IntroductionSummer time
This is a daily learning and note-sharing chapter, where I mainly share some notes I wrote during my learning process. I hope to help everyone learn. The content of this chapter is not limited to evasion techniques, malicious development, reverse engineering, etc. Please note that do not use the knowledge gained for illegal testing. Any adverse consequences arising from this are not the responsibility of the author.
PART.01
The Principle of Transfer Instructions

Instructions that can modify the IP, or simultaneously modify both CS and IP, are collectively referred to as transfer instructions. The transfer behaviors of the 8086 can be categorized as follows:
- When only the IP is modified, it is called an intra-segment transfer, such as jmp ax
- When both CS and IP are modified, it is called an inter-segment transfer, such as jmp 1000:0
Due to the different ranges of IP modification by transfer instructions, intra-segment transfers are further divided into: short transfer and near transfer
- The modification range of IP for short transfer is -128 to 127
- The modification range of IP for near transfer is -32768 to 32767
The transfer instructions of the 8086 CPU can be classified into the following categories:
- Unconditional transfer instructions, such as jmp
- Conditional transfer instructions
- Loop instructions, such as loop
- Procedures
- Terminals

 PART.02Operator offset
PART.02Operator offset
In assembly language, offset is a symbol processed by the compiler, which functions to obtain the offset address of a label. For example, in the following program:
assume cs:codesg
codesg segment
start:
mov ax,offset start
s:
mov ax,offset s
codesg ends
end start
 PART.03jmp Instruction
PART.03jmp Instruction
jmp is an unconditional transfer instruction that requires two pieces of information
- The destination address of the transfer
- The distance of the transfer (inter-segment transfer, intra-segment short transfer, intra-segment near transfer)

 PART.04jmp Instruction Based on Displacement
PART.04jmp Instruction Based on Displacement
This format of jmp instruction implements an intra-segment short transfer, with an IP modification range of -128 to 127, where short indicates a short transfer
assume cs:codesg
codesg segment
start:
mov ax,0
jmp short s
add ax,1
s:
inc ax
codesg ends
end startDuring program execution, it directly skips add ax,1 and runs inc ax
|
Assembly Instruction |
Machine Instruction |
|
mov ax,0123h |
BB 23 01 |
|
mov ax,ds:[0123h] push ds:[0123h] |
A1 23 01 FF 36 23 01 |
We can check the corresponding machine instructions for other assembly instructions. The immediate data in assembly instructions, whether it is a data or an offset address of a memory unit, will appear in the corresponding machine instructions
We will translate the program into machine code and view it in debug
mov ax,0000
jmp 0008
add ax,0001
inc axIt can be seen that debug represents s in jmp short s as the offset address of inc ax, which is 8, while the corresponding machine code is EB 03 which does not contain the destination address of the transfer. How does the CPU know where to transfer?
assume cs:codesg
codesg segment
start:
mov ax,0
jmp short s
add ax,1
s:
inc ax
codesg ends
end startWe modify the program and then use debug to view the machine code. The machine code for both jmp instructions is EB 03 , which indicates that the jmp instruction does not require the destination address for the transfer
mov ax,0000
mov bx,0000
jmp 000B
add ax,0001
inc axThe jmp instruction contains the transfer displacement, calculated through the label
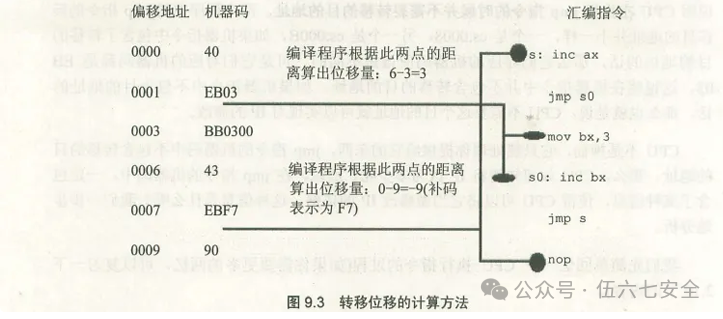
In fact, jmp short label functions as (IP) = (IP) + 8
- 8-bit displacement = address at label – address of the first byte after the jmp instruction
- short indicates that this is an 8-bit displacement, with a range of -128 to 127, represented in two’s complement
- The 8-bit displacement is calculated by the compiler during compilation
There is another instruction format similar to the function of jmp short label, jmp near ptr which implements an intra-segment near transfer, (IP) = (IP) + 16-bit displacement
- 16-bit displacement = address at label – address of the first byte after the jmp instruction
- near ptr indicates that this is a 16-bit displacement, performing an intra-segment near transfer
- The range of 16-bit displacement is -32768 to 32767
- The 16-bit displacement is calculated by the compiler during compilation

 PART.05The Destination Address in the Instruction of jmp
PART.05The Destination Address in the Instruction of jmp
The previously discussed jmp instruction relies on displacement for transfer, while jmp far ptr label implements inter-segment transfer, also known as far transfer, with the following functions:
- (cs) = segment address of the label, (ip) = offset address of the label in the segment
- far ptr indicates that the segment address and offset address of the label modify CS and IP
assume cs:codesg
codesg segment
start:
mov ax,0
mov bx,0
jmp far [tr s
db 256 dup (0)
s:
add ax,1
inc ax
codesg ends
end start
 PART.06The Destination in the Register of jmp Instruction
PART.06The Destination in the Register of jmp Instruction
The format is jmp 16-bit reg, which functions as (IP) = (16-bit reg)

 PART.07The Transfer Address in Memory of jmp Instruction
PART.07The Transfer Address in Memory of jmp Instruction
There are two formats for jmp instructions with transfer addresses in memory:
jmp word ptr memory address (intra-segment transfer)
Function: The memory address contains a word that is the destination offset address. The memory address can be given in any addressing format, for example:
mov ax,0123h
mov ds:[0],ax
jmp word ptr ds:[0]After execution, (IP) = 0123h
Another example
mov ax,0123h
mov [bx],ax
jmp word ptr [bx]After execution, (IP) = 0123h
jmp dword ptr memory address (inter-segment transfer)
Function: The memory address contains two words, where the high address word is the destination segment address, and the low address word is the destination offset address
(CS) = (memory address) + 2
(IP) = (memory address)
The memory address can be given in any addressing format, for example:
mov ax,0123h
mov ds:[0],ax
mov word ptr ds:[2],0
jmp dword ptr ds:[0]After execution, (CS) = 0, (IP) = 0123h

 PART.08Previous Notes
PART.08Previous Notes
Assembly Language Day 07 Assembly Language Day 03
Assembly Language Day 06 Assembly Language Day 02
Assembly Language Day 05 Assembly Language Day 01
Assembly Language Day 04 Basic Knowledge of Assembly Language

 ENDSummer time
ENDSummer time Share
Share Collect
Collect View
View Like
Like

Scan to Follow UsBe an excellent network security guard