Introduction
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) are targeted therapies that consist of antibodies, linkers, and cytotoxic drugs, using monoclonal antibodies as carriers to efficiently deliver cytotoxic drugs to target tumor cells in a targeted manner, combining the powerful killing effect of traditional chemotherapy with the tumor-targeting capability of antibody drugs.
An ideal ADC maintains stability in the bloodstream, accurately reaches the treatment target, and ultimately releases its cytotoxic payload near the target (such as cancer cells). To achieve the desired efficacy and safety of ADCs, five core factors must be comprehensively considered when constructing ADCs: target, antibody, linker, toxin, and conjugation method.
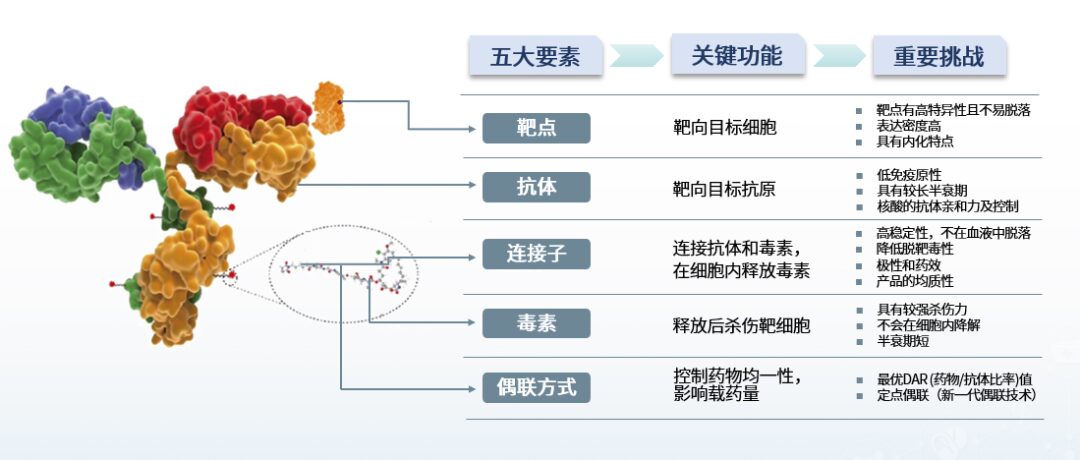
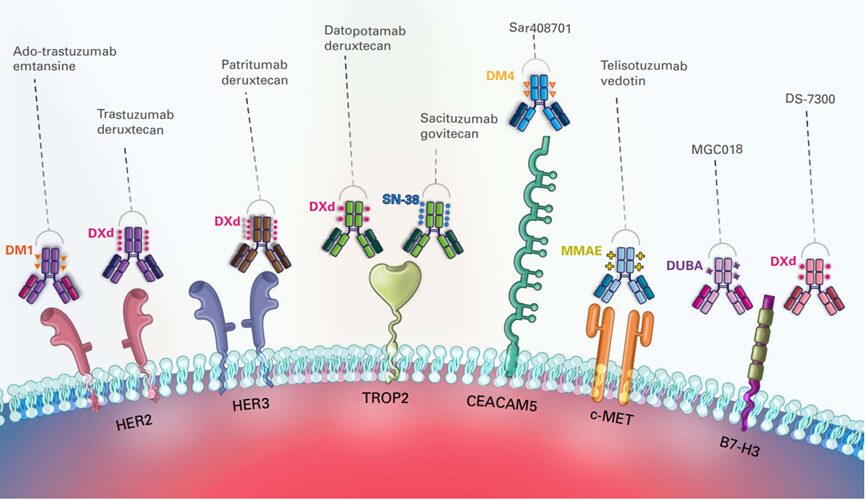
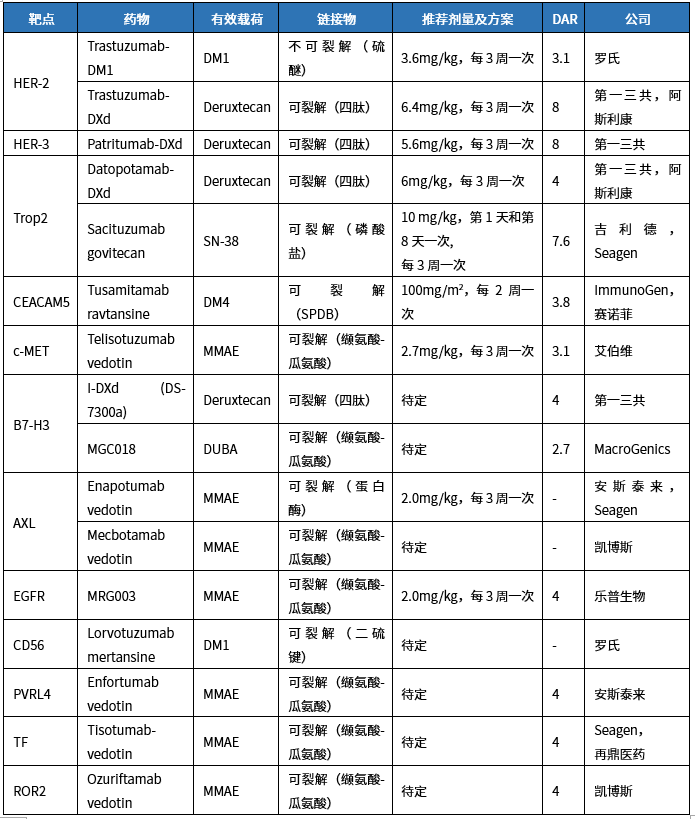
Target Characteristics
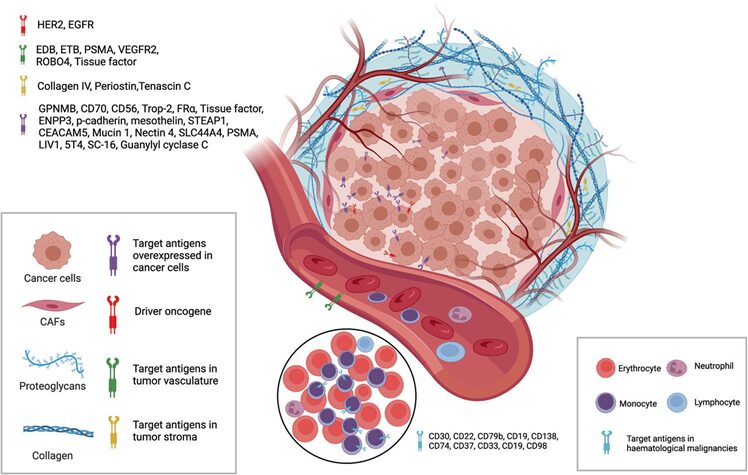
Approved ADC Targets
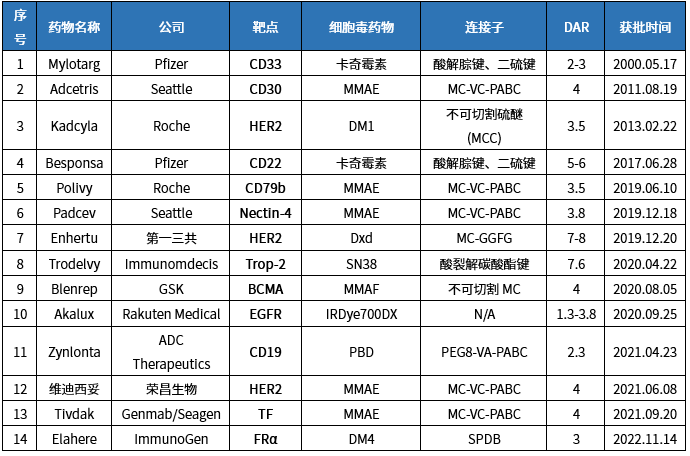
Development Status of ADC Targets
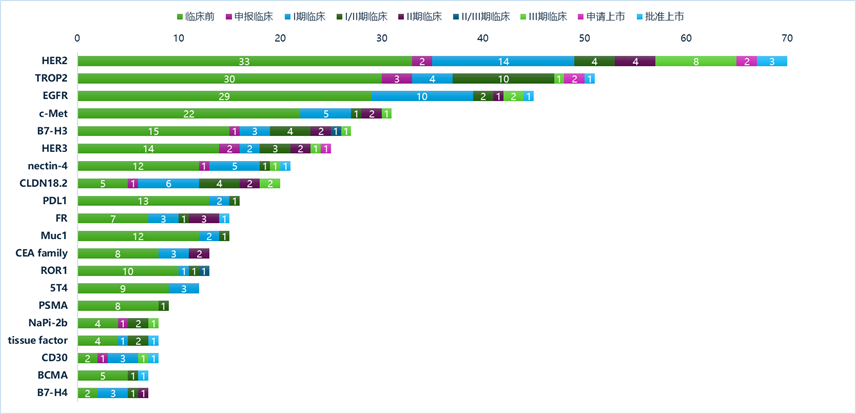
Common ADC Targets in Lung Cancer
Conclusion



