic interface is connected to the CAN H wire, and pin 14 is connected to the CAN L wire. If two sets of CAN buses are connected to the diagnostic interface, then the power CAN bus uses pins 6 and 14, while the comfort bus uses pins 3 and 11. The significance of the pins on the diagnostic interface is shown in the figure below.
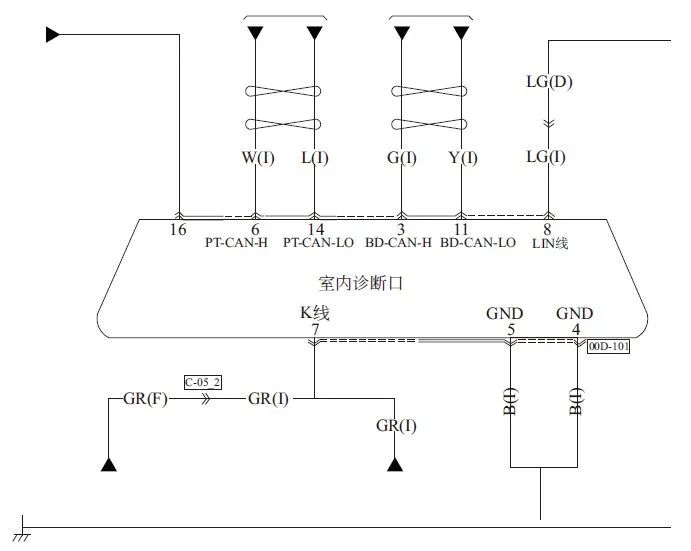
Under normal circumstances, after the CAN bus wakes up, the voltage of CAN H to ground is about 2.656V, and the voltage of CAN L to ground is about 2.319V, and the sum of both is 4.975V ▼


Common causes of CAN faults include short circuits in CAN wires, short circuits to power supply, short circuits to ground, and reversing connections.
1. Short Circuit Between CAN H and CAN L
When there is a short circuit between CAN H and CAN L, the CAN network will shut down and communication will no longer be possible. There will be corresponding network fault codes. The bus waveform of the short circuit between CAN H and CAN L is shown in the figure below.
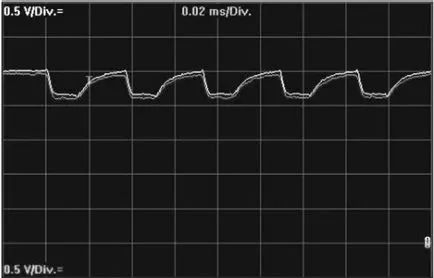
After the two are short-circuited, the CAN voltage will be at the hidden voltage value (about 2.5V). Actual measurements of the voltages of the two CAN wires will show that they remain around 2.5V, with little change, as shown below.

Troubleshooting method: By unplugging the control modules (nodes) on the CAN bus, it can be determined whether the short circuit is caused by a node or by a wiring connection.
Disconnect each node one by one; if the voltage returns to normal, it indicates that the node has a problem. If the voltage does not change after disconnecting all nodes, it indicates a wiring short circuit.
2. Short Circuit of CAN H to Power Supply (Positive)
When a short circuit of CAN H to the power supply (positive) occurs, due to the fault tolerance characteristics of the CAN bus, the entire CAN network may be unable to communicate or generate relevant fault codes.
Taking a short circuit to a 12V power supply as an example, at this point, the voltage of CAN H will be set to 12V, and the hidden voltage of the CAN L wire will be set to approximately 12V. The bus waveform of CAN H short-circuited to the power supply is shown in the figure below.
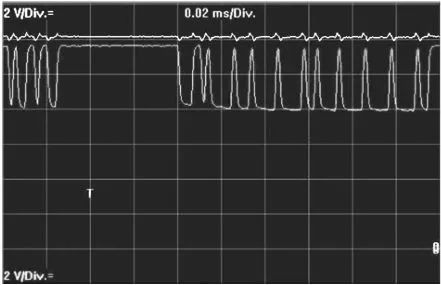
When measuring the voltage, if the voltage of CAN H is 12V and that of CAN L is approximately 11V, it indicates that this type of fault has occurred. The voltage of CAN H short-circuited to the power supply is shown in the figure below.

The voltage of CAN L short-circuited to the power supply is shown in the figure below.

Fault cause: If the fault is not caused by a short circuit of the CAN H wire to the external power supply, then this fault may be caused by damage to the CAN transceiver inside the control module. The fault finding method is the same as above.
3. Short Circuit of CAN H to Ground
When a short circuit of CAN H to ground occurs, due to the fault tolerance characteristics of the CAN bus, the entire CAN network may be unable to communicate or generate relevant fault codes.
The voltage of CAN H is at 0V, and the voltage of CAN L is also at 0V, but a small portion of voltage variation can still be seen on the CAN L wire. The bus waveform of CAN H short-circuited to ground is shown in the figure below.
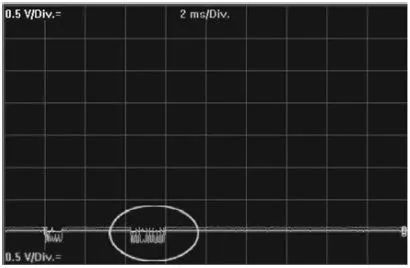
When measuring the voltage, if both CAN H and CAN L voltages are approximately 0V and there are no open circuit issues, it indicates that this type of fault has occurred. The voltage of CAN H short-circuited to ground is shown in the figure below.

The voltage of CAN L short-circuited to ground is shown in the figure below.

Fault cause: If the fault is not caused by a short circuit of the CAN H wire to the external ground, then this fault may be caused by damage to the CAN transceiver inside the control module. The fault finding method is the same as above.
4. Short Circuit of CAN L to Ground
When a short circuit of CAN L to ground occurs, due to the fault tolerance characteristics of the CAN bus, the entire CAN network may be unable to communicate or generate relevant fault codes.
However, for certain vehicle models, such as Haima, the fault tolerance characteristics of CAN L short-circuited to ground are relatively good, and the vehicle can generally operate normally, meaning there are no obvious abnormal phenomena from the customer’s experience. However, from a diagnostic perspective, it can affect network transmission speed.
At this time, the voltage of CAN L is approximately 0V. The hidden voltage of the CAN H wire is reduced to 0V, but the explicit voltage remains basically unchanged, so the waveform is stretched, and data can still be transmitted. This explains why the fault tolerance characteristics of CAN L short-circuited to ground are good. The bus waveform of CAN L short-circuited to ground is shown in the figure below.
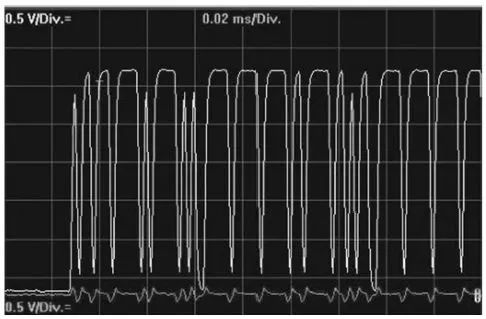
When measuring the voltage of the CAN wire, if the voltage of CAN L is 0V and CAN H is around 1V, it indicates that this type of fault has occurred. The voltage of CAN L short-circuited to ground is shown in the figure below.

The voltage of CAN H short-circuited to ground is shown in the figure below.

Fault cause: If the fault is not caused by a short circuit of the CAN L wire to the external ground, then this fault is likely caused by damage to the CAN transceiver inside the control module. The fault finding method is the same as above.
Source | Wire Harness Engineer
Click the mini program below to see more repair cases
















