
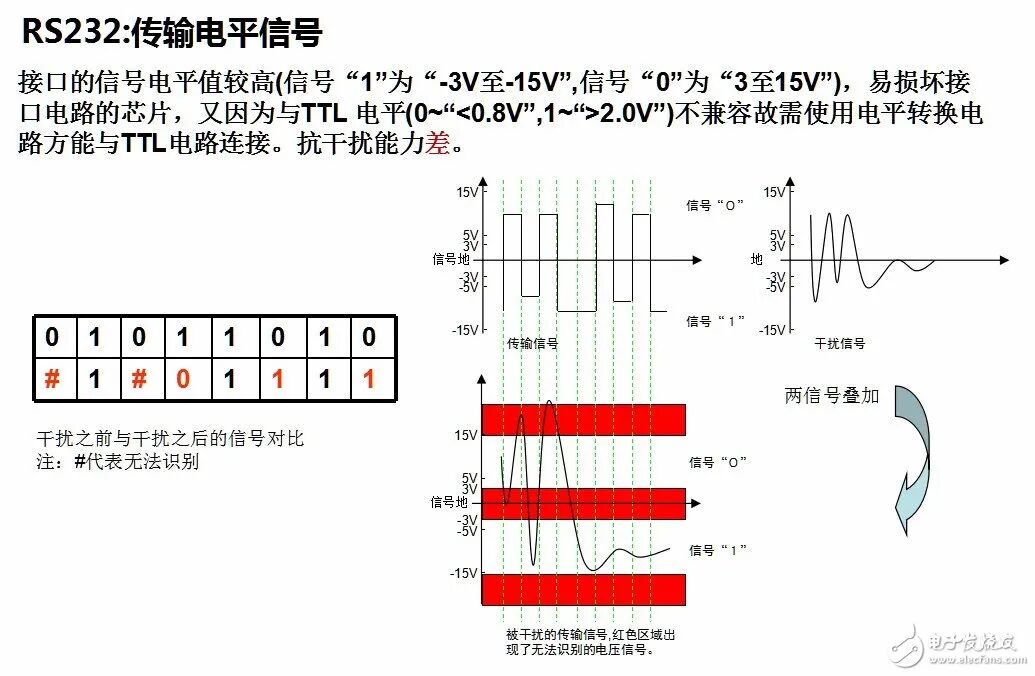
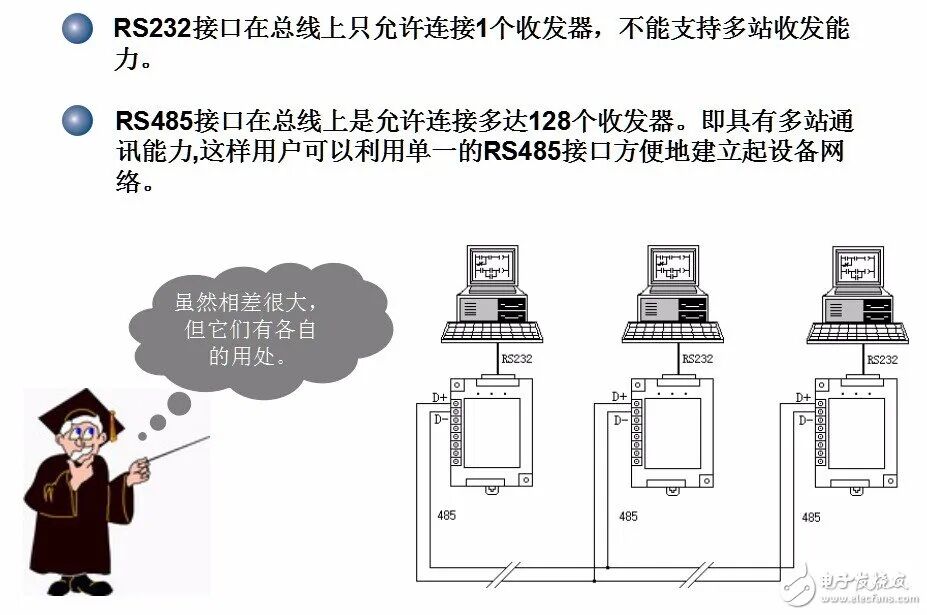
RS232 and RS485 are common interfaces in low-voltage applications, but some people always struggle to distinguish their differences. Below is an analysis of the RS232 and RS485 interfaces.Due to the early emergence of the RS232 interface standard, it inevitably has some shortcomings, mainly including the following four points:(1) The signal voltage levels of the interface are relatively high, which can easily damage the chips in the interface circuit. Additionally, because it is not compatible with TTL levels, a level conversion circuit is required to connect with TTL circuits.(2) The transmission rate is relatively low, with a baud rate of 20Kbps during asynchronous transmission.(3) The interface uses one signal line and one signal return line to form a common ground transmission method, which is prone to common-mode interference, resulting in weak noise immunity.(4) The transmission distance is limited, with a maximum standard transmission distance of 50 feet, and in practice, it can only be used for about 50 meters.In response to the shortcomings of the RS232 interface, new interface standards have continuously emerged, with RS-485 being one of them. It has the following characteristics:(1) The electrical characteristics of RS-485: Logic “1” is represented by a voltage difference of + (2-6) V between the two wires; Logic “0” is represented by a voltage difference of – (2-6) V between the two wires. The signal voltage levels of the interface are lower than those of RS-232, making it less likely to damage the chips in the interface circuit, and this level is compatible with TTL levels, facilitating connection with TTL circuits.(2) The maximum data transmission rate of RS-485 is 10Mbps.(3) The RS-485 interface uses a combination of balanced drivers and differential receivers, enhancing common-mode rejection, thus providing good noise immunity.(4) The maximum standard transmission distance of the RS-485 interface is 4000 feet, which can actually reach up to 3000 meters. Additionally, the RS-232 interface allows only one transceiver to be connected on the bus, meaning it has a single-station capability. In contrast, the RS-485 interface allows up to 128 transceivers to be connected on the bus, providing multi-station capability, enabling users to easily establish a device network using a single RS-485 interface.
1. Physical Structure of the Interface
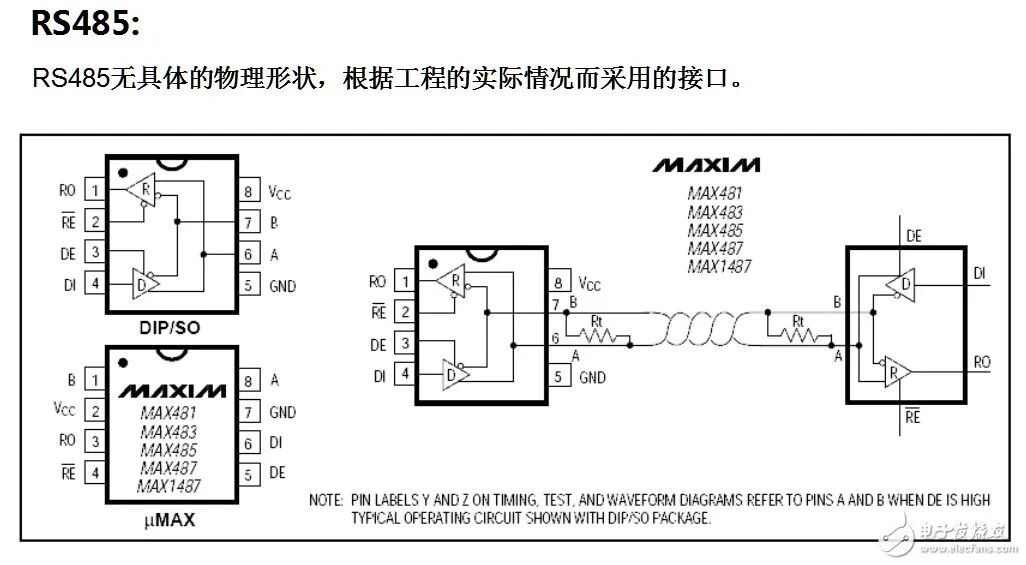

2. Electrical Characteristics of the Interface
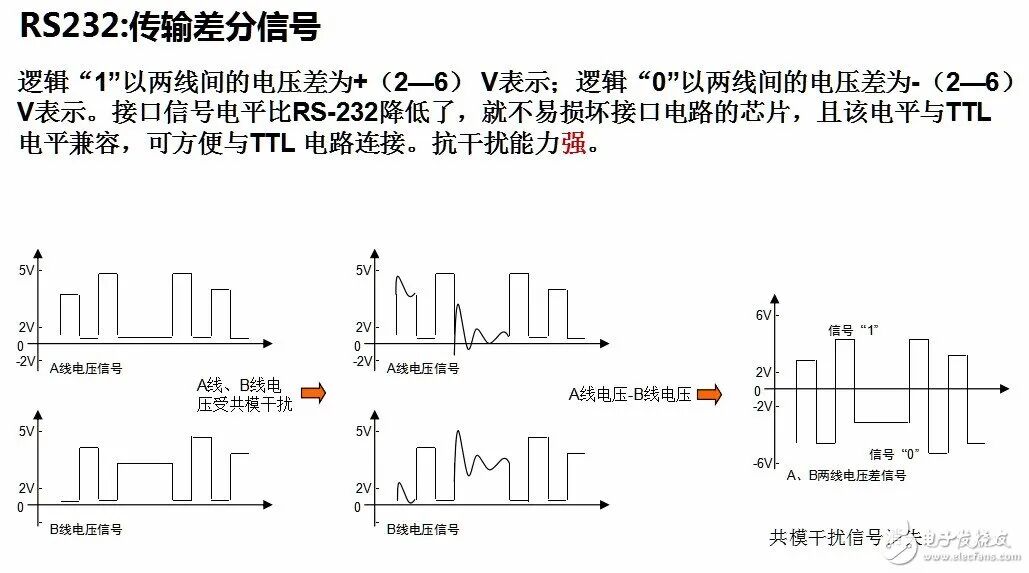
3. Communication Distance

4. Support for Multi-Point Communication
5. Differences in Communication Wires

6. Maximum Baud Rate for Data Transmission
 Because the RS485 interface forms a half-duplex network, it generally only requires two wires (commonly referred to as A and B lines), so RS485 interfaces use shielded twisted pairs for transmission.Since some devices have RS232 interfaces while others have RS485 interfaces, if a device with an RS232 interface needs to communicate with a device with an RS485 interface, an RS232/RS485 converter is required to convert the RS232 signals from the RS232 device into RS485 signals, allowing communication with the RS485 device. If two devices with RS232 interfaces need to communicate over long distances, only two RS232/RS485 conversion circuits need to be added.
Because the RS485 interface forms a half-duplex network, it generally only requires two wires (commonly referred to as A and B lines), so RS485 interfaces use shielded twisted pairs for transmission.Since some devices have RS232 interfaces while others have RS485 interfaces, if a device with an RS232 interface needs to communicate with a device with an RS485 interface, an RS232/RS485 converter is required to convert the RS232 signals from the RS232 device into RS485 signals, allowing communication with the RS485 device. If two devices with RS232 interfaces need to communicate over long distances, only two RS232/RS485 conversion circuits need to be added.


Screenshots of Electronic Books in the Resource Collection

[Complete Set of Hardware Learning Materials Collection]
