Today, let’s talk about one-dimensional arrays in C language—this “data treasure trove” in the programming world. A one-dimensional array is like your personal library, helping you store and manage a large amount of data in an orderly manner. Mastering the principles and usage of one-dimensional arrays will make your programming more efficient and precise.
The Principles of One-Dimensional Arrays
A one-dimensional array is a very basic and important data structure in C language. It allows us to group together items of the same type, forming an ordered sequence. Imagine you have a bunch of apples, each with a number; you can use an array to store these apple numbers. In C language, each element of the array can be accessed via an index, starting from 0.
Defining and Declaring Arrays
In C language, defining a one-dimensional array requires specifying the type and size of the array. For example, if you want to define an array that contains 10 integers, you can write:

Here, int is the type of the array elements, numbers is the name of the array, and 10 is the size of the array, indicating that this array can store 10 integers.
Array Initialization
When defining an array, we can directly initialize it. For example, you can define and initialize an array like this:
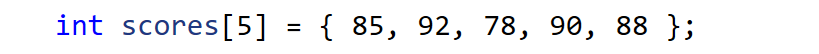
Here, the scores array is initialized to contain 5 integers: 85, 92, 78, 90, and 88.
Accessing and Manipulating Arrays
Once an array is defined and initialized, we can access and manipulate the elements of the array using their indices. For example, to access the first element of the array, you can write:

We can also iterate through all elements of the array using a loop. For example, to calculate the sum of the array elements:

Array Boundaries and Safety
When using arrays, it is crucial to pay attention to the array boundaries. Accessing an index that exceeds the array’s range may lead to undefined behavior or even program crashes. For example, trying to access scores[5] is incorrect because the valid index range for the array is from 0 to 4.
To avoid this situation, you can use conditional checks to ensure the index is within a valid range:

Optimizing Arrays
In practical programming, we can optimize the use of arrays through various techniques. For example, using pointers to traverse the array can enhance the flexibility of the code:

Application of Arrays in Functions
One-dimensional arrays also play an important role in function calls. Since the array name in C language is essentially a pointer to the first element of the array, we can pass arrays as parameters to functions. However, it is important to note that the size of the array is not passed when doing so, so we typically need to pass the length of the array as an additional parameter.
For example, we can define a function to print all elements of the array:

In this example, the printArray function takes an integer array and an integer representing the size of the array as parameters, then prints all elements of the array.
Memory Layout of Arrays
A one-dimensional array is stored contiguously in memory. For example, defining an array that contains 10 integers:

This array will occupy 40 bytes in memory (assuming each integer occupies 4 bytes). The first element of the array is stored at the starting address, and subsequent elements are stored in the following memory locations.
Array Initialization Techniques
When initializing an array, we can assign values in different ways. For example, we can assign values to only some elements:

Or, we can initialize all elements to 0:

Conclusion
A one-dimensional array is an important tool for handling bulk data in C language. By properly defining, initializing, and manipulating arrays, we can efficiently manage data. Mastering the principles and usage of one-dimensional arrays will make your programming more intuitive.
END