Server Related
- $server_addr: Server address
- $server_name: Virtual host name (configured by the server_name directive)
- $server_port: Server port
- $document_root: Path configured by the root or alias command, which may be a symbolic link.
- $realpath_root: The actual path corresponding to the current request, absolute path.
- $request_filename: The file path of the current request, derived from the configuration of root or alias
- $host: The value from the Host header if present, otherwise the server_name (from nginx configuration)
- $hostname: Hostname of the server running nginx
- $nginx_version: Version of nginx
- $pid: Worker process ID
- $limit_rate: Value set by the limit_rate directive.
Example of variable usage for logging:
http {
log_format about_server_log 'server_addr: $server_addr, server_name: $server_name, server_port: $server_port\n'
'document_root: $document_root, realpath_root: $realpath_root, request_filename: $request_filename\n'
'host: $host, hostname: $hostname, nginx_version: $nginx_version\n'
'pid: $pid, limit_rate: $limit_rate';
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
access_log logs/server.log about_server_log;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8009/api/;
limit_rate 100k;
}
}
}
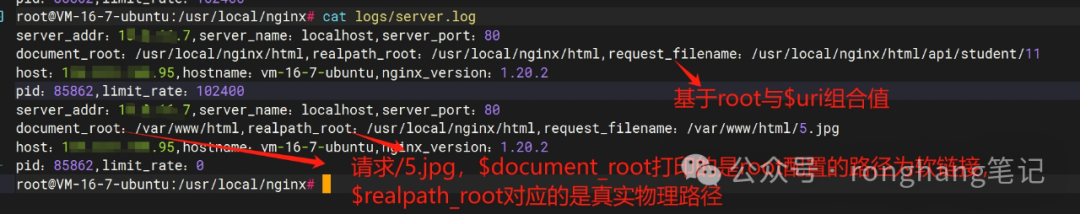
When requesting<span>http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/5.jpg</span>, the value of $document_root is the path configured by the root directive, which is a symbolic link, while the value of $realpath_root is the actual physical path. When requesting<span>http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/api/student/11</span>, the response comes from the proxy service, and the value of $request_filename is derived from the combination of the root configuration and$uri:
Client Related
- $binary_remote_addr: Binary representation of the client IP
- $remote_addr: Client IP
- $remote_port: Client port
- $remote_user: Username during HTTP Basic authentication
- $request: HTTP request, including method, URI, protocol, and version
- $request_method: Request method
- $request_uri: Complete URI
- $request_completion: Value is OK when the request is complete, otherwise an empty string
- $args or $query_string: Request parameters
- $arg_name: Value of the name parameter in the request
- $is_args: If there are request parameters, the value is ?, otherwise an empty string
- $scheme: Request protocol, http or https
- $https: Connection protocol, if https, the value is on, otherwise an empty string
- $http_host: Value of the Host header in the request
- $http_name: Value of the name header in the request
- $content_length: Content-Length in the request header
- $content_type: Content-Type in the request header
- $cookie_name: Value of the cookie with key name, name can also be other names
- $document_uri: This is$uri
- $server_protocol: HTTP protocol version
Example for if condition:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /api/ {
# Pass the username from HTTP Basic authentication to the upstream service
proxy_set_header X-User $remote_user;
# Check the request method
if ($request_method != "GET") {
return 405 "method not allowed";
}
# Check the Content-Type type that can be handled
if ($content_type != "application/json") {
return 415 "Unsupported Media Type";
}
proxy_pass http://localhost:8009/api/;
}
}
server {
listen 81;
server_name localhost;
location / {
# Redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS:
if ($scheme = "http") {
return 301 https://$host:443$request_uri;
}
...
}
}
Response Related
- $status: Response status code
- $sent_http_name: Name value in the response header
- $body_bytes_sent: Number of bytes sent in the response body
- $bytes_sent: Number of bytes sent in the response
Proxy Related
- $upstream_addr: IP and port of the upstream server
- $upstream_status: Response status code from the upstream server
- $upstream_response_time: Response time from the upstream service
- $proxy_host: Hostname and port of the target server in the proxy_pass directive
- $proxy_port: Port of the target server in the proxy_pass directive