
With the increasing living standards of the people, dietary structures and habits have also changed accordingly. Some cold and spicy foods have gradually become popular among the public. However, due to individual differences in constitution, coupled with the irregular lifestyle and diet of most people in current society, the number of patients with digestive system diseases has increased geometrically.

In addition to common diagnostic methods for digestive diseases such as gastroscopy, colonoscopy, abdominal ultrasound, and abdominal CT, are there any other safe, painless, and flexible imaging examination methods?Of course there are!Our hospital introduced the digital gastrointestinal imaging system as early as 2013. As a multifunctional digital imaging device, its clinical applications are very extensive. It can be used for various system imaging examinations and can provide imaging diagnostics for various diseases of the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, jejunum, and colon. It is one of the main examination methods for various diseases such as ulcers, tumors, and foreign bodies. Because it can perform fluoroscopy, it is also a good assistant for certain vascular and non-vascular interventional treatments.
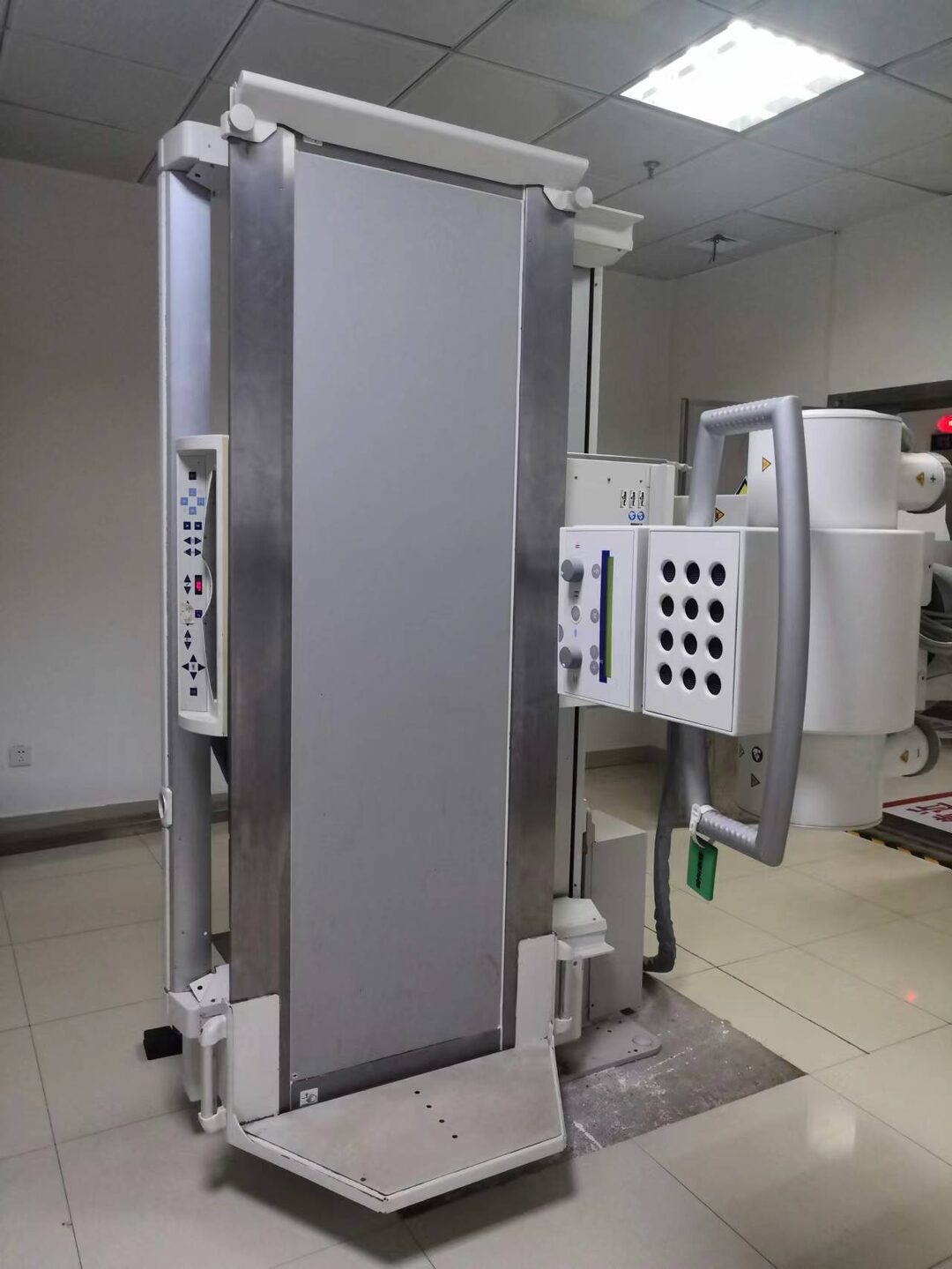

As the only hospital in Gao’an to introduce a digital gastrointestinal imaging system, our hospital strives to provide better examinations and treatments for patients, allowing the people of Gao’an to have access to quality diagnostics right at their doorstep.

Characteristics of Digital Gastrointestinal Imaging System
1. High grayscale resolution of images; 2. Images can be optimized before printing; 3. Digital image data stored on a computer is small in size and easy to manage; 4. The advantages of X-ray barium meal imaging over gastroscopy include being simple, painless, and non-invasive, providing rich and high-quality images, and being able to discover submucosal lesions of the gastrointestinal tract and the functional status of hollow organs, which cannot be replaced by gastroscopy or CT examinations.
Applications of Digital Gastrointestinal Imaging System
Upper Gastrointestinal Imaging
The digital gastrointestinal imaging system can clearly diagnose lesions such as esophageal erosion, esophageal varices, esophageal cancer, laryngeal syndrome, gastric cancer, gastric antrum lesions, and duodenal ulcers.
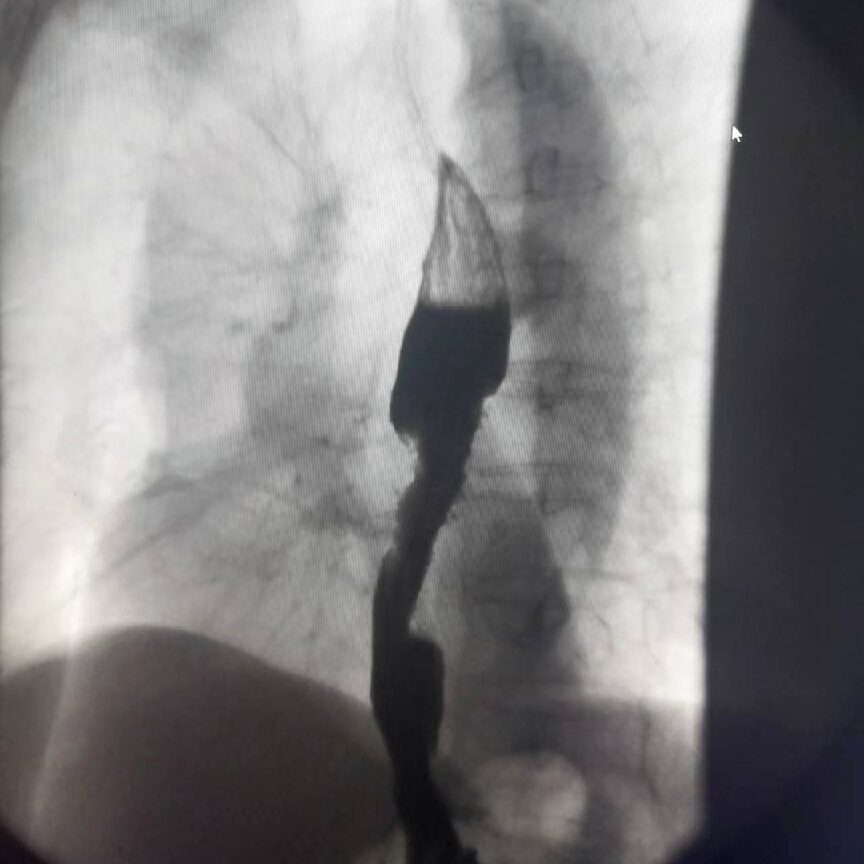
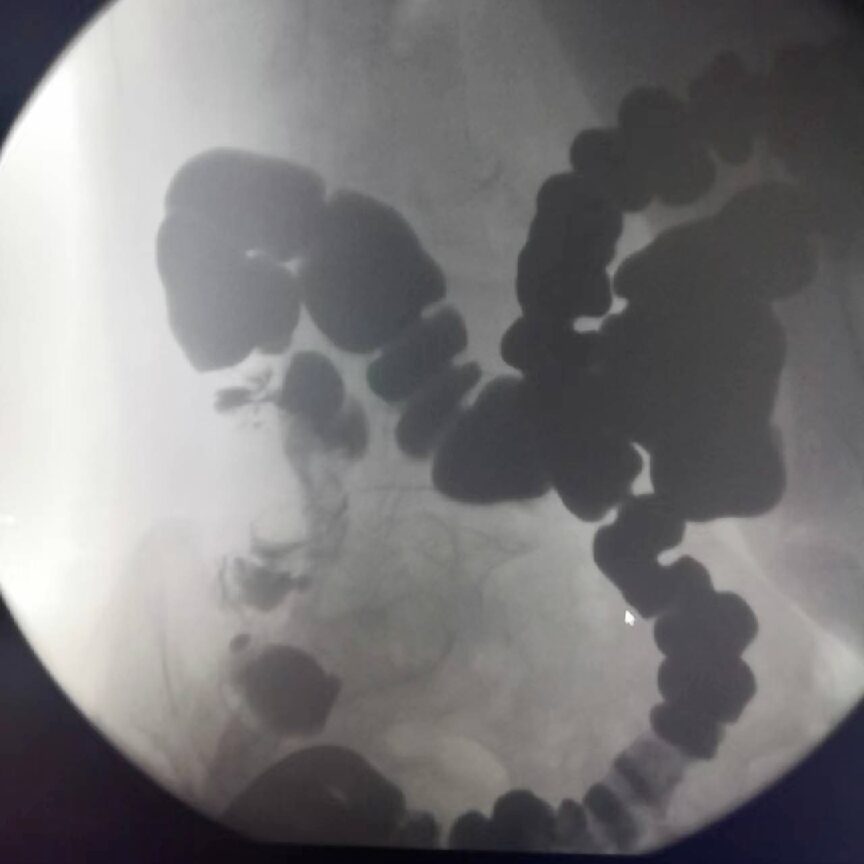
Lower Gastrointestinal Imaging
It can display images of the jejunum, ileum, and colon, clearly diagnosing lesions such as intussusception, rectal colon polyps, and diverticula.
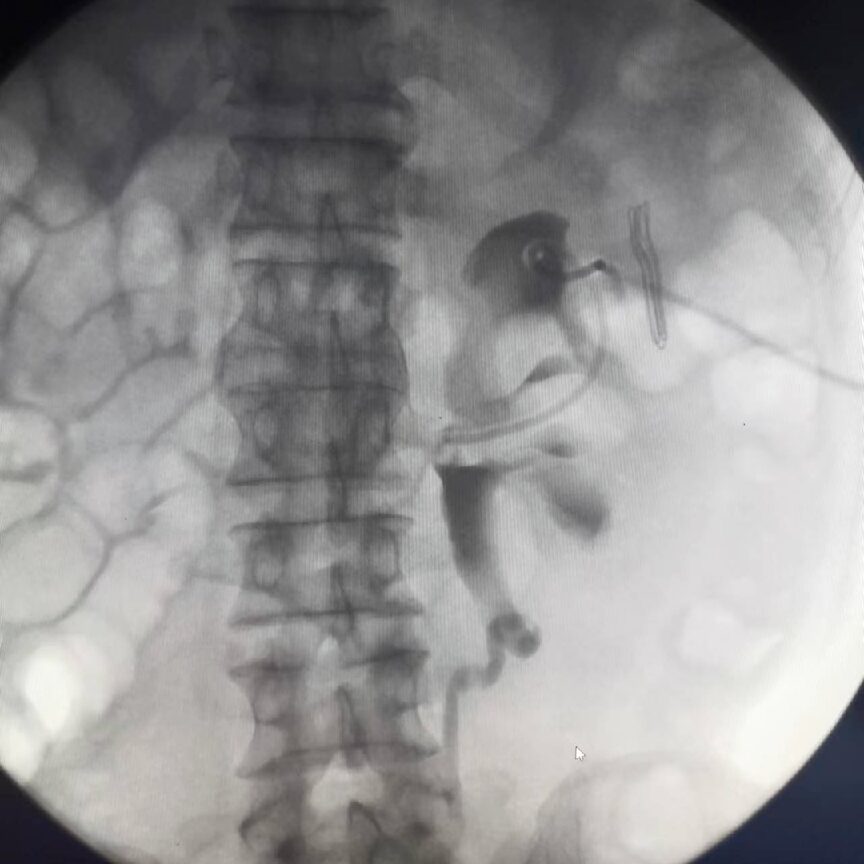
Urological Imaging
It can display the entire imaging of the urinary system, clearly diagnosing lesions such as urinary stones, ureteral deformities, urinary tumors, renal tuberculosis, and ureteral tuberculosis.
Hysterosalpingography
Real-time observation helps determine the type and location of lesions, with minimal damage and stimulation. It can display uterine abnormalities, the patency of the fallopian tubes, and has a certain therapeutic effect on clearing blocked fallopian tubes.
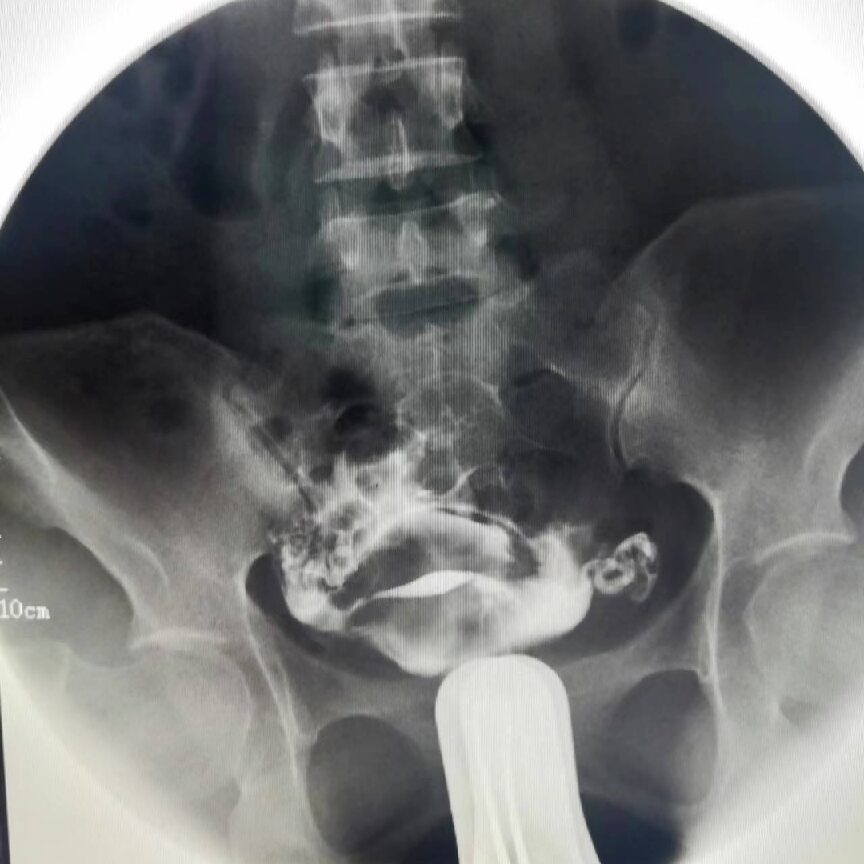
ERCP
Imaging displays effects, and using an endoscope for ERCP operation is a minimally invasive treatment method for removing stones from the intrahepatic bile ducts.
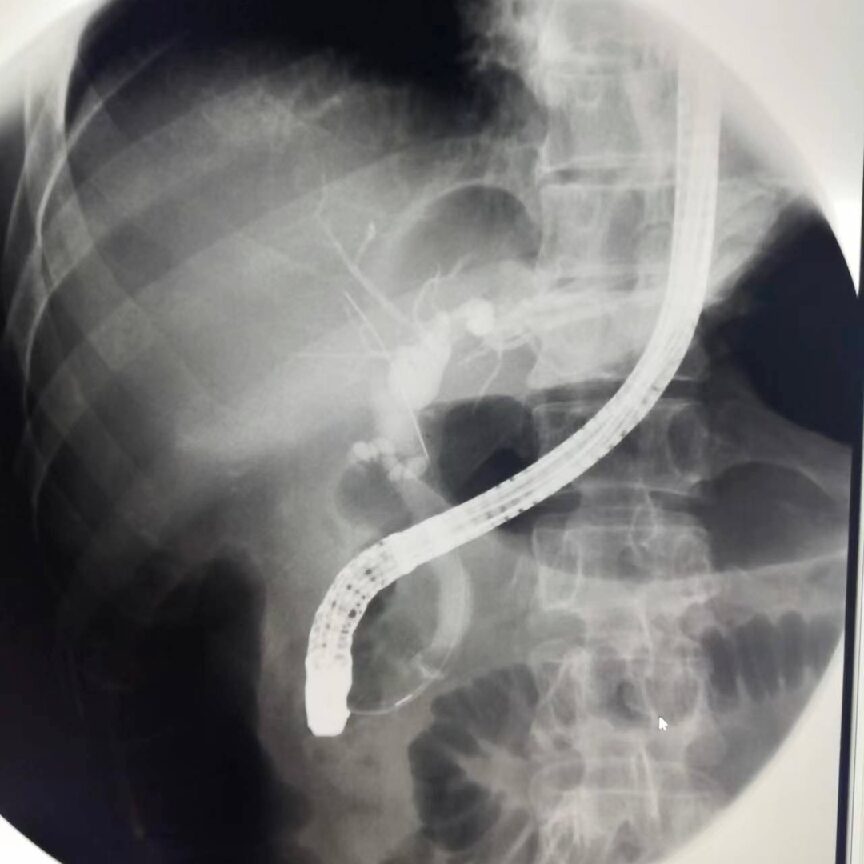
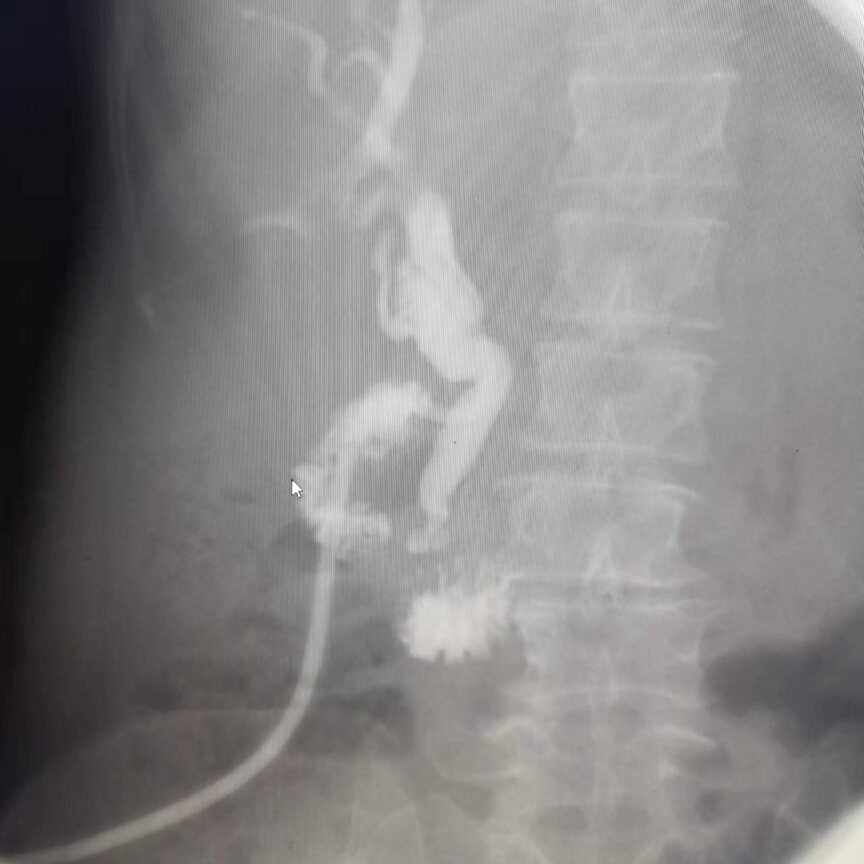
T-tube Imaging
This is a routine examination method for patients with T-tube drainage after biliary surgery, which can help determine if there are residual stones in the bile duct, bile duct stenosis, and the patency of the Oddi sphincter.
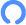
The digital gastrointestinal imaging system, in addition to the aforementioned “skills”, can also perform some vascular imaging (such as lower limb varices). At times when gastrointestinal examinations are not frequent, it can also be used for routine DR photography, achieving multi-use of one machine.
Precautions Before Digital Gastrointestinal Imaging Examination
1. For upper gastrointestinal imaging, fasting and drinking are prohibited for 4-6 hours before the examination, and medications (including iron, iodine, silver, and other high-density substances) should not be taken within 24 hours prior. Generally, fasting in the early morning is sufficient. 2. For colon imaging, a cleansing enema should be performed, and this type of examination is prohibited for those with gastrointestinal perforation, intestinal obstruction, or massive gastrointestinal bleeding. 3. For urological examinations, gastrointestinal preparation is required first, and a cleansing enema may be necessary. On the day of examination, fasting and drinking are prohibited, medications should not be taken within 24 hours, and iodine allergy tests should be performed. Those with positive results are prohibited from undergoing this type of examination. 4. Individuals with metabolic disorders, acute infectious diseases, high fever, severe cardiovascular and liver diseases, acute urinary infections, severe kidney dysfunction, pregnancy, and postpartum periods are prohibited from undergoing this type of examination.

Scan to Follow for More Hospital Information


Submitted by: Radiology Department, Lu Yong
Edited by: Xing Qiong, Zhang Qiaoqi
Reviewed by: Deng Zhishi
Final Review: Zhou Guoping