


















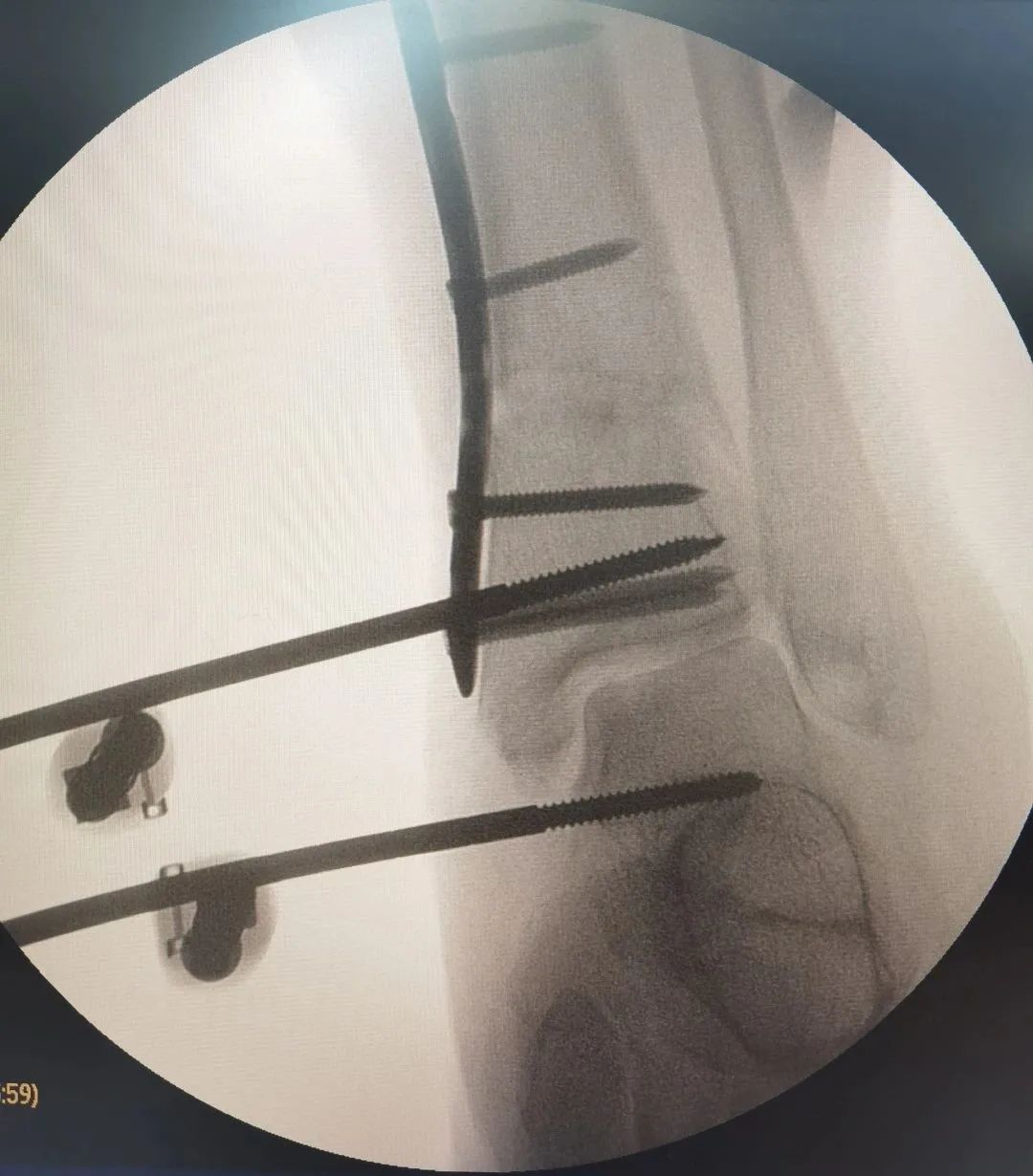








Mr. Li, 43 years old, suffered a serious fracture of the ulnar coronoid process due to a fall while walking.
Dr. Guo Yingbin, head of the upper limb department at our hospital, stated, “Such a severely shattered ulnar coronoid process fracture is indeed rare.”
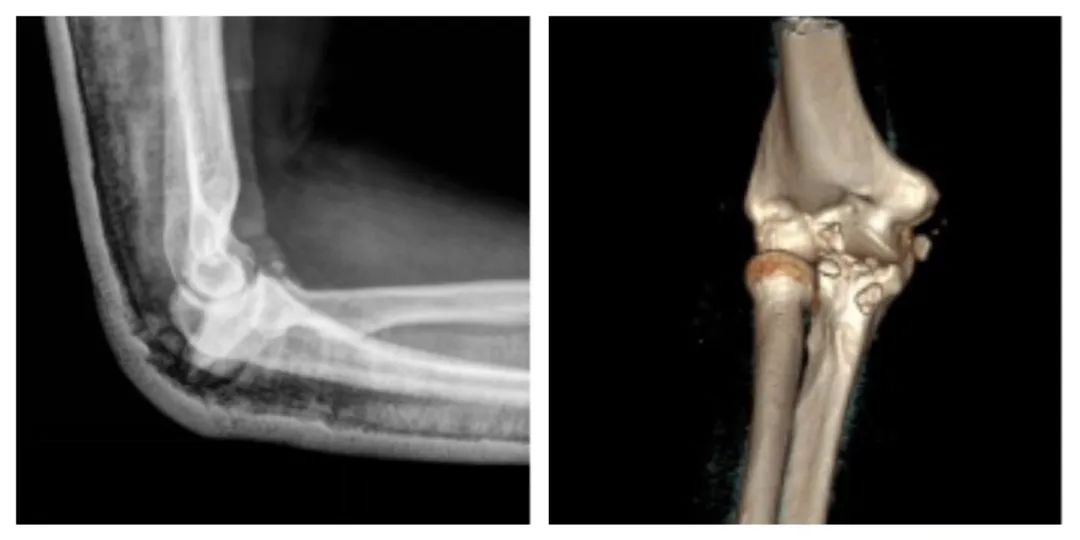
After Mr. Li’s injury, he visited a local hospital where X-rays indicated a fracture and dislocation of the right elbow. After reduction and plaster fixation, he was referred to Quanzhou Orthopedic Hospital.
“Without proper treatment,
the arm will lose strength in the future.”
After a detailed examination and reviewing the X-rays, Dr. Guo informed him, “Although the fracture ends are not large, without proper treatment, this arm will lose strength, and he won’t be able to lift heavy objects. It could also lead to repeated dislocations of the elbow joint due to exertion.“
Based on Mr. Li’s condition, Dr. Guo suggestedremoving the shattered bone fragments and then taking a small piece of iliac bone from Mr. Li to shape it to fit the defect at the fracture site, achieving bone reconstruction.
The majority of the surgery time would be spent on shaping the bone piece, as creating an identical bone piece requires repeated comparisons and modifications, which demands high surgical skills from the doctor. Additionally, the increased surgical time raises the risk of intraoperative bleeding and infection.
3D Printing Technology
Assists Patients in “Rapid Recovery”
“Let’s try 3D printing,” Dr. Guo suggested during a pre-surgical discussion with his team.
3D printing technology enables doctors to scan the patient’s skeletal structure using CT scans. Based on the scanning results, not only can doctors design and print a model that matches the patient’s missing bone piece, but they can also quickly design and shape the iliac bone piece according to the model. Thisnot only improves the surgical success rate but also effectively saves surgical time.
For this rare fracture, Dr. Guo tailored a treatment plan for Mr. Li that involvedusing 3D printing technology to assist in reconstructing the coronoid process defect with autologous iliac bone.
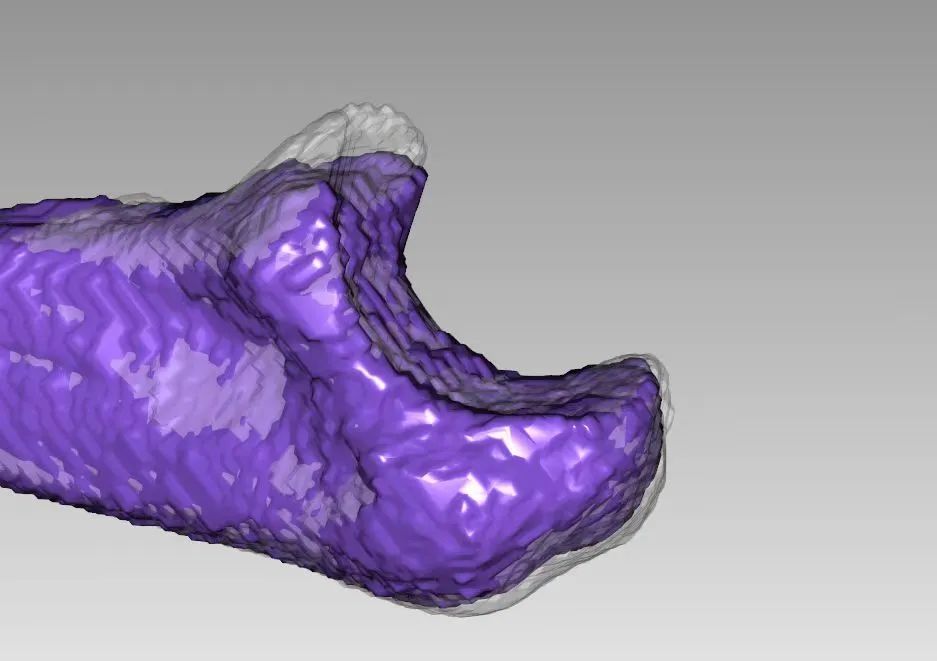
▲ Comparison of the normal left elbow joint and the injured right elbow joint after CT reconstruction
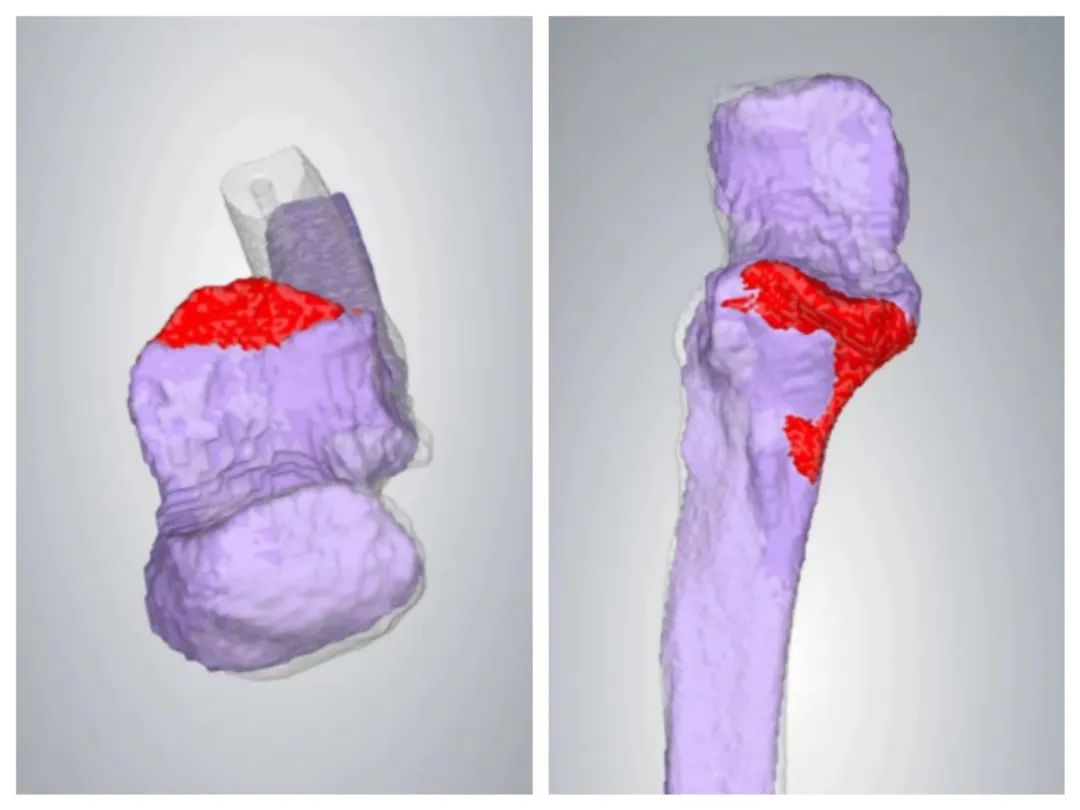
▲ The marked part after comparison indicates the size of the missing coronoid process fracture piece

▲ Using 3D printing technology, the marked missing bone piece and the injured elbow joint were printed, showing a high degree of match.
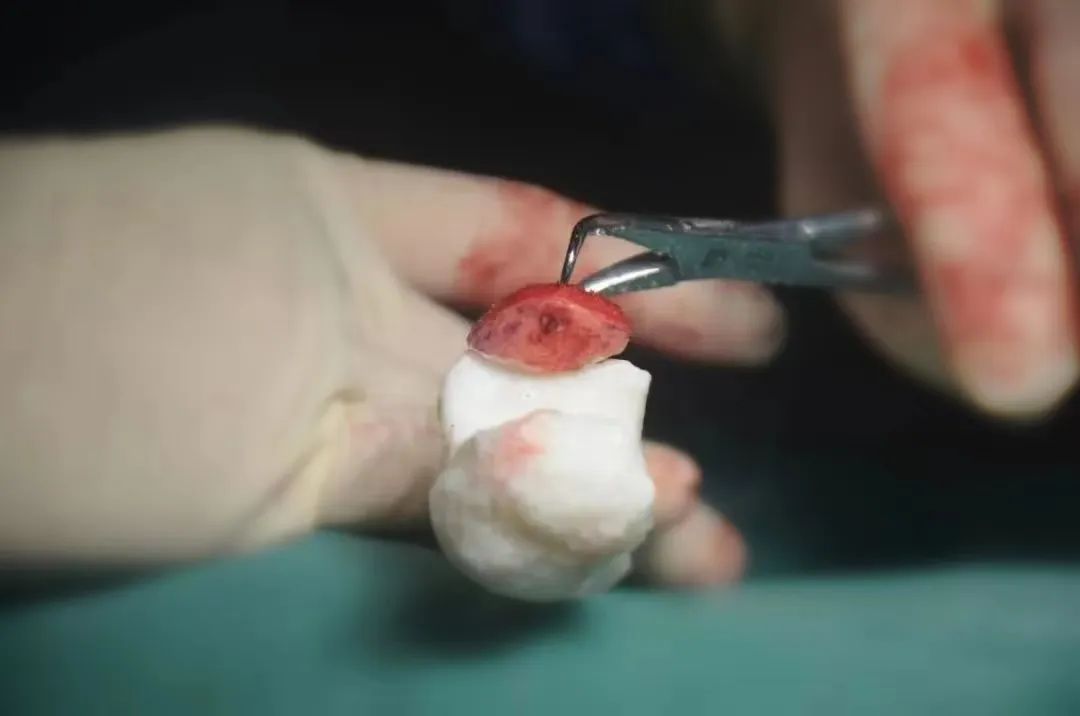
On the operating table, Dr. Guo first checked the patient’s elbow joint movement and found that the elbow joint became dislocated when extended under anesthesia, just as anticipated. The elbow joint was extremely unstable. According to the treatment plan, Dr. Guo first removed the shattered bone fragments, then shaped the autologous iliac bone piece according to the 3D printed model. Through both external and internal matching comparisons, the iliac bone piece also showed a high degree of match.
As a demonstration ward for “Trauma Orthopedics ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery)” awarded by the National Orthopedic Medical Center – Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, our orthopedic department is committed to tailoring personalized treatment plans for patients and providing rehabilitation exercise guidance immediately after surgery. Since the establishment of our Digital Orthopedic Center in 2021, 3D printing technology has been applied in pre-surgical planning, intraoperative guides, and postoperative auxiliary applications for various complex orthopedic cases, effectively reducing surgical time and risks, while providing doctors with more comprehensive information, helping patients quickly and clearly understand treatment plans, and achieving a high-quality diagnosis and treatment experience.

Expert Introduction for Case Treatment

Guo Yingbin
Hospital Position: Chief Physician, Head of Upper Limb Department, Master’s Supervisor, Associate Professor
Specialization: Skilled in manual reduction of fresh or old limb fractures, minimally invasive or open surgical treatments; as well as secondary revision surgery for limb fracture malunion or nonunion; particularly adept at diagnosing and treating complex fractures and dislocations around the shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints. Able to proficiently and standardly apply advanced fracture fixation concepts and surgical techniques from both domestic and international sources, and to carry out orthopedic minimally invasive therapies maturely.
Social Positions: Member of the Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Professional Committee of the International Society of Orthopaedic and Traumatology (SICOT), Member of the Non-Public Medical Group of the Orthopaedic Physician Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, Member of the Elbow Surgery Research Group of the Joint Surgery Professional Committee of the Chinese Research Hospital Association, Director of the Osteoporosis Branch of the Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Member of the Osteoporosis Branch of the Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Further Training Background: Completed further training at Shanghai Sixth Hospital, Huashan Hospital in Shanghai, and Beijing Jishuitan Hospital in 2009 and 2018 respectively. In 2015, participated in the International AO Internal Fixation Research Association as an AO Fellow (MGH, Boston), and spent six months studying at Massachusetts General Hospital affiliated with Harvard Medical School in Boston, USA.
Introduction to the Upper Limb Department

1. Department Overview
The Upper Limb Department, established in July 2013, is a secondary discipline under the Orthopedic Department and is the first department in Fujian Province to independently treat bone and joint injuries of the upper limb. Currently, the department has 23 specialized medical staff, including 2 senior titles, 3 associate senior titles, 2 attending physicians, 2 deputy chief nurses, and 10 master’s degree students.
2. Diagnostic and Treatment Scope
The department strictly follows international classification standards for diagnosing each patient, inheriting and promoting traditional Chinese medicine techniques while actively introducing cutting-edge concepts and technologies from both domestic and international sources, effectively applying them in clinical practice. The department has accumulated rich experience in minimally invasive treatment of fractures, forming unique minimally invasive techniques with significant clinical efficacy.
The department advocates for personalized treatment plans, employing manual reduction and external fixation combined with traditional Chinese medicine for conservative treatment, or manual reduction with percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation, or open reduction and internal fixation, among other treatment methods, to ensure optimal treatment outcomes for patients.
For patients with complex periarticular fractures and dislocations, advanced domestic and international technologies such as proximal humeral fractures treated with Multiloc intramedullary nails, shoulder joint replacements, elbow joint replacements, etc., can be employed in conjunction with rapid recovery concepts to achieve better treatment outcomes.
4. Academic Publications
The department has published over 40 papers, including 2 indexed in SCI and more than 20 in core journals. Over ten projects at the district level and above. Five national patents.
Consultation phone: 0595-22586650
Contributed by/Upper Limb Department Chen Kaiyu
Edited by/Comprehensive Management Department Wu Jiahong
Reviewed by/Quanzhou Orthopedic Hospital Publicity Review Group
Warm Reminder
The hospital outpatient department fully implements real-name appointment visits. Please search for “Quanzhou Orthopedic Hospital” on WeChat or Alipay, and make an appointment in advance on the platform to improve outpatient efficiency. Some outpatient services offer noon, evening, and weekend appointments. The consultation phone for the Citu Hospital is 0595-22576423, and for the Beifeng Hospital is 0595-22586116.
Selected Previous Articles
1. [Orthopedic Warmth] “Flag” Represents Heartfelt Voice, “very good (Bone Virtue)”! He Finally Said Goodbye to a Decade-Long Problem!
2. [Orthopedic Good News] Our Hospital Added Two Municipal-level Intangible Cultural Heritage Projects
3. [Orthopedic Good News] Vice President of Quanzhou Orthopedic Hospital Li Bingzuan Awarded the Fujian Provincial May Day Labor Medal
4. [Orthopedic News] “Seeking Quality through Innovation, ‘Bone’ Moving into the Future” – Quanzhou Orthopedic Hospital Attended the 15th Annual Meeting of the Chinese Medical Association Orthopedic Physicians in Nanjing
