Previously, we could run Waydroid using the official image through software rendering, as referenced in the Waydroid research, allowing Android applications to run on Linux. This time, by porting Panthor, we can utilize the official Mesa for rendering. Based on related articles from the external community, we will verify the performance of Waydroid running on Panthor. It is worth noting that for the latest Waydroid to run on Panthor, the internal Mesa of Android needs to be updated to version 24 or higher, enabling pure hardware rendering for Waydroid. The action of porting Android Mesa has been completed by someone, and we only need to obtain the corresponding firmware. For articles on using Panthor on RK3588, please refer to the RK3588 Panthor driver porting documentation.
1. Installing Waydroid on the System
We can refer to the official Waydroid website to install the Waydroid binary, which means we do not need to recompile the Waydroid source code, as follows:
sudo apt install curl ca-certificates -y
curl https://repo.waydro.id | sudo bash
sudo apt install waydroid
At this point, Waydroid should be successfully installed on our system.
2. Building the Kernel According to LXC Requirements
After installing Waydroid, we need to enable the corresponding kernel configurations based on LXC requirements. We need to run the command <span>lxc-checkconfig</span>, as shown below:
LXC version 5.0.0
--- Namespaces ---
Namespaces: enabled
Utsname namespace: enabled
Ipc namespace: enabled
Pid namespace: enabled
User namespace: enabled
newuidmap is not installed
newgidmap is not installed
Network namespace: enabled
--- Control groups ---
Cgroups: enabled
Cgroup namespace: enabled
Cgroup v1 mount points:
Cgroup v2 mount points:
/sys/fs/cgroup
Cgroup v1 systemd controller: missing
Cgroup v1 freezer controller: missing
Cgroup ns_cgroup: required
Cgroup device: enabled
Cgroup sched: enabled
Cgroup cpu account: enabled
Cgroup memory controller: enabled
Cgroup cpuset: enabled
--- Misc ---
Veth pair device: enabled, notloaded
Macvlan: enabled, notloaded
Vlan: enabled, notloaded
Bridges: enabled, loaded
Advanced netfilter: enabled, loaded
CONFIG_IP_NF_TARGET_MASQUERADE: enabled, notloaded
CONFIG_IP6_NF_TARGET_MASQUERADE: enabled, notloaded
CONFIG_NETFILTER_XT_TARGET_CHECKSUM: enabled, loaded
CONFIG_NETFILTER_XT_MATCH_COMMENT: enabled, notloaded
FUSE (for use with lxcfs): enabled, notloaded
--- Checkpoint/Restore ---
checkpoint restore: enabled
CONFIG_FHANDLE: enabled
CONFIG_EVENTFD: enabled
CONFIG_EPOLL: enabled
CONFIG_UNIX_DIAG: enabled
CONFIG_INET_DIAG: enabled
CONFIG_PACKET_DIAG: enabled
CONFIG_NETLINK_DIAG: enabled
File capabilities:
Note : Before booting a new kernel, you can check its configuration
usage : CONFIG=/path/to/config /usr/bin/lxc-checkconfig
If we find that some configurations are not enabled, we need to enable them in the kernel. We need to enable all of its features. Pay attention to the following configurations:
CONFIG_IPV6=y
CONFIG_NF_CT_NETLINK=y
CONFIG_PSI=y
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_LOOP=y
CONFIG_ANDROID=y
CONFIG_ANDROID_BINDER_IPC=y
CONFIG_ANDROID_BINDERFS=y
CONFIG_ANDROID_BINDER_DEVICES="binder,hwbinder,vndbinder"
We can disable RK’s feature configuration as follows:
# CONFIG_DRM_IGNORE_IOTCL_PERMIT is not set
At this point, the relevant kernel configurations can be enabled properly, and we can compile the kernel.
3. Waydroid Android Firmware
To run Android firmware based on Panthor, we need to upgrade the Android Mesa package. We can either compile Mesa ourselves or use a pre-ported Mesa repository to replace the compiled version, as follows:
https://github.com/WillzenZou/android_external_mesa3d
If we only need the binary, I directly used the binary, so we can obtain it as follows:
https://github.com/WillzenZou/armbian_fork_build/releases/download/willzen-armbian-24.5.0/2.waydroid-panthorv10-240416-v1.img.tar.gz
At this point, we extract the image as follows:
tar xvzf 2.waydroid-panthorv10-240416-v1.img.tar.gz
Then we copy it to the firmware loading directory:
cp -rf 2.waydroid-panthorv10-240416-v1.img/* /usr/share/waydroid-extra/images
Finally, we initialize Waydroid:
waydroid init -f -i /usr/share/waydroid-extra/images
4. Starting Waydroid
We can start Waydroid directly according to the instructions on the official website, as follows:
waydroid show-full-ui
If there are issues starting, we can check the logs as follows:
waydroid logcat
For specific cmdline configurations, please refer to the official website:
https://docs.waydro.id/usage/waydroid-command-line-options
At this point, we should be able to successfully start Waydroid through Panthor after a short wait, as shown below:
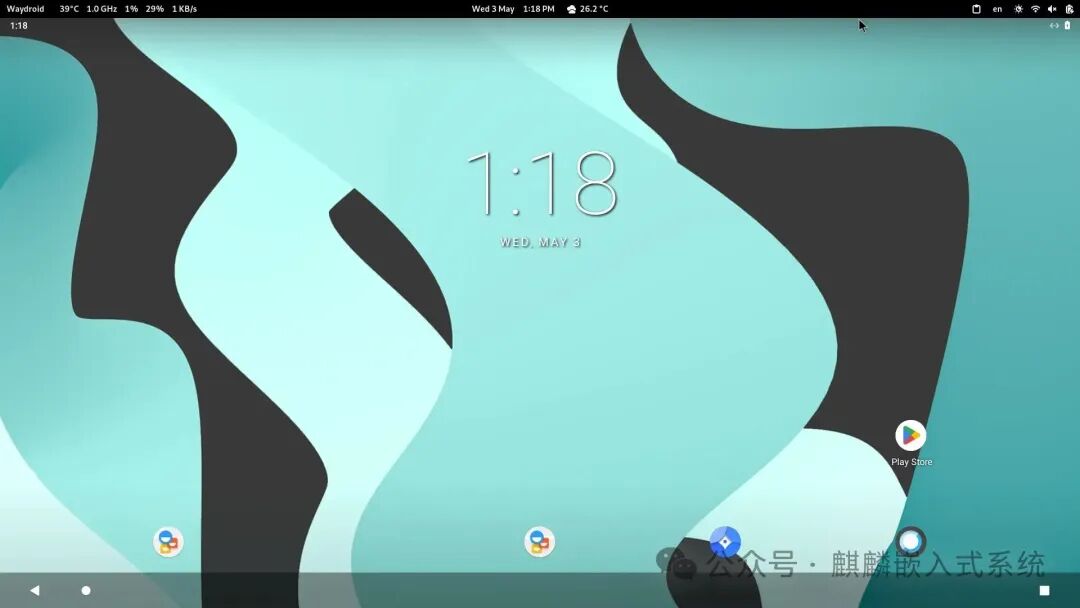
5. Conclusion
Based on the information above, we have successfully run an Android device on a Linux device via Panthor with hardware rendering, and it runs very smoothly!!!
# Building a World-Class Operating System
For more articles, please follow our public account: Kirin Embedded.