1
What is Reliability?
Reliability refers to “trustworthy” or “dependable,” indicating the ability of a product to perform its specified functions under defined conditions and for a specified period. For end products, the higher the reliability, the greater the assurance of use.PCB reliability refers to the ability of a “bare board” to meet the production conditions for subsequent PCBA assembly and to maintain normal operational functions over a certain period under specific working environments and operating conditions.
2
How did Reliability become a Social Focus?
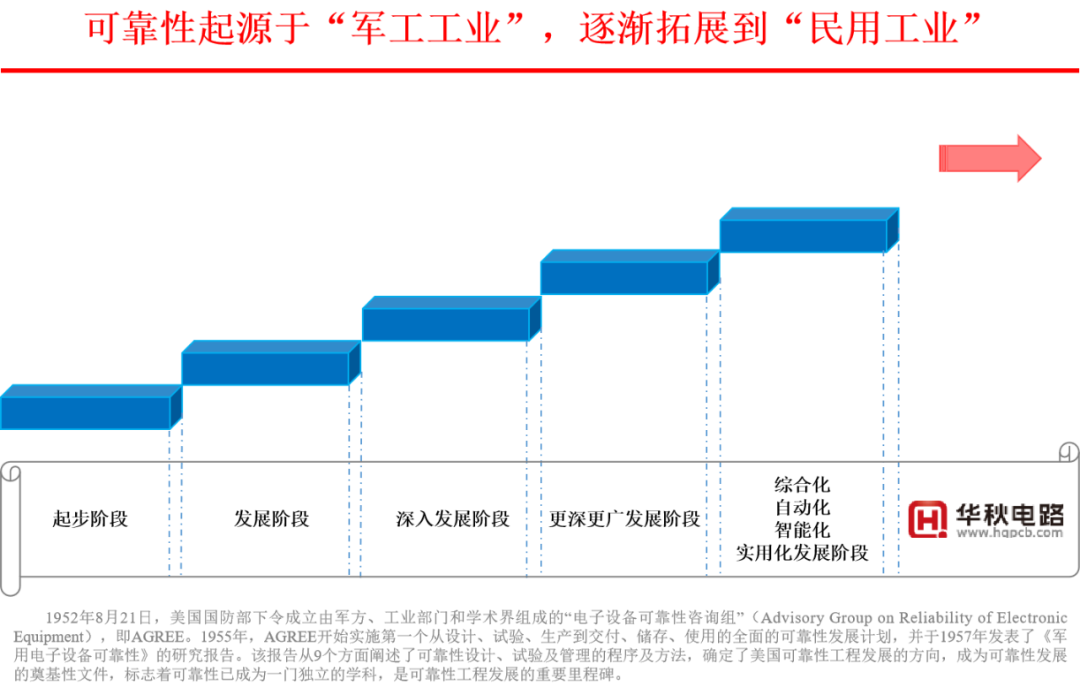
In the 1950s, during the Korean War, 50% of U.S. electronic equipment failed during storage, and 60% of airborne electronic devices were unusable upon arrival in the Far East. The U.S. discovered that unreliable electronic equipment affected the conduct of war, and the annual maintenance costs were twice the procurement costs of the equipment.In 1949, the American Institute of Radio Engineers established the first professional academic organization for reliability—the Reliability Technical Group. In December 1950, the U.S. established the “Electronic Equipment Reliability Special Committee,” involving the military, weapon manufacturers, and academia in reliability research. By March 1952, they proposed far-reaching recommendations; the research results were first applied in aerospace, military, and electronic industries, gradually expanding to civilian industries.In the 1960s, with the rapid development of the aerospace industry, reliability design and testing methods were accepted and applied in avionics systems, leading to rapid development in reliability engineering! In 1965, the U.S. issued the “Outline Requirements for the Reliability of Systems and Equipment,” integrating reliability engineering activities with traditional design, development, and production, achieving good results. The Rom Aerospace Development Center established a reliability analysis center to conduct reliability research related to electronic devices, including reliability forecasting, reliability allocation, reliability testing, reliability physics, reliability data collection, and analysis.In the 1970s, the lifecycle cost issues of U.S. defense weapon systems became prominent, leading to a deeper understanding that reliability engineering is an important tool for reducing lifecycle costs. Reliability factories further developed, adopting stricter, more practical, and more effective design and testing methods, driving rapid advancements in failure research and analysis techniques.Since the 1990s, reliability engineering has expanded from military enterprises to civilian electronic information industries, transportation, services, energy, and other sectors, transforming from a specialized field to a “universal industry.” The ISO9001 quality management system has included reliability management as an important review item, and relevant professional technical standards for reliability have been incorporated into quality management system documents, becoming management clauses that must be adhered to.Today, reliability management is widely accepted across various industries, and corporate philosophies have shifted from “I need to pay attention to product reliability” to “I must pay great attention to product reliability!”
3
Why is Reliability Increasingly Valued?
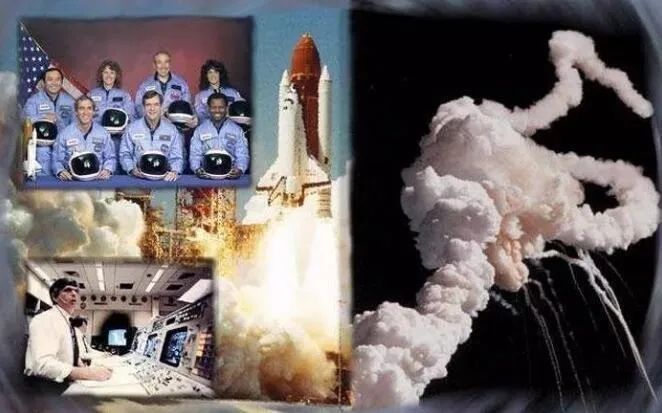
In 1986, the U.S. Space Shuttle Challenger exploded 76 seconds after launch, resulting in the deaths of seven astronauts and a loss of $1.3 billion, with the root cause being the failure of a sealing ring!

In the 1990s, the U.S. UL reported that PCBs produced in China caused multiple equipment fires in the U.S. due to the use of non-flame-retardant materials, despite bearing the UL mark.According to official statistics, compensation due to reliability failures in PCBA accounts for over 90% of external failure costs!GE analyzed that for equipment in continuous operation in energy, transportation, mining, communications, industrial control, and medical fields, even a 1% increase in reliability with a 10% cost increase is worthwhile. High reliability in PCBA can significantly reduce maintenance costs and downtime losses, ensuring asset and life safety!Today, globally, competition between nations has evolved into competition between enterprises, and reliability engineering is the threshold for companies to engage in global competition, as well as a winning strategy for companies to stand out in an increasingly fierce market.
4
Why Should High Reliability in PCBs be Taken Seriously?
As the carrier of various electronic components and the hub for circuit signal transmission, PCBs determine the quality and reliability of electronic packaging. With the ongoing trend towards miniaturization, lightweight, multifunctionality, and environmental requirements such as lead-free and halogen-free, the PCB industry is exhibiting a development trend of “fine lines, small holes, multiple layers, thin boards, high frequency, and high speed,” leading to increasingly higher reliability requirements.
High reliability PCBs can serve as robust carriers, ensuring the long-term and stable operation of PCBA, thereby guaranteeing the safety, stability, and lifespan of end products. This, in turn, enhances corporate competitiveness, improves reputation, expands market share, and increases economic benefits.

5
How to Evaluate Whether a PCB has High Reliability?
High reliability combines “engineering technology” and “management art” into a practical science. To produce high reliability PCBs robustly, a complete set of “standardized, efficient, collaborative, and controllable” management procedures must be established, requiring factories to comprehensively control a series of influencing factors such as “engineering design, production materials, manufacturing equipment, process technology, quality assurance facilities, production environment, management system, and team quality.”
Therefore, assessing whether a PCB possesses “high reliability” requires a thorough confirmation that the following control items in the factory are fully controlled.
01
Preventive Mechanisms
1) Engineering Design: Customer requirement identification, information management, automated operations, specialized skills; design standards and specifications, manufacturability corrections based on factory process capabilities; standardized work specifications and processes, automated engineering production;
2) Manufacturing Process: Systematic management of control objectives, operational processes, and work specifications for all process steps;
3) Quality Control Management: Standardized quality monitoring standards, improved quality assurance systems, and assistance in process quality improvement;
02

Process Management
1) Quality and Product Safety Systems: IATF16949, ISO9001, GJB9001, UL, CQC, RoHS;
2) Engineering Design: Layer structure, impedance, minimum line width, minimum spacing, minimum hole diameter, copper thickness, etc., DFM specifications; production process design, material selection, manufacturability documentation design, etc.;
3) Production Materials: Supplier evaluation, material assessment, raw material inspection, raw material storage, etc.;
4) Process Technology: Process capability, production parameters, chemical usage, first article FA, etc.;
5) Equipment Facilities: Evaluation, routine inspections, progress testing, predictive maintenance, preventive maintenance, periodic repairs, etc.;
6) Operating Environment: Dust-free, constant temperature, constant humidity, illumination, etc.;
7) Quality Monitoring: Incoming IQC, process IPQC, process IPQA, final inspection FQC, outgoing OQC, reliability testing, etc.;
8) Management Team: Operational specifications, risk identification, problem analysis, strategy analysis, etc.;
03

Quality Assurance Inspection
1) Quality Yield: Real-time monitoring;
2) Quality Reliability: Real-time/periodic verification;
3) Quality Consistency: Real-time/on-demand inspection;
4) Average Time Between Failures: Periodic/on-demand validation;
04

Testing and Validation
1) Signal Performance: Impedance testing, signal loss;
2) Thermal Performance: Thermal stress, Tg testing, TMA testing;
3) Interconnection Performance: IST testing, current resistance, thermal shock;
4) Mechanical Performance: Peel strength, tensile strength, solder mask hardness, adhesion;
5) Insulation Performance: Dielectric strength testing, humidity insulation resistance, CAF resistance testing;
6) Soldering Performance: Cleanliness testing, solderability testing;
7) Corrosion Resistance: Solder mask resistance to chemical agents, gold finger porosity.