First, let me report on the work; we have completed the testing of the MacBook Pro. If all goes well, we will be able to post the review article on WeChat tomorrow, and the video will be filmed and released promptly. After we receive the customized 16GB version of the Mac, we will also create a video on how to choose a laptop. Thank you all for your support!
To be honest, before receiving the latest ARM architecture M1 processor Mac, I was quite skeptical about the capabilities of this chip. After all, Microsoft had released the ARM architecture Surface Pro X, which was not a great device, and I still believed in the traditional x86 architecture.
However, after in-depth testing, I found that ARM architecture processors can achieve a high level of performance if well-designed and paired with excellent “compatibility patches” (such as Rosetta2).
The M1 processor may not be a huge success, but it is definitely on the path to success. So, are there any suitable notebooks for ARM architecture processors in the Windows PC realm?
Today, we will discuss a very typical notebook that is suitable for ARM processors:
Huawei MateBook X

Swipe left to see the ports

Left side of the body

Right side of the body
Its configuration is as follows:
i7-10510U Processor
16GB RAM
512GB SSD
13-inch 3000*2000 resolution 100% sRGB color gamut IPS touchscreen
Battery capacity 42Wh
Thickness 13.6mm
Weight 1kg
Adapter weight 134g
Launch price 9999 yuan

Its advantages and disadvantages are as follows:
Advantages!
1. Excellent touchpad feel
2. Good screen quality with a high screen-to-body ratio
3. Fanless design, dustproof + silent
Disadvantages!
1. Limited variety of ports, requires adapters
2. UHD620 integrated graphics performance is weak, struggles with high-resolution screens
3. Fanless design, conservative long-term performance release

【Upgrade Suggestions】
This notebook is not difficult to disassemble; just unscrew the bottom screws to open the back cover, but be careful as there are hidden screws under the four foot pads.
Dual-channel 16GB RAM can meet most usage needs, but the memory is soldered and cannot be replaced.
The SSD is a 512GB Samsung PM981a, supporting PCIe 3.0×4 and NVMe, the SSD is covered under a large heat sink, and replacing the SSD requires removing the heat sink, and the VC vapor chamber can easily deform under stress, so disassembly is not recommended.

【Purchase Suggestions】
1. Extremely high requirements for thin and portable
2. Extremely high requirements for silent and dustproof
3. Users who do not play games or do “heavy work”
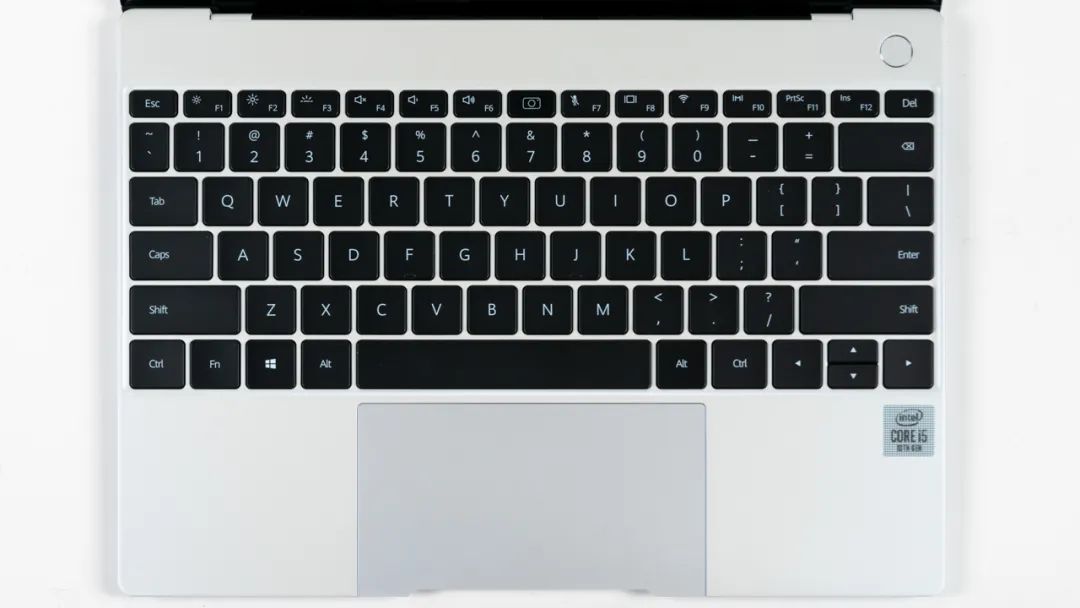
The biggest feature of the Huawei MateBook X is the touchpad, which uses a “borderless” design on the bottom side, and when pressed hard, it simulates the feeling of clicking through vibration, making it the best touchpad experience among Windows laptops.
Regarding the screen, this 3K screen has a measured color volume of 96.6% sRGB, a color coverage of 93.2% sRGB, an average △E of 1.83, and a maximum △E of 3.93.
In terms of battery life, its PCMark10 battery life test score is 7 hours and 21 minutes.(Scenario: Modern office)
Regarding noise, since it has no fan, there is no noise issue during operation.
The Huawei MateBook X has not yet updated to Intel’s 11th generation Core processors and still uses a 14nm process, so it does not come with “G7 integrated graphics,” resulting in average graphics performance.
This laptop comes in many exterior colors, and if you have high aesthetic requirements for the laptop, and low performance requirements, not doing “heavy work”, then this laptop is worth considering.
However, if you want to use it as a primary machine, I suggest considering laptops with fans, such as the MateBook 14, X Pro, etc., which all offer better performance than the X.

【Concluding Remarks】
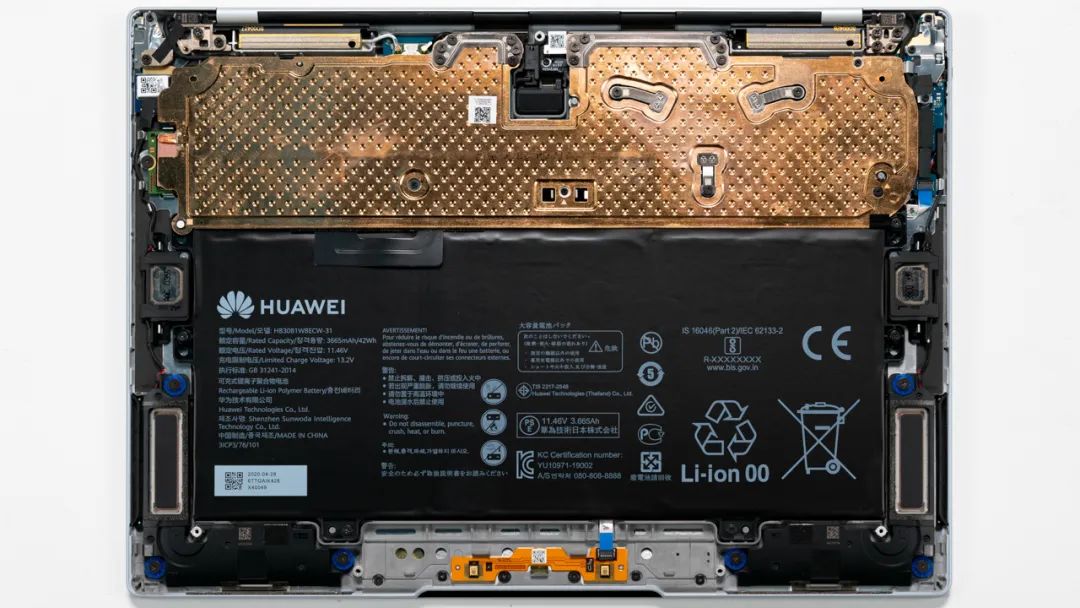
The above image is a teardown shot of the MateBook X, with the motherboard covered by a large VC vapor chamber and no fan.
Room temperature 25℃
Reflectance 1.00
BIOS version: 1.04
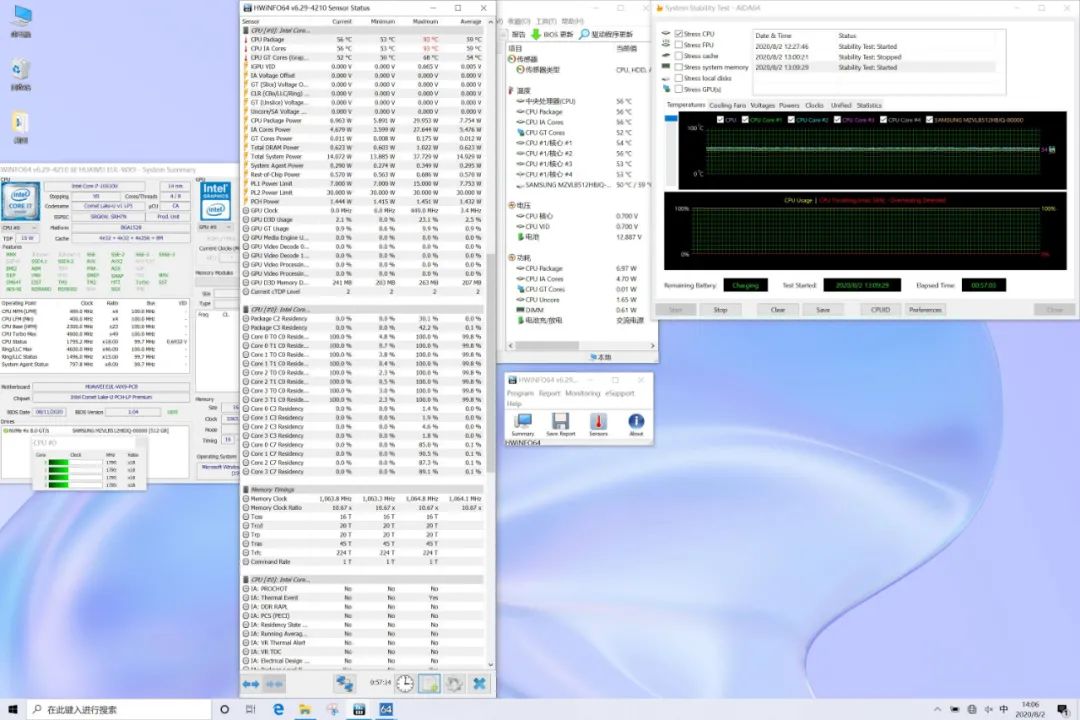
For lightweight laptops without dedicated graphics, we used a low-load Stress CPU for stress testing.
Under full load, the CPU temperature peaked at 93℃, stabilized at 56℃, power consumption was 7W, and frequency maintained at 1.8GHz.
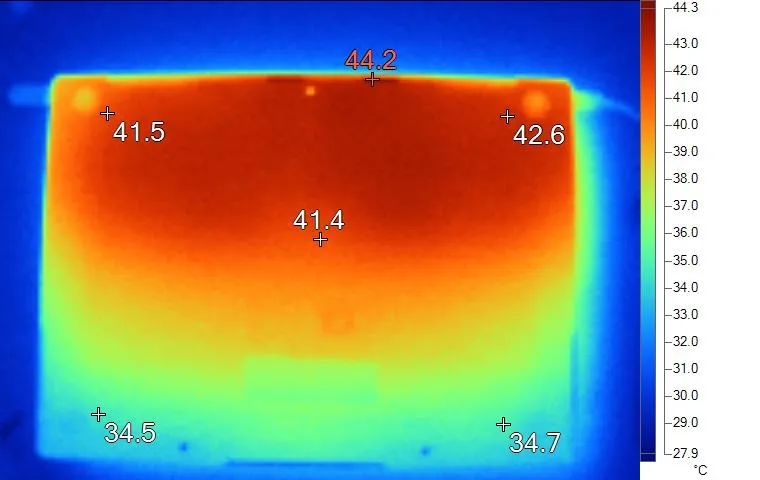
Swipe left to see the bottom temperature
Bottom of the body
The surface temperature is shown in the above image, with the highest keyboard keycap temperature at 40.8℃, WASD key area around 37℃, arrow keys at 33.7℃, left wrist rest temperature at 34.3℃, and the center point temperature on the back at 39.8℃.
Overall, the cooling performance of the MateBook X is average, as it relies on passive cooling and cannot be compared to laptops with fans.
Fanless cooling+Vibration-simulating touchpad, these two features remind me of an ARM notebook – the Apple MacBook Air.
The new M1 processor MacBook Air, thanks to the energy efficiency of the ARM architecture processor, has eliminated the fan, resulting in increased performance, reduced heat, and “zero noise,” leading to significant improvements.
This clear advancement makes me start to imagine… what if a【design as excellent as Apple’s M1 chip】 was equipped in the MateBook X, and Microsoft generously collaborated with developers to better build the Win+ARM ecosystem, what a wonderful scene would that be?
For example… a Huawei MateBook X equipped with a 5nm “Kirin Q1” chip????
Hope this day comes soon!