Case provided by:Associate Chief Physician Ye Weihua, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
【Patient Basic Information】: Male, 17 years old
Main Complaint: Post-operative recovery from left mandible cyst curettage for over 2 months
Present Illness: The patient was admitted to our hospital’s oral and maxillofacial surgery ward 2 months ago due to a “left mandible mass for two years”. Subsequently, he received root canal treatment for the left anterior teeth and first molar in the dental clinic, followed by a “left mandible cyst curettage” under general anesthesia. Post-operative pathology indicated a bone cyst lesion. The left lower first premolar, affected by the cyst, had not yet undergone root canal treatment and was referred to our department.
Past Medical History: Denies systemic diseases
Drug Allergy History: None
【Clinical Examination】
Teeth 31, 32, 33, 36 show color restorations on the occlusal surface, while teeth 34 and 35 show no abnormalities. The vestibular groove of the left mandible is shallow, and the gingival area from 31 to 35 is slightly raised. Teeth 31 to 36 show no mobility or caries. The left mandible and facial area are slightly swollen, with slight asymmetry on both sides of the face.
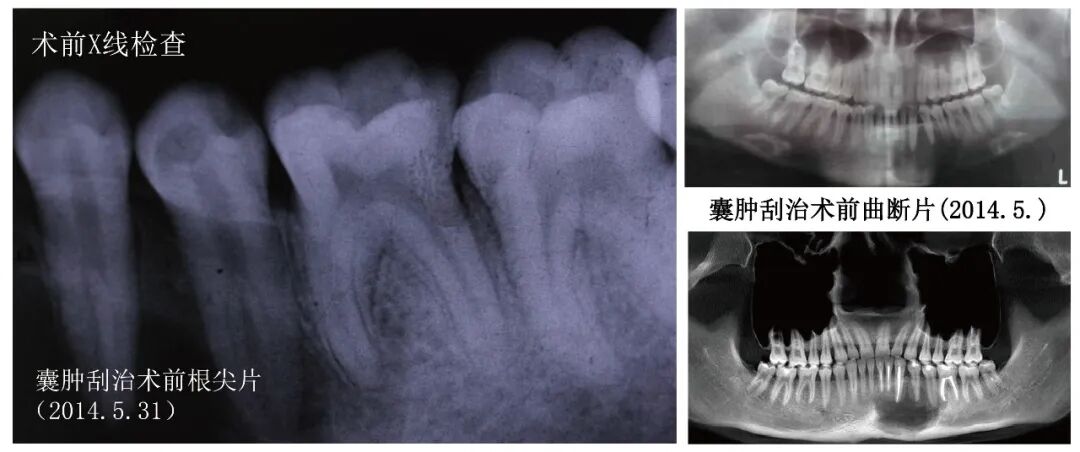
Auxiliary Examination: Pre-operative periapical radiographs indicate that the main canals of teeth 34 and 35 split into two smaller canals in the middle segment of the root, with a visible longitudinal root surface groove in tooth 35. Post-operative CBCT after cyst curettage shows dense filling material in the canals of teeth 31, 32, 33, and 36; no filling material is seen in the canals of teeth 34 and 35, and the cross-section of the roots and canals is C-shaped.
【Diagnosis】 Post-operative from left mandible cyst curettage, chronic apical periodontitis of teeth 34 and 35
【Treatment Plan】1. Root canal treatment for teeth 34 and 35; 2. Direct composite resin restoration for teeth 34 and 35.
【Treatment Process】
Pre-operativeX-ray examination
 Post-curettage, pre-treatment CBCT for teeth 34 and 35 (2014.8.12)
Post-curettage, pre-treatment CBCT for teeth 34 and 35 (2014.8.12)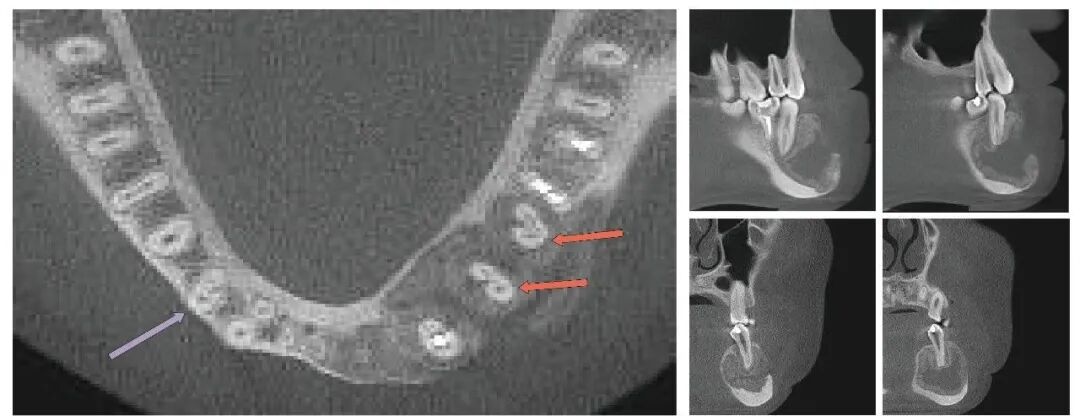
Pulp opening, using sharp files under a microscope to prepare the root canal, tooth 34 has two canals, tooth 35 has three canals (2014.8.12)
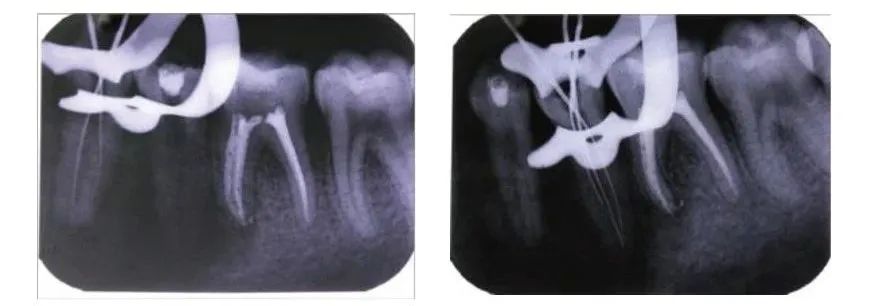 Trial apex and root filling for tooth 35 (2014.8.21)
Trial apex and root filling for tooth 35 (2014.8.21)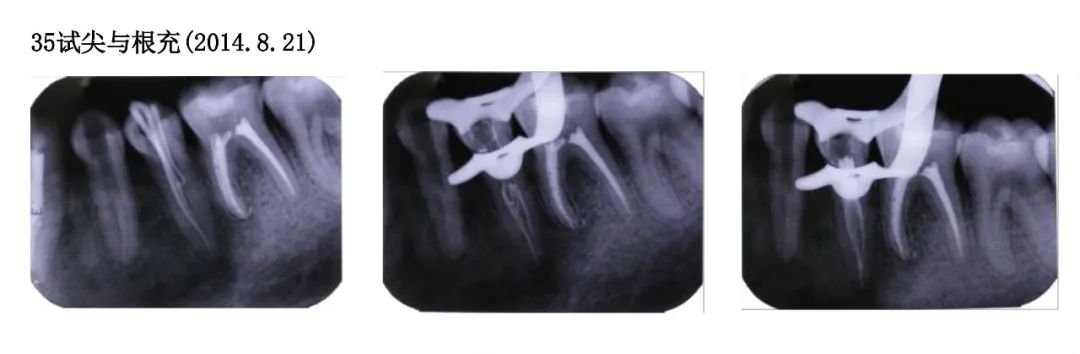 Trial apex and root filling for tooth 35 (2014.8.21)
Trial apex and root filling for tooth 35 (2014.8.21)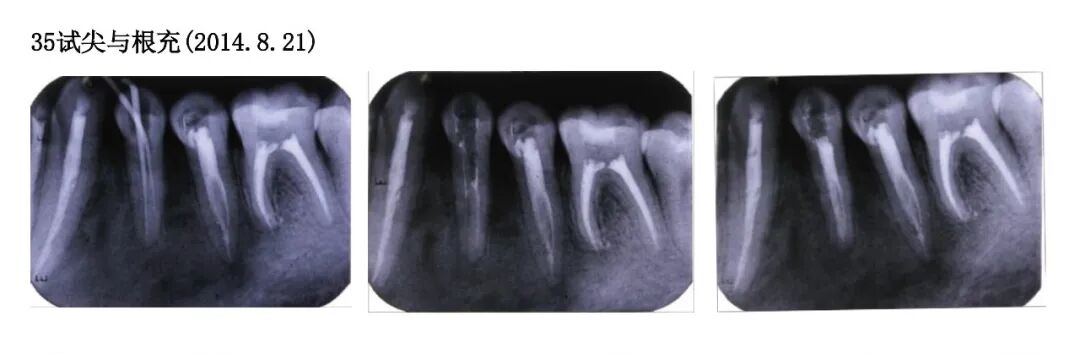 Direct filling of composite resin for teeth 34 and 35 (2014.8.21)
Direct filling of composite resin for teeth 34 and 35 (2014.8.21)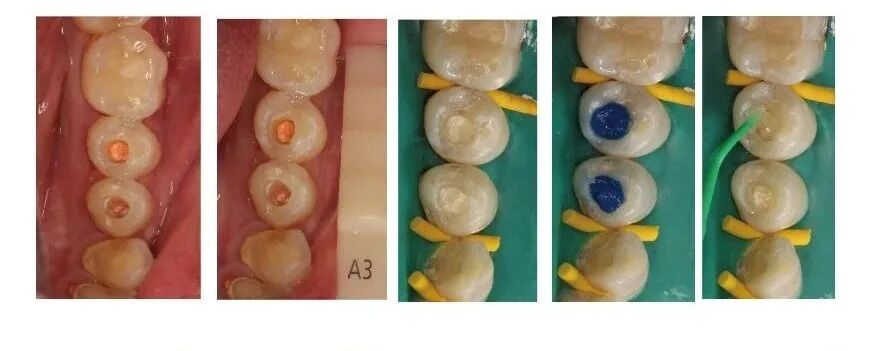 Occlusal adjustment, polishing for teeth 34 and 35 (2014.8.21)
Occlusal adjustment, polishing for teeth 34 and 35 (2014.8.21)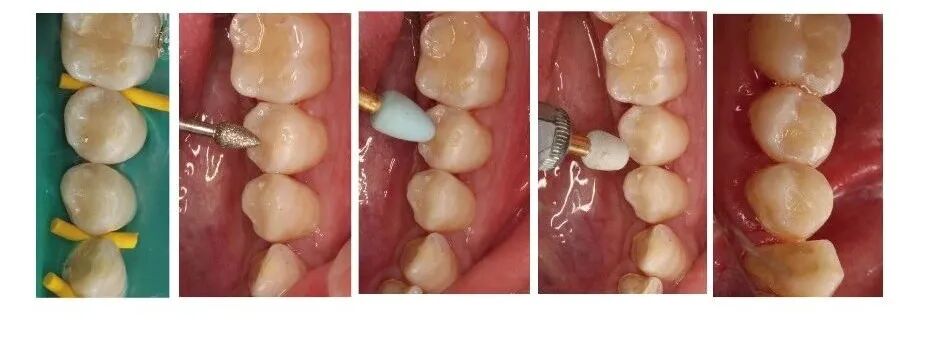 【Follow-up】
【Follow-up】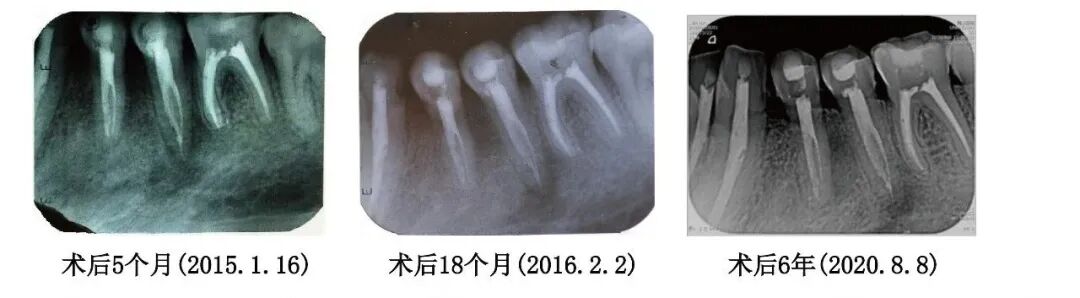
【Discussion】
The main anatomical feature of the C-shaped root canal system is the presence of a connecting isthmus between the mesial and distal canals, commonly found in the mandibular second molars and first premolars [1]. The incidence of C-shaped root canals in Chinese individuals is as high as 31.5% for mandibular second molars, 18% to 19.6% for mandibular first premolars, and 0.6% for mandibular second premolars [1]. Slowey pointed out that among all teeth, the mandibular premolars present the greatest anatomical challenge for root canal treatment [2]. Gu noted that the mesial canal wall of the C-shaped root canal in mandibular first premolars is the thinnest, measuring 0.54 to 1.03 mm, necessitating caution during canal preparation and filling [3].
C-shaped canals require flexible root canal files that adapt to the canal morphology to achieve proper preparation. The Sufeng Sharp File GF-FILE Blue Diamond combines gradient flexibility with dual patents from both domestic and international sources, maintaining high centering ability in the rigid shaft while the flexible tip penetrates deep into the lower part of the canal, highly adapting to C-shaped canal preparation.

References:
1. Kato A, Ziegler A, Higuchi N, Nakata K, Nakamura H, Ohno N. Aetiology, incidence and morphology of the C-shaped root canal system and its impact on clinical endodontics. Int Endod J. 2014;47(11):1012-1033.
2. Slowey RR. Root canal anatomy. Road map to successful endodontics. Dent Clin North Am. 1979;23(4):555-573.
3. Gu YC, Zhang YP, Liao ZG, Fei XD. A micro-computed tomographic analysis of wall thickness of C-shaped canals in mandibular first premolars. J Endod 2013; 39(8):973-6