It seems that everyone is curious about the world of humanoid robots! Imagine having a robotic butler at home in the future, helping you with cleaning, cooking, and even chatting with you. Doesn’t it sound like life would become more interesting and easier? Here are the points you need to know about humanoid robots:
1. Is there a consensus in the industry regarding the form, power sources, and future application scenarios of humanoid robots?
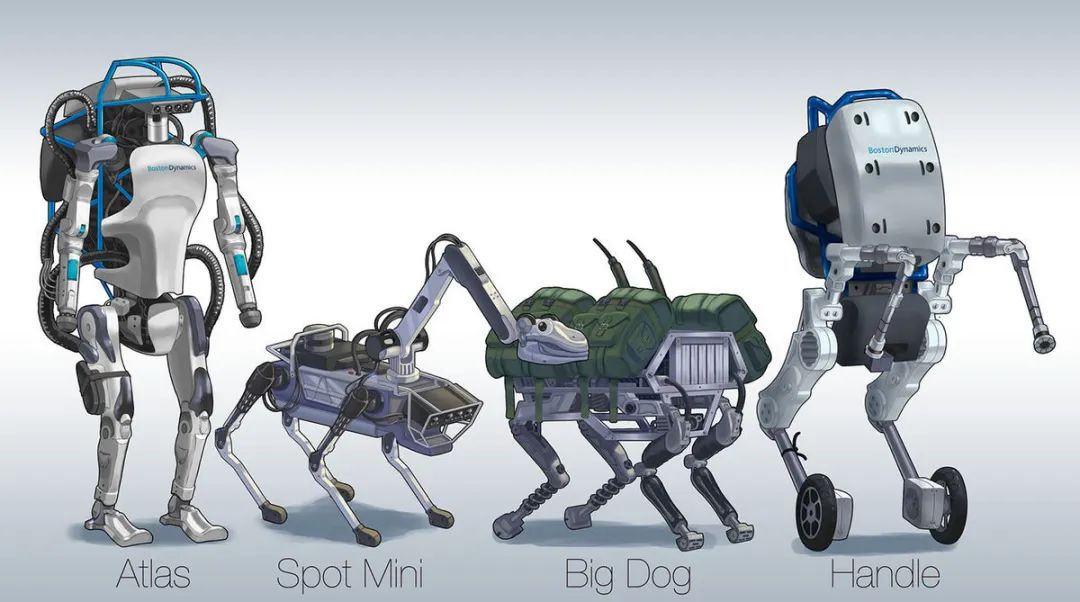
– Form: Rapidly developing, with a diverse range of forms emerging.
– Power source: Electric drive is gradually replacing hydraulic systems as the mainstream option.
·Electric drive performance is improving.
·Stability, maintainability, and cost advantages are significant.
– The vision for future application scenarios is largely consistent:
Starting with simple and stable B2B scenarios, such as factories and hazardous environments, gradually advancing to more complex commercial services, ultimately reaching households.
2. What are the challenges and barriers to the development of humanoid robots?

– Requires breakthroughs in multiple interdisciplinary fields.
The development of humanoid robots relies on advancements in various fields such as mechanical engineering, electronic engineering, computer science, and artificial intelligence, particularly in motion control technology, environmental perception systems, and the independent development and upgrading of core components (like reducers, servo systems, and controllers).
– The industry chain is complex, requiring collaboration across upstream and downstream.
The robotics industry chain is very complex; no company or organization can accomplish everything alone. It requires collaboration across the supply chain to tackle each technical challenge.
3. What are the current application scenarios for humanoid robots, and what are the future commercial directions?

– Short-term application scenarios:
·Manufacturing: Performing repetitive and tedious tasks, such as assembly line work, and handling and sorting items in logistics centers.
·Hazardous scenarios: In dangerous environments like mines, construction sites, nuclear facilities, or disaster scenes, humanoid robots can replace humans in high-risk tasks such as search and rescue, sampling, and monitoring.
– Medium-term application scenarios:
·Commercial services: Serving as receptionists, guides, or sales assistants in the commercial service sector, leveraging their human-machine interaction advantages to provide information consulting, shopping guidance, and customer assistance.
·Specialized tasks: In special fields such as military, firefighting, and police, executing tasks like reconnaissance, bomb disposal, and hazardous materials handling to reduce personnel risk.
– Long-term application scenarios:
·Home services: Becoming smart assistants in households, performing cleaning, cooking, laundry, and other household chores to enhance the intelligent living experience.
·Senior care services: Providing daily care for the elderly, such as health monitoring, medication reminders, and companionship, to improve quality of life.
·Child-rearing services: Acting as companions or educational assistants for children, providing companionship, education, and entertainment to promote healthy growth.
4. How do humanoid robots differ from industrial robots and service robots? Why has the development of humanoid robots become a hotspot?

First, humanoid robots represent a new form of productive force. Humanoid robots are the culmination of artificial intelligence technology and a concentrated embodiment of advanced manufacturing capabilities, expected to become a disruptive product following computers, smartphones, and smart cars. The development of the humanoid robot industry will drive advancements in mechanical, electronic, sensing, software, communication, chip, and artificial intelligence industries, promoting technological breakthroughs, product enhancements, and industry chain collaboration.
Second, humanoid robots are a window for artificial intelligence to enter the physical world. Artificial intelligence acts like a brain, capable of decision-making and computation, but it does not perform actions; it shines in the digital world but cannot enter the physical realm. Humanoid robots mimic human forms and behaviors, allowing for more natural communication and interaction with humans. They can use tools and environments designed for humans without special modifications, enhancing productivity and life experiences.
Third, many tasks can only be completed by “humanoid” robots. Humanoid robots can perform actions similar to humans, enabling more natural communication and interaction, using human tools and devices without special modifications or environments. Tasks involving complex hand movements, such as delicate assembly work, surgical operations, or daily household chores, are challenging for non-humanoid robots.
5. What is the current global competitive landscape in the humanoid robot field? What advantages and challenges does China face in the humanoid robot industry?

– Global landscape: China and the US have become the most important participants.
· United States: Leading in cutting-edge advancements and commercialization.
The US has the largest number of leading companies in the humanoid robot field, such as Boston Dynamics, 1X Technologies, and Agility Robotics. Tesla has also made rapid progress in humanoid robots.
· China: Rich in technology R&D achievements, with a vast market space.
China leads the world in humanoid robot technology patent applications and is very active in technology research and development. Domestic companies are actively developing humanoid robot-related technologies and have made significant progress in certain areas.
· Japan: The “ancestor” of humanoid robots.
Japan has a long history of research and development in humanoid robots, with Honda’s ASIMO being one of the early representatives, possessing technical advantages in certain fields.
– Global: Diverse competition.
In addition to the aforementioned countries, companies in the UK, Canada, South Korea, and other nations are also engaged in research and market promotion in the humanoid robot field, forming a diverse global competitive landscape.
– China’s advantages: Strong manufacturing base and vast market.
China has a complete supply chain and manufacturing foundation.
China’s robust manufacturing infrastructure and supply chain system provide strong support for the research, production, and industrialization of humanoid robots, while also offering significant advantages in cost control.
– The humanoid robot industry has government policy support and vast market potential.
The government actively introduces policies to support high-tech industries, including the development of humanoid robots, while the vast potential of the domestic market provides significant space for the practical application and promotion of humanoid robots.
– China’s humanoid robot industry is achieving rapid technological innovation and talent cultivation.
China is continuously making progress in artificial intelligence and robotics technology, combined with a focus on talent development, providing sustained innovation momentum and a reserve of technical talent.
– China’s challenges: Late start and urgent need for improved industrial collaboration mechanisms.
– Core technologies still need breakthroughs.
For instance, there is a gap in core algorithms for motion control compared to the most advanced global products, and core technology bottlenecks need to be addressed urgently.
– Lack of end-to-end core toolchain and platform that matches general integration platform products.
The technical barriers of humanoid robots limit the participation of system integrators and independent software developers in building the humanoid robot ecosystem. There is an urgent need to develop a core toolchain aimed at the entire process of “design-research-simulation-testing” to enhance autonomous controllability.
– Lack of industrial collaboration mechanisms. China’s humanoid robot industry has not yet formed a complete collaborative innovation system, and there is insufficient synergy among the various links of the industry chain.
It is necessary to establish cross-departmental and cross-industry cooperation mechanisms to promote deep integration of production, education, research, and application. This is also the reason and goal for the establishment of the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center.
6. How do we envision the future development trends of the humanoid robot industry?
Currently, the humanoid robot industry is expected to undergo the following changes:
– Significant cost reduction.
As mass production and technology mature, the cost of humanoid robots will gradually decrease to a level comparable to that of a family car, greatly enhancing their commercial value and gradually increasing market penetration.
– Expanding application fields.
From factories and commercial services to households, humanoid robots will gradually replace tedious, repetitive, and dangerous tasks, addressing issues related to aging and labor shortages.
– Entering thousands of households.
Like computers, smartphones, and smart cars, humanoid robots will become one of the most important electronic consumer products, entering thousands of households where every family will own one or even more humanoid robots.