On March 28, 2025, global semiconductor giant Texas Instruments (TI) announced layoffs at its Lehi, Utah facility, involving adjustments to certain positions. This announcement comes as the company receives $1.61 billion in funding support from the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act, accelerating the expansion of its second 300mm wafer fab (LFAB2) in Utah, sparking widespread speculation about its strategic intentions.
Details of the Layoffs and Company Response
Texas Instruments stated in a press release that the layoffs are aimed at “efficiently supporting long-term operational plans,” including capacity expansion and technology upgrades at the new factory. The company did not disclose the specific number of layoffs but emphasized that the scale is below the mandatory notification threshold set by the U.S. Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) Act (which typically requires 60 days’ notice for layoffs affecting more than 500 employees), indirectly confirming that the layoff ratio is below 33%. Reports from employee forums indicate that about 30% of the workforce at the Lehi facility received layoff notices, affecting multiple departments, including process engineering and equipment technology.
Texas Instruments also emphasized that Utah remains a core part of its global manufacturing network, with the LFAB2 construction proceeding as planned, expected to add 800 new positions. The company stated, “We are building geopolitically reliable capacity to meet customer demand for decades to come.”
Financial Pressure from Industry Downturn
The layoffs are closely related to Texas Instruments’ declining performance in recent years. In the fourth quarter of 2024, the company’s revenue fell by 2% year-over-year, and net profit decreased by 12%. This marks the second consecutive year of revenue and profit decline, primarily due to weak demand in the industrial and automotive markets (which together account for 70% of the company’s revenue), inventory buildup, and rising manufacturing costs.
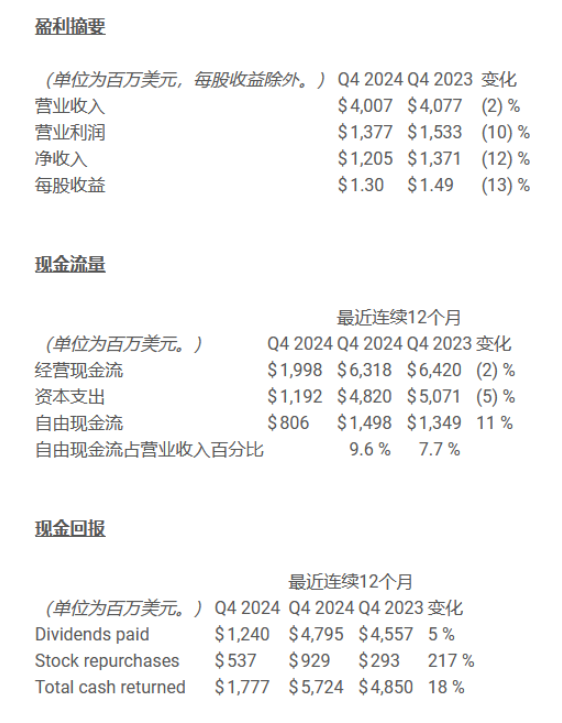
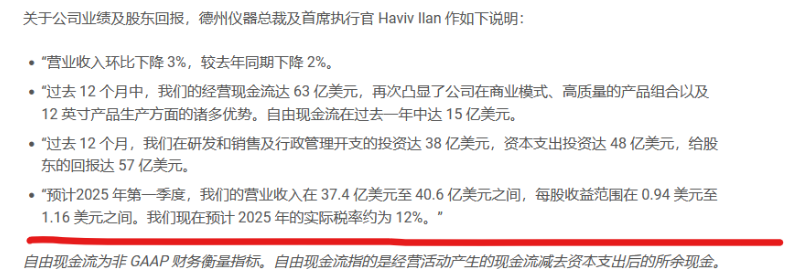
In the first quarter of 2025, the company expects revenue to be between $3.74 billion and $4.06 billion, a year-over-year decline of about 2%; earnings per share (EPS) are projected to be between $0.94 and $1.16, down 11%-28% from $1.20 in the same period of 2024.
The global semiconductor industry is undergoing a cyclical adjustment, with slow recovery in demand in sectors such as industrial automation and energy infrastructure, compounded by inventory buildup, putting pressure on power semiconductor manufacturers. Competitors such as NXP, ON Semiconductor, and STMicroelectronics have also recently implemented layoffs or cost-cutting plans.
The layoffs have sparked strong dissatisfaction among employees. The Lehi facility was formerly IMFlash, a joint venture between Micron Technology and Intel, and has faced integration challenges since being acquired by Texas Instruments in 2021. Employee forums indicate that many of those laid off were high-performing engineers and technical staff, while some low-efficiency positions were retained. Some employees have accused management of chaotic decision-making, stating that “TI treats employees like disposable batteries,” and questioned the synergy between the layoffs and the new factory construction.
Future Outlook
Texas Instruments plans to increase capital expenditures to $5 billion in 2025 to accelerate the construction of the LFAB2 factory, which is expected to begin production in 2026, primarily manufacturing analog and embedded processing chips. In this context, the layoffs may be a necessary measure for Texas Instruments to integrate existing resources and ensure efficient operations once the new factory is operational.
CEO Haviv Ilan stated that while the industrial market is nearing a bottom, there are still no clear signs of recovery in the industrial automation and energy infrastructure sectors. Despite short-term pressures, the long-term outlook for structural growth in the industrial and automotive markets remains positive, especially regarding the demand for new energy vehicles and smart technologies in China.
Industry analysts point out that Texas Instruments’ layoffs may be aimed at optimizing resource allocation, shifting costs toward high-growth areas. However, in the short term, the recovery of the global semiconductor market still depends on a rebound in end-user demand, with a mild inventory replenishment expected in the industrial and automotive sectors in the second half of 2025.
Scan to Join
Semiconductor Industry Group Chat
