Learning notes for the software examination, all experts are welcome to provide corrections.
<span>June 21, 2025</span>
1 Introduction
A bus refers to a common data channel for transmitting information between devices in a computer. The classification of buses is as follows:
-
Internal Bus: The bus that connects the arithmetic unit, controller, and various register components within the CPU.
-
System Bus: The bus that connects the CPU with other high-speed functional components in the computer system. Depending on the type of information transmitted over the system bus, it can be further divided into data bus, address bus, and control bus.
-
Data Bus: Used for transmitting data information between various functions, it is a bidirectional transmission bus, the number of bits (the number of lines in the data bus) is related to the machine word length and storage word length. (The width usually matches the machine word length (e.g., a 32-bit CPU with a 32-bit bus), but high-speed systems may extend this (e.g., a 64-bit CPU using a 128-bit bus).)
-
Address Bus: Used to indicate the address of the source or destination data on the data bus, which is the address of the main memory unit or IO port. It is a unidirectional transmission bus, the number of bits in the address bus is related to the size of the main memory address space,
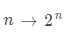 bytes.
bytes. -
Control Bus: Used for transmitting control information, including control commands sent by the CPU and feedback signals returned to the CPU from main memory (or peripherals).
-
IO Bus: A bus that connects medium to low-speed IO devices.
If we classify buses by transmission format, they can be divided into serial buses and parallel buses:
| Bus Type | Data Lines | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serial Bus | One bidirectional data line or two unidirectional data lines | Low speed, suitable for long distance connections | Communication bus (between computers or between a computer and other systems) |
| Parallel Bus | Multiple bidirectional data lines | Has transmission delays, suitable for short distance connections | System bus (various components of the computer) |
2 Common Buses
- PCI Bus: The PCI bus is currently a widely used internal bus in microcomputers, using parallel transmission.
- SCSI Bus: The Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) is a parallel external bus widely used for connecting floppy disks, hard disks, optical disks, scanners, etc.
- RS-232C (serial external bus), USB (serial external bus), IEEE-1394 (serial external bus), IEEE-488 (parallel external bus), etc.