
iNature
Sonochemotherapy (SCT) triggers an excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and controlled release of chemotherapeutic drugs through ultrasound, becoming a powerful cancer treatment method. However, achieving spatiotemporal controlled release of chemotherapeutic drugs during ROS generation remains a significant challenge.
On December 17, 2024, a collaborative research paper titled“Cascade-Activatable Nanoprodrug System Augments Sonochemotherapy of Bladder Cancer” was published online by Xu Wanhai from Harbin Medical University, Chen Xiaoyuan and You Qing from National University of Singapore, and Cheng Dongbing from Wuhan University of Technology in ACS Nano .
The study developed a cascade-activatable nanoprodrug (CAN) system by mixing a reversible covalent Schiff base with a hypoxia-activated camptothecin (CPT) prodrug.
In brief, the fluorinated CAN system self-assembles into nanoparticles under aqueous conditions, capable of penetrating deep tumors and providing sufficient oxygen for ultrasound-triggered ROS production. Thus, the nanoparticles significantly exacerbate the hypoxia of the tumor microenvironment (TME) by increasing oxygen consumption. The aggravated hypoxia, in turn, acts as a positive amplifier, promoting tumor-specific release of the Azo-CPT prodrug, compensating for the insufficient therapeutic effects of sonodynamic therapy (SDT). On this basis, the authors observed a significant reduction in the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of the CAN system in bladder cancer cell lines (T24) compared to free CPT, approximately 3.5 times lower. Furthermore, the CAN system demonstrated effective antitumor efficacy with reduced side effects, leading to effective regression and eradication of T24 tumors in various mouse models. In summary, the CAN system has the potential to revolutionize clinical treatment for bladder cancer by combining different chemotherapeutic agents.
Bladder cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in the urinary system, primarily treated by transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT). To prevent cancer progression and recurrence, intravesical therapy is recommended after TURBT to avoid the systemic toxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs. However, the inherent drawbacks of clinical chemotherapeutic drugs, including poor urothelial uptake, weak specificity, chemoresistance, and severe local toxicity, limit therapeutic efficacy, resulting in a recurrence rate of bladder cancer as high as 78% within five years. Consequently, the overall prognosis for bladder cancer has remained unchanged over the past thirty years, making bladder cancer one of the most expensive cancers to treat among all cancer types. Therefore, developing an alternative treatment method that enhances therapeutic efficacy with fewer side effects will play a significant role in improving treatment outcomes for bladder cancer patients.
Sonochemotherapy (SCT) utilizes ultrasound (US) to trigger excessive ROS production, causing oxidative damage to tumors and increasing local drug delivery, making it an effective method for cancer treatment. Compared to photodynamic therapy (PDT), which requires light and results in limited tissue penetration depth, SCT has a deeper penetration capability in tumor tissues, effectively treating large or deep tumors. SCT increases the concentration and retention time of chemotherapeutic drugs in tumors while minimizing side effects on healthy tissues, making it a potential alternative for conventional chemotherapy in bladder cancer. It has been reported that continuous activation of sonochemotherapy nanoprodrugs can enhance the tumor delivery of therapeutic molecules across physiological barriers, but achieving highly spatiotemporally controlled release of chemotherapeutic drugs during SCT remains a significant challenge.
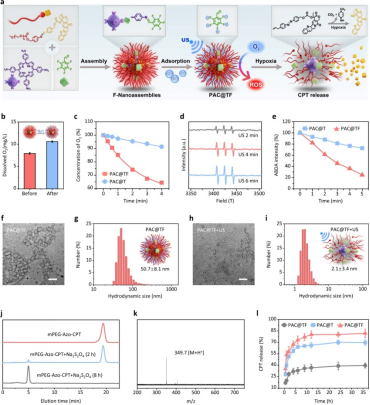
Figure 1: CAN system carrying oxygen, promoting ROS production, and hypoxia-responsive CPT release (excerpted from ACS Nano)
This study proposed a CAN system that utilizes a reversible covalent Schiff base mixed with a hypoxia-activated CPT prodrug. The self-assembled and fluorinated CAN nanoparticles formed in aqueous solution have the advantage of deep tumor penetration and cytoplasmic delivery by enhancing the affinity between the polymer and cell membranes, as well as between endosomal/lysosomal membranes during intravenous injection. Subsequently, CAN nanoparticles enhanced the oxygen availability in tumors, promoting ultrasound-triggered ROS production, thereby enhancing the hypoxia-activated release of CPT, ultimately improving the efficacy of SCT for bladder cancer. On this basis, the CAN system can achieve effective tumor delivery and antitumor effects. Compared to CPT, the CAN system reduces the side effects and local toxicity to the bladder caused by SDT exacerbating tumor hypoxia, thereby specifically activating CPT release. The authors anticipate that with modular molecular modifications, the new method provided by this study can successfully achieve spatiotemporal controlled release of chemotherapeutic drugs during SDT, thereby improving clinical treatment for bladder cancer. Importantly, the flexibility of the CAN system allows for the coupling of various functional drugs, holding great potential for significant transformations in the clinical treatment of various cancers.
Reference:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.4c12967

—END—
The content is original from 【iNature】,
please specify the source as 【iNature】
Add WeChat Group
iNature gathers 40,000 life science researchers and doctors. We have formed 80 comprehensive groups (16 PI groups and 64 doctoral groups), and also established specialized groups for relevant fields (plants, immunology, cells, microbiology, gene editing, neuroscience, chemistry, physics, cardiovascular, oncology, etc.).Note: Please indicate when joining the group (format: school + major + name; if you are a PI/professor, please indicate as PI/professor, otherwise, it will be assumed you are a doctoral student, thank you).You can first add the editor’s WeChat ID (love_iNature), or long press the QR code to add the editor, and then enter the relevant group. Serious inquiries only.

Submission, collaboration, and reprint authorization matters
Please contact WeChat ID:13701829856 or email:[email protected]
If you find this article interesting, please click here!