👇1000-person technical exchange QQ group, note 【public account】 for faster approval

Introduction to Linux Ecosystem:
yum (Package Manager)
Types of Software Installation in Linux:
Source Code Installation (For experienced programmers)
rpm Installation – Linux Installation Package (Has many dependencies, not recommended for beginners)
yum Installation – Resolves Installation Source, Installation, Version, and Installation Dependencies
Introduction: Linux Software Ecosystem
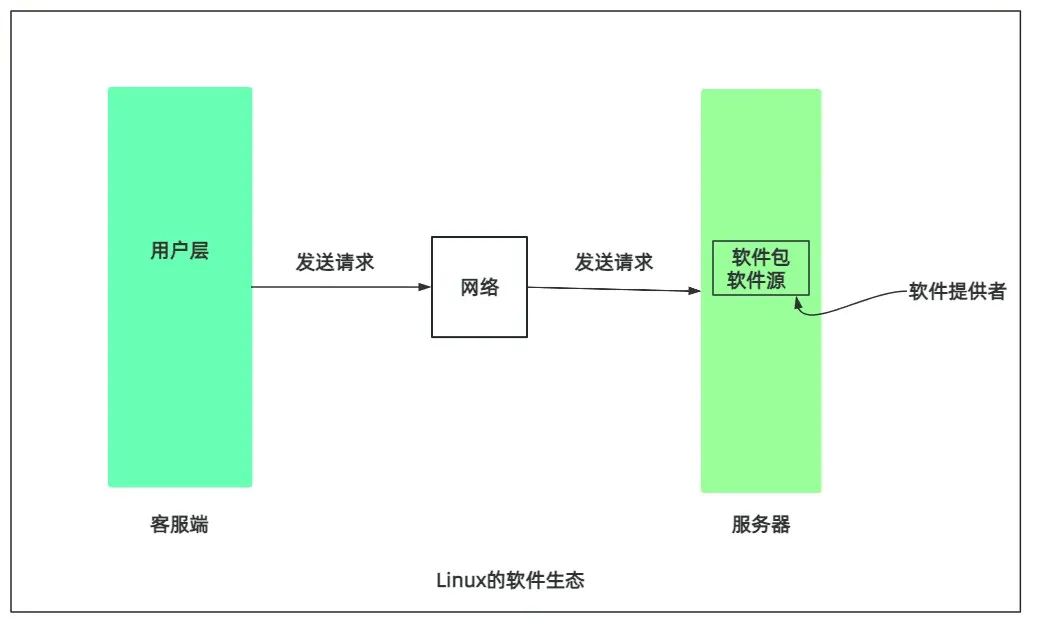
As we all know, Linux is open source.It is important to understand that open source is not charity:
Open source is a business strategy (Surviving big companies rapidly capture market share, Android and Linux are the best examples)
Open source can also be quite expensive (The open source dependencies generated by companies, schools, etc. are highly connected to the underlying systems in the open source ecosystem; when an avalanche occurs, no one can escape, so no one wants it to fail.)
Linux Tools
lrzsz (Used for transferring files between Windows machines and remote Linux machines via Xshell)
Operations in Linux
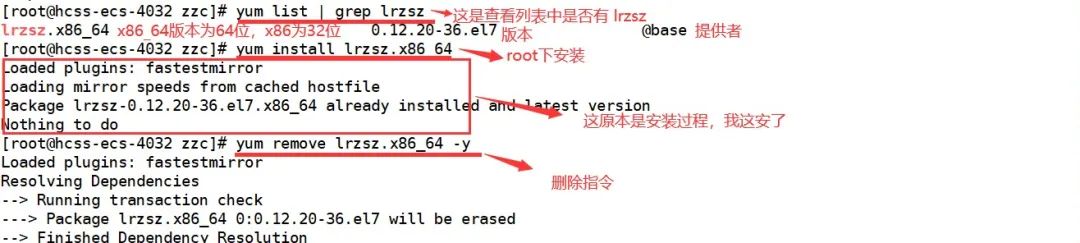
lrzsz is part of the standard library.
Library Includes
Standard Library
The official library contains stable and secure software.
Extended Library
Contains certain risks, unstable software.

Practice in Linux:
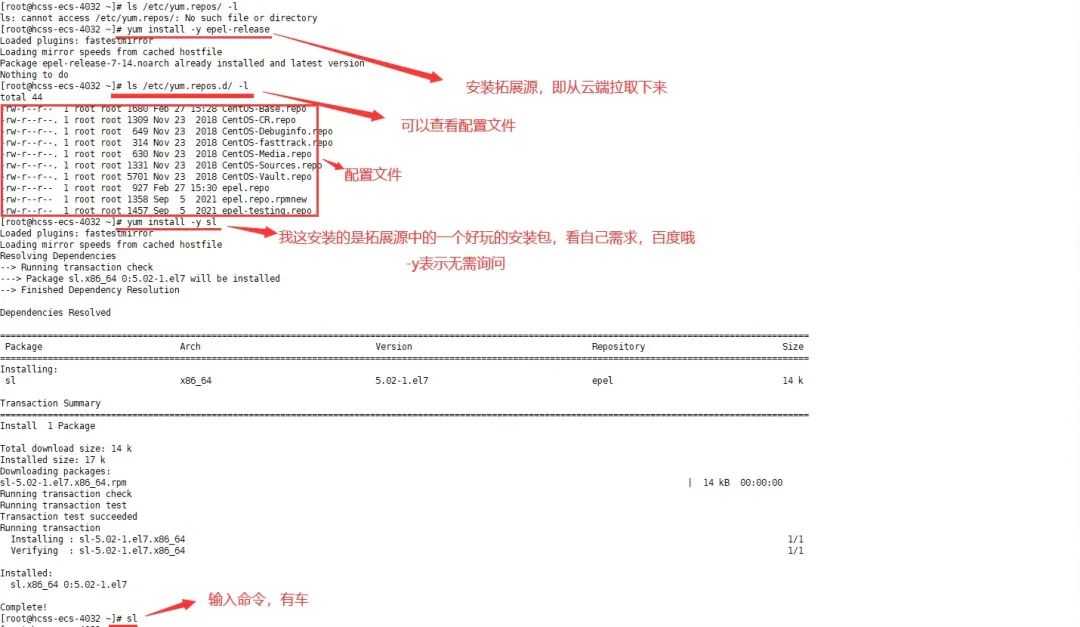
As we all know, the Linux website is abroad. Therefore, the software downloaded from the yum source will be very slow. But if you are using a cloud server, don't worry, well-known domestic cloud servers have replaced the mirrors with domestic ones. If you are using a virtual machine, you can go to Tsinghua University's mirror site for installation.vim Tool
Multi-mode Editor
Default Command Mode
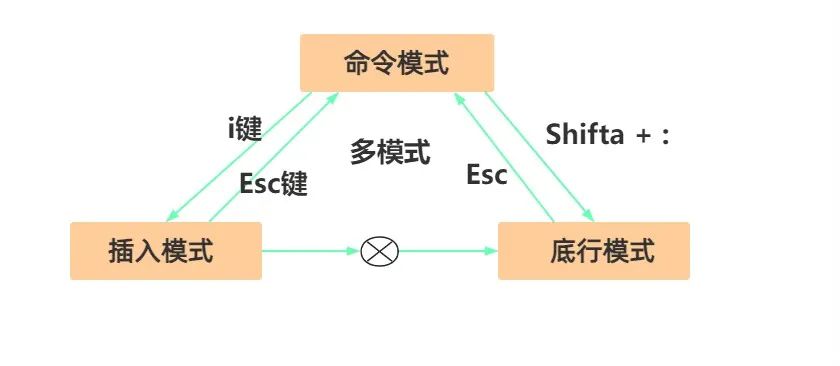
There are many multi-mode editors on the market, such as Markdown, Rich Text Editors, Jupyter Notebook, etc., but vim has a learning curve and is very useful once mastered.Shortcut Key Operations
Next, we will take specific operations in Linux as an example:
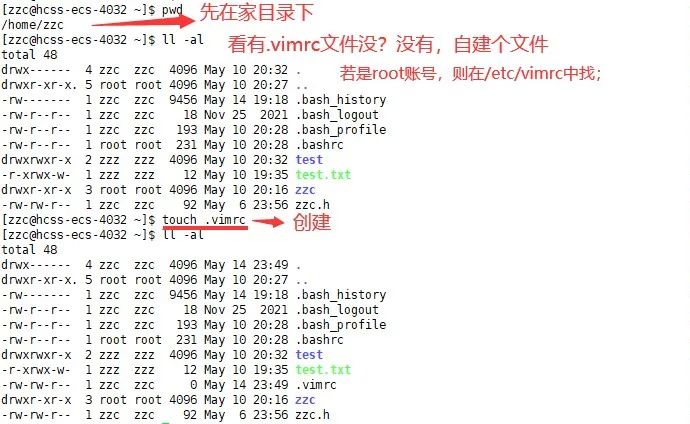
First, configure the vim file.
There is a hidden file .vimrc in the home directory. If not, create one yourself.

Common shortcut keys, some will be specifically mentioned:
In Command Mode:
Movement Keys
Note: Here, n uniformly refers to a number.
gg Move cursor to the first line
shift + g Move cursor to the last line
n + shift + g Move cursor to any line
shift + ^ Move cursor to the leftmost side of the current line
shift + $ Move cursor to the rightmost side of the current line
wb Move cursor to the middle of the current line (counting by words,
does not count)
h j k l represent left down up right, although there are arrow keys on the keyboard now, it is not recommended to use them, because the original old-fashioned keyboard was like this.

Common Commands:
yy Copy the current line
nyy Copy the next n lines after the cursor
dd Cut one line
x Delete the character under the cursor
u Undo
ctrl + ~ Change lowercase letters to uppercase
ctrl + r Redo
(n)p Paste (n) lines after the cursor
(n)r + content to be replaced must be the same
shift + r can modify content freely
Bottom Line Mode Commands
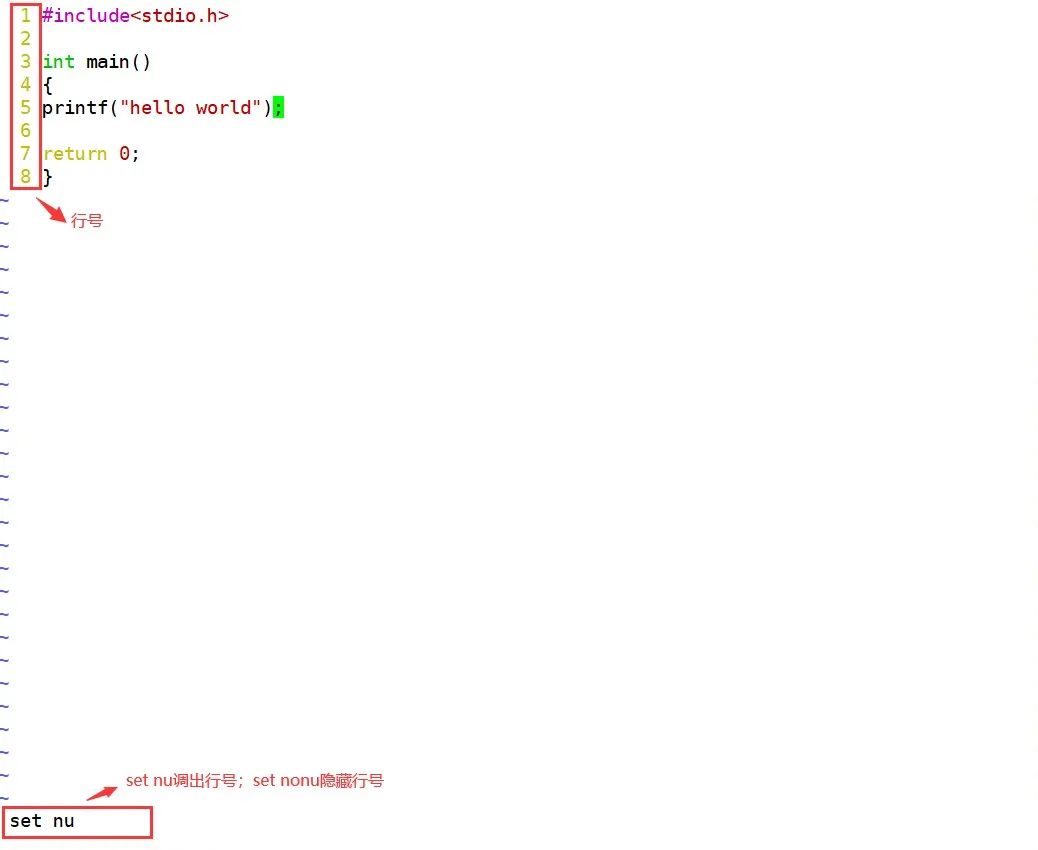
shift + : can enter bottom line mode from command mode.set nonu Hide line numbers
set nu Show line numbers
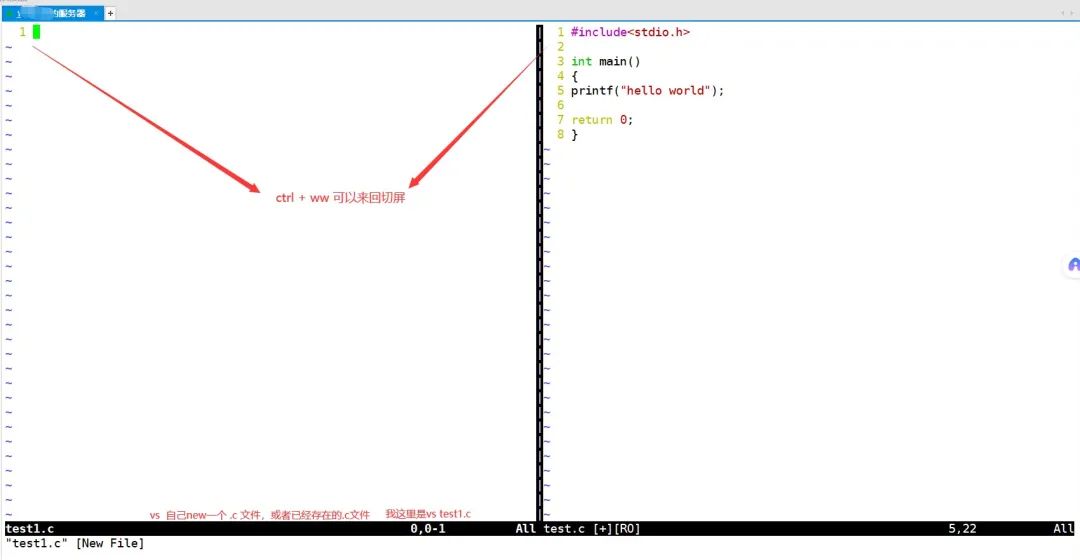
vs filename can split the screen
ctrl + ww can switch screens back and forth
wq Save and exit
w! Force save
q! Force exit
! Execute compile command directly
For course inquiries, add: HCIE666CCIE
↑ Or scan the QR code above ↑
If you have any technical points or content you want to see
You can leave a message below to let me know!