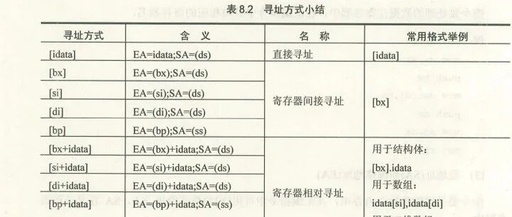
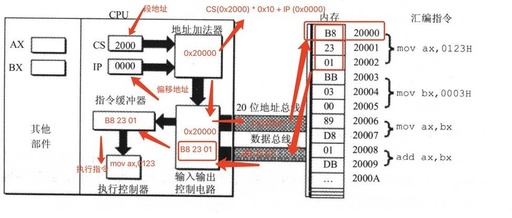
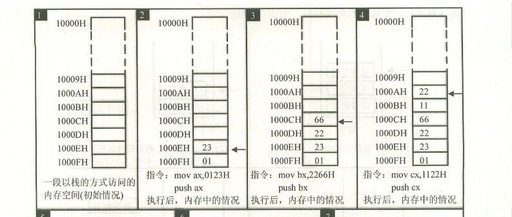
Analysis of Checkpoint 9.2 in Assembly Language
“Assembly Language”, 3rd Edition by Wang ShuangChapter 9: Principles of Transfer Instructions, Checkpoint 9.2 (Page 184) Complete the programming task using the jcxz instruction to find the first byte with a value of 0 in the memory segment starting at 2000H. Once found, store its offset address in dx. assume cs:codecode segment start: mov ax, … Read more