Knowledge of Baby Care
Essential Baby Care Guide for New Mothers
KNOWLEDGE OF
BABY-REARING

Neonatal swimming, also known as neonatal hydrotherapy, refers to the autonomous movement of babies in water after birth. It continues the activities of the baby in the amniotic fluid, making it a natural experience for them. Neonatal swimming can promote the physical and mental development of the baby, contributing to their healthy growth.
Benefits of Neonatal Swimming
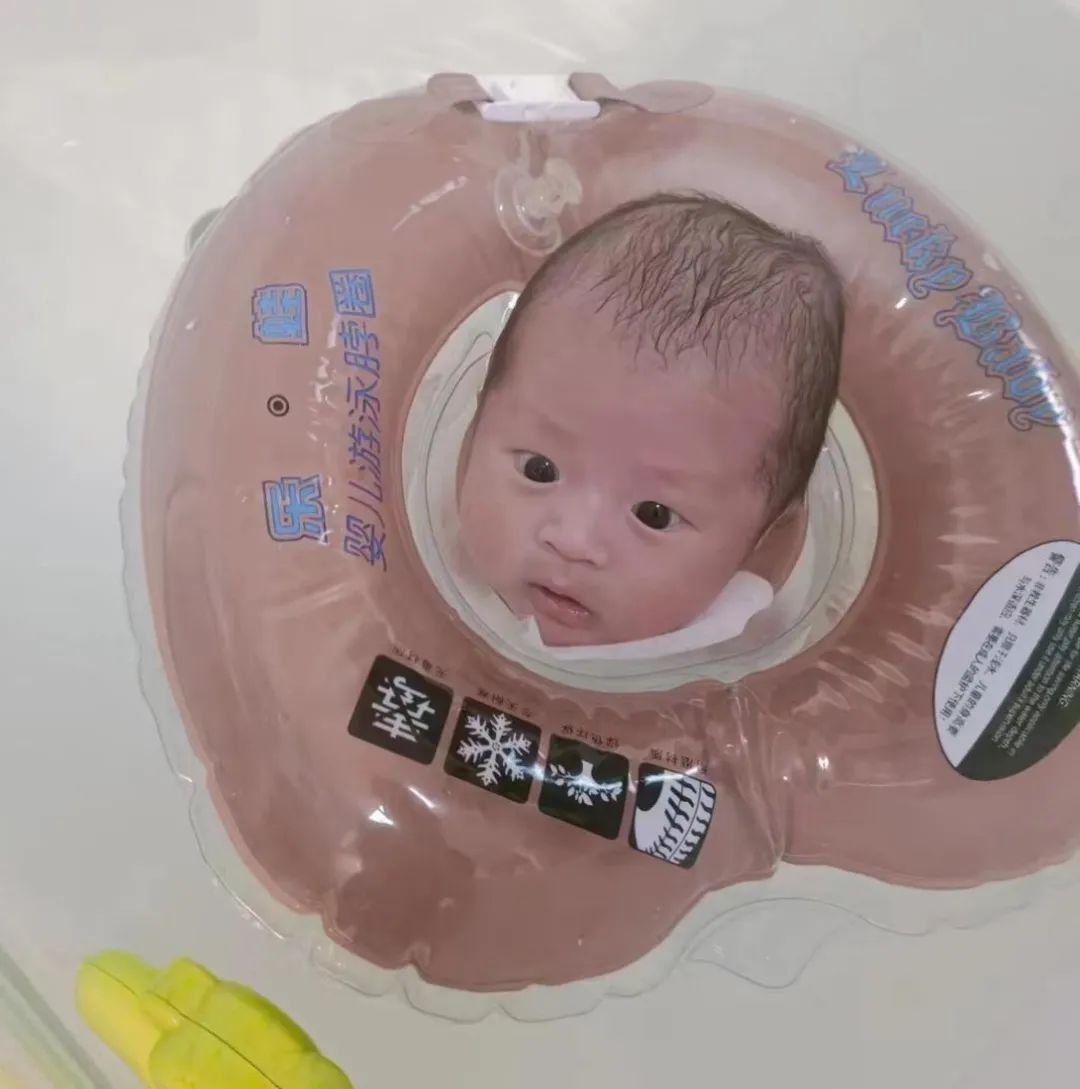
Stimulates and Promotes Brain Nerve Development
Fosters Confidence and Adaptability
Improves Physical Coordination
Enhances Food Digestion and Absorption
Promotes Growth in Height and Weight
Boosts Immunity

Contraindications for Neonatal Swimming
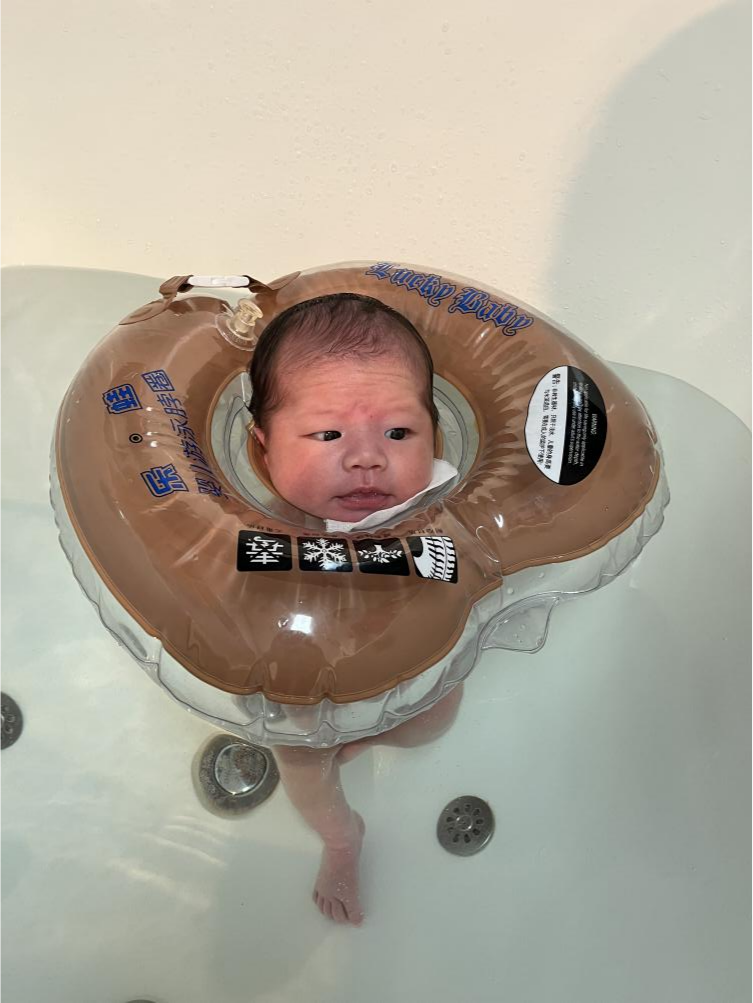
Apgar score < 8 within one minute of birth
Presence of neonatal complications or need for special treatment
Gestational age < 32 weeks or birth weight < 2000g
Skin lesions or infections
Within 24 hours of vaccination

Precautions
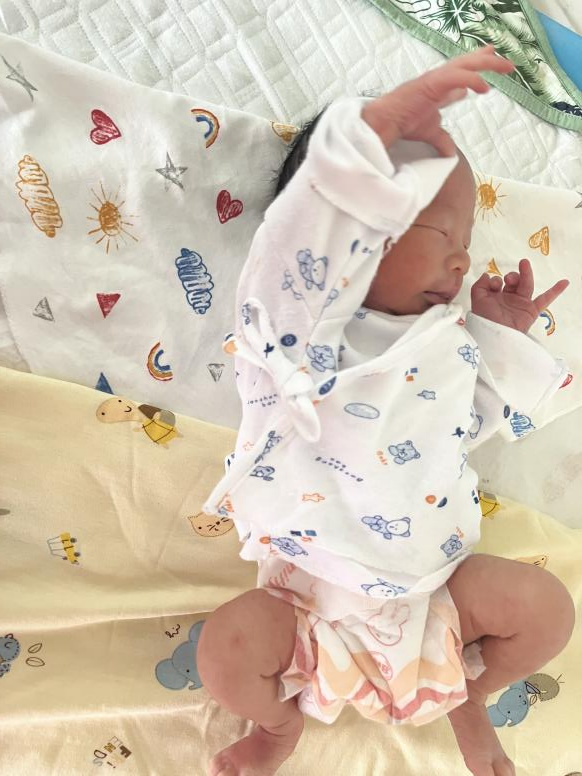 ① Swimming duration: Should not be too long, control each swimming session to 10-15 minutes.② Exercise amount: The baby should not float motionless, nor should they constantly move their limbs; you can hold the baby’s hands to help them move in the water.③ Post-swimming care: Wrap the baby in a towel, dry them off, perform a full-body massage with moisturizing oil, and allow them to rest before drinking water or breastfeeding to relieve fatigue.④ Swimming should be done 30 minutes to 1 hour after feeding, when the baby is in a good mood.References:[1] Zhao Shaofei, Infant Swimming and Touch, Beijing Science and Technology Press, 2004:42-43.[2] Li Heng, Lin Hui, Lai Ailian. Nursing Experience of Neonatal Swimming, Chinese Modern Nursing Journal, 2005, 2 (16):1445.[3] Huang Heqing. Clinical Observation of the Impact of Neonatal Hydrotherapy on Neural Development, Chinese Journal of Child Health Care, 2006, 14 (02):182-183.
① Swimming duration: Should not be too long, control each swimming session to 10-15 minutes.② Exercise amount: The baby should not float motionless, nor should they constantly move their limbs; you can hold the baby’s hands to help them move in the water.③ Post-swimming care: Wrap the baby in a towel, dry them off, perform a full-body massage with moisturizing oil, and allow them to rest before drinking water or breastfeeding to relieve fatigue.④ Swimming should be done 30 minutes to 1 hour after feeding, when the baby is in a good mood.References:[1] Zhao Shaofei, Infant Swimming and Touch, Beijing Science and Technology Press, 2004:42-43.[2] Li Heng, Lin Hui, Lai Ailian. Nursing Experience of Neonatal Swimming, Chinese Modern Nursing Journal, 2005, 2 (16):1445.[3] Huang Heqing. Clinical Observation of the Impact of Neonatal Hydrotherapy on Neural Development, Chinese Journal of Child Health Care, 2006, 14 (02):182-183.
END
▌Contributor:He Ruiying
Chief Supervisor: Gao Chengdong
Supervisor: Lei Quan
Duty Editor: Mao Jing
Submission Email:[email protected]
