Source: Tom Talks Chips Manufacturing
Original Author: Chip Manufacturing
What is the role of metal materials in chip manufacturing? How are they chosen?
There are three main types of materials for chips: semiconductor materials, dielectric materials, and metal materials.
This section mainly introduces the common metal materials used in chip processes and their characteristics.
What is the role of metal materials?
1. Conductivity: The primary use of metals is to conduct electricity. Metal layers are deposited to interconnect different parts of the chip and transmit electrical signals.
2. Thermal conductivity: When the chip operates, current flowing through transistors generates heat. If this heat cannot be effectively dissipated from the chip, it will lead to overheating. Metals are commonly used as thermal conductive fillers to help transfer heat from inside the chip to the outside, reducing potential mechanical stress.
3. Protection: Metal layers often serve as passivation layers, covering other sensitive structures to provide physical protection against moisture, oxygen, and other substances that could corrode the chip.
Copper (Cu):
Interconnect Wires: Copper is widely used for interconnect wires due to its low resistivity and excellent conductivity, connecting different parts of the chip.
Seed Layer: Provides a seed layer for electroplated copper.
Aluminum (Al):
Interconnect Wires: Aluminum was the primary interconnect material in early CMOS processes.
Electrodes and Contacts: Forms good ohmic contacts with silicon or other materials.
Tungsten (W):
Contact Fill: Used to fill contact holes with active silicon areas.
Local Interconnect: In some processes, tungsten is used as vertical or horizontal local interconnect.

Titanium (Ti) and Titanium Nitride (TiN):
Barrier Layer: Used to isolate aluminum or copper from silicon, preventing the diffusion of metals into silicon.
Adhesion Layer: Improves adhesion between the metal and the underlying layer.
Gate Electrode: Used in some metal gate technologies.
Cobalt (Co) and Cobalt Alloys:
Silicide Formation: Reacts with silicon to form cobalt silicide.
Electroplating: Used for electroplating gold bumps, etc.
Sensor Electrodes: Used in some MEMS or biosensors.
Conductive Paste: Used in some advanced packaging technologies.
Electroplating: Electroplated tin-silver alloys.
Silicide Formation: Reacts with silicon to form nickel silicide, used in some contact applications.
Magnetic Metals: Widely used in magnetic applications such as magnetic heads, magnetic shielding, and magnetic core materials.
Sensor Electrodes: Used in some high-temperature or chemical sensors.
Ferroelectric Random Access Memory (FeRAM) Electrodes: Used with ferroelectric materials like PZT.
Metal Isolation Layer: Due to its excellent corrosion resistance, tantalum is often used as a metal isolation layer, especially in copper interconnect technology.
Commonly used as electrodes for RF chips.
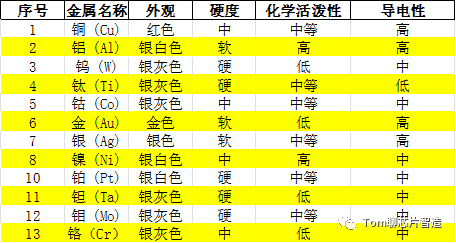
Common Properties of Metals:
END
This content is reprinted and represents the author’s views only.
It does not represent the position of the Semiconductor Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Editor: Schrödinger’s Cat
Editor-in-charge: Six Dollar Fish
Submission Email: [email protected]
1. Scientific Observation | Seizing the