Zigbee/Z-Wave/WiFi Tremble Together! Three Major Advantages of the Matter Protocol Disrupt Industry Standards
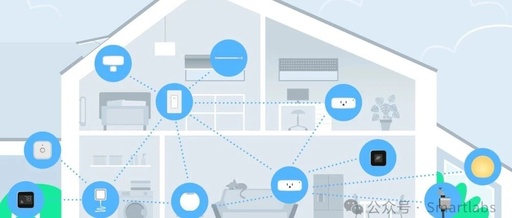
The Matter protocol is the ultimate next-generation smart home protocol. But how does it compare to other protocols like Zigbee, Z-Wave, and WiFi? What advantages and disadvantages does it bring? Let’s explore in this article: Smart home protocols refer to the guidelines and regulations for transmitting information between internet-connected appliances and devices. Although some protocols … Read more