DSP Digital Signal Processing, or 数字信号处理.
In 1971, Intel released a microcontroller, also known as a microprocessor, which can be programmed to issue commands to data.
These commands operate on the numerical calculations and movements within registers, such as adding or subtracting two numbers, or incrementing a number a thousand times, which is equivalent to multiplication… moving data from one register to another, etc.
The earliest microcontrollers were based on the Von Neumann architecture, where instructions and data are together.For example, it is like a teacher directing students (data)
to assign tasks to each student, A through G, where the teacher allocates roles, and the students execute, with A and B starting language studies, C doing arithmetic; they execute commands when given, and remain idle when none are provided.All actions are directed.
Later, it was discovered that this could easily lead to data bottlenecks, for instance, every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday morning, A and B would study language while C does arithmetic, and on Tuesday and Thursday, D and F would do math, while C and G study English.This creates a rhythm, but every day these students have to listen to the same repeated instructions.The waiting time for instructions is quite long.
In this context, the idea of a “Harvard architecture” microcontroller was proposed, where instructions and data are separated; that is, at the beginning of each semester, the teacher issues instructions on what tasks the students will perform throughout the week, commonly referred to as a schedule.There is no need for the teacher to allocate tasks daily, allowing students to execute their learning process in an orderly manner.
When the next instruction arrives, students execute according to the new directive in an orderly fashion.
The entire microcontroller’s data processing speed can be very fast.
This concept of a microcontroller based on the “Harvard architecture” is excellent.It is named DSP, Digital Signal Processing.
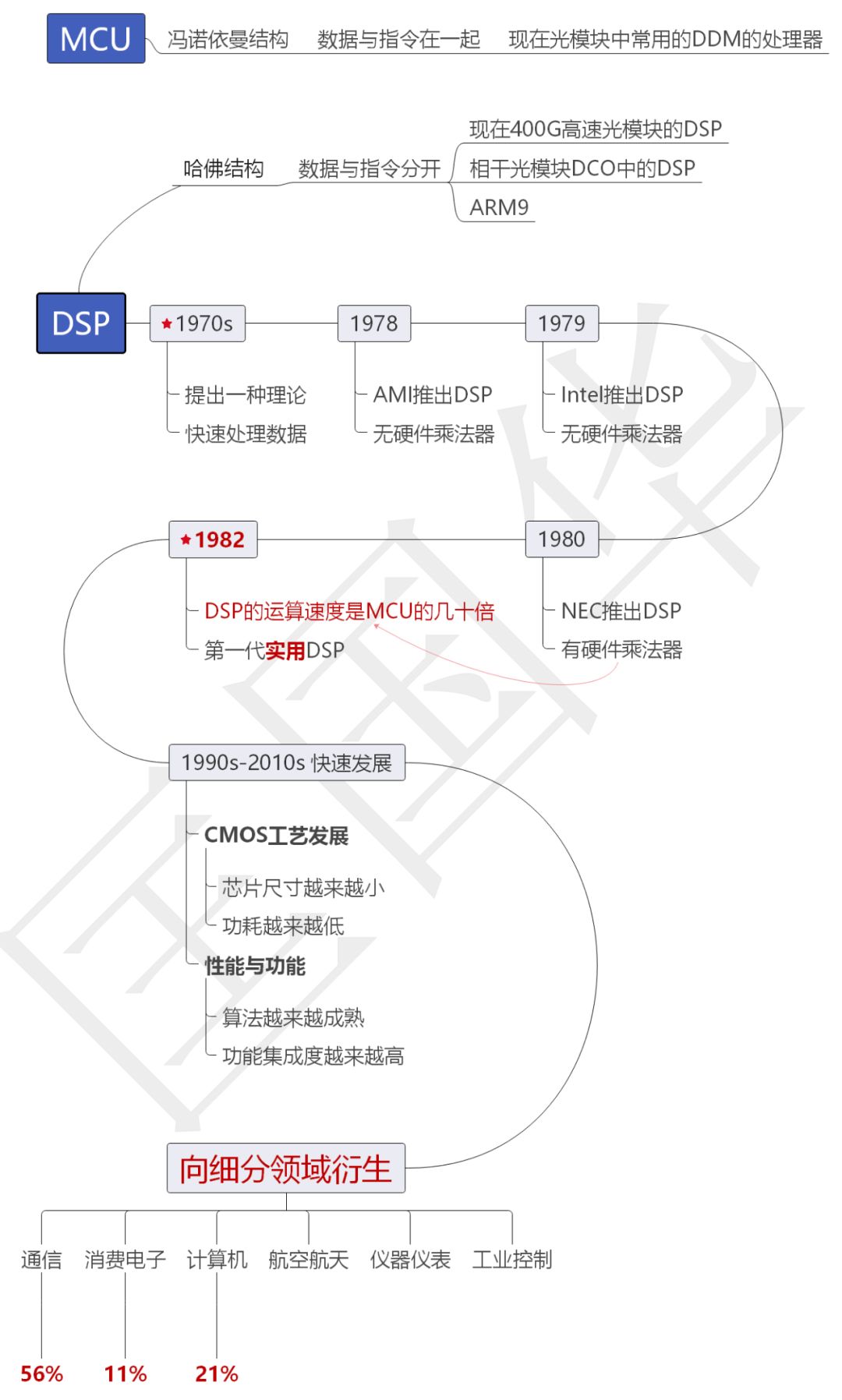
After the theory of DSP was proposed, the industry continuously explored it. In 1980, NEC launched a DSP with hardware multiplication capabilities, and by 1982, the data processing speed of DSP was dozens of times that of the traditional Von Neumann architecture.
This was the first generation of practical DSP.
The following twenty years marked a period of rapid development in semiconductor integrated circuits, with process sizes becoming increasingly refined; the feature size of CMOS devices has reached 7nm this year.
The smaller the feature size, the lower the power consumption, the smaller the chip, and the higher the integration, making DSP increasingly practical.
Applications have driven the maturity of algorithms, leading to branching and maturation in different subfields. In our optical modules,
the issue of optical dispersion caused by fiber transmission can be addressed using the electrical dispersion compensation technology in DSP, with multi-channel FFE, DFE, MLSE, etc., compensating for performance degradation in optics.
Phase processing in coherent communication can also be corrected using algorithms in DSP,
and high-order waveform encoding and decoding can be performed using algorithms, such as QPSK and PAM4.
For long-distance or high-speed transmission, signals are prone to misjudgment, which can be addressed with standardized FEC, forward error correction algorithms, which DSP can implement.
Analog signal modulation and transmission are susceptible to noise, and DSP can perform digital filtering.
….
The maturity of algorithms has made the segmentation of application fields possible.Different fields such as communication, control, and video have their own technological development routes.
DSP is derived from microcontrollers and has a faster data processing speed than MCUs, but it is still a software structure, differing from FPGAs.
FPGAs are pure hardware, without the execution delays caused by software instructions, allowing for faster data processing.However, FPGAs lack the flexibility of DSP.
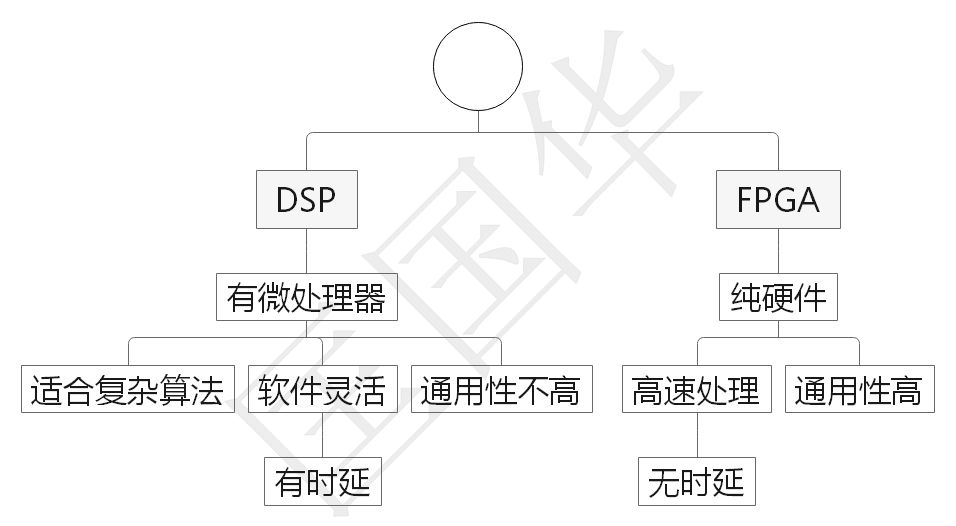
For deterministic data processing, FPGAs can be developed and then solidified into ASICs, while embedding a DSP for parts that require flexible processing; the integration of both is a superior combination.