Hello everyone, today we are going to discuss a topic that is both frustrating and rewarding in the industrial field—how to make the “old gentleman” Modbus and the “modern youth” TCP/IP shake hands and make peace. Last year, while debugging a sewage treatment plant project, I encountered a “generation gap” issue between these two protocols, which extended the debugging time from 3 days to 2 weeks, only to find out that it was caused by byte order! (I will elaborate on this painful lesson later)
unsetunset1. The “age-gap friendship” basics of protocolsunsetunset
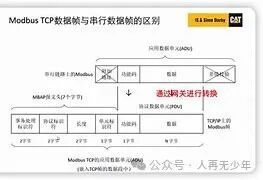
1.1 Modbus’s “paper letter” and TCP/IP’s “express delivery”
Imagine Modbus RTU as sending messages via carrier pigeons, where every character must be strictly aligned. In contrast, TCP/IP is like a courier service, where data is packaged into standard delivery boxes (data frames). The biggest difference is akin to handwritten love letters versus sending emails—one emphasizes format, while the other pursues transmission efficiency.
1.2 Three methods of protocol conversion
- Hardware Gateway: Like a translator (recommended! A certain brand’s gateway has been tested with a response time of <10ms)
- Software Conversion: Using a Python script as an intermediary (suitable for small data volumes)
- PLC Built-in Functionality: For example, the Modbus TCP library of Siemens S7-1200 (the most cost-effective solution)
unsetunset2. Step-by-step guide to building a conversion systemunsetunset
2.1 Hardware selection pitfalls guide
Last year, I bought a 99 yuan converter from a certain online store, only to find:
- It dropped packets when connected to more than 5 devices
- It stopped working at temperatures above 50℃. When choosing an industrial-grade gateway, pay special attention to:
- The number of clients that can be connected simultaneously
- Adjustable message interval
- Support for custom port numbers
2.2 The devil is in the details of software configuration
Taking Modbus RTU to TCP as an example, key parameter settings:
# Virtual serial port service configuration example
serial_port = '/dev/ttyUSB0'
tcp_port = 502
# Note this timeout setting! I've suffered losses three times
timeout = 1.5 # in seconds, should be longer than device response time2.3 Essential debugging techniques on-site
With my debugging toolkit:
- Modbus Poll software (packet capturing tool)
- Network debugging assistant
- Adjustable terminal resistor (savior for 485 bus)
I encountered the most bizarre fault: a certain flow meter’s temperature register was clearly 16 bits but occupied two register addresses! The solution was to use the byte swap function:
Original data: [0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04]
Processed data: [0x02, 0x01, 0x04, 0x03]unsetunset3. Summary of painful lessons in the FAQunsetunset
Q1: Why is all the data I read garbled?
A: Check the three layers of the protocol:
- Physical layer: terminal resistors, cable type (twisted pair!)
- Protocol layer: whether RTU/TCP modes are confused
- Data layer: byte order issue (big-endian vs little-endian)
Q2: What should I do if the TCP connection keeps dropping?
Try the “heartbeat packet” mechanism:
// Ladder diagram heartbeat maintenance program
Network1
| Every 10 seconds OUT1
|----[TON T37,100]--( )
|
Network2
| T37 MSG
|----[ ]------------[SEND]Q3: How can I improve communication stability?
- Set QoS priority in busy networks
- Use message intervals (recommended ≥3.5 character times)
- Use isolated 485 to TCP modules
unsetunset4. Safety operation red linesunsetunset
- Before hot-plugging communication lines, first power down the gateway
- For field bus lengths exceeding 100 meters, a repeater must be added
- Backup configuration files before modifying parameters (a previous misoperation caused a factory shutdown for 1 hour)
unsetunset5. From beginner to advancedunsetunset
Recommended practical route:
- Use Modbus Slave software to simulate devices
- Achieve PC to PLC communication within a local area network
- Attempt cross-segment communication (pay attention to firewall settings)
Advanced techniques:
- Use WireShark to analyze packets
- Configure load balancing for gateways
- Implement JSON and Modbus conversion
Finally, here’s a universal debugging mantra: “First check the wiring, then look at the lights, capture the packets, and match the frames. Set parameters slowly, and when in doubt, stay calm and you will succeed!”
Next time you encounter a protocol conversion problem, remember to brew a cup of tea, open the packet analysis tool—after all, there’s nothing that a packet capture can’t solve; if there is, then capture it twice!