
1. Product Description
2. ESD Test Results and Problem Description
a) Contact discharge on the fixed metal screws of the motherboard causes the operation panel to freeze, and the control indicator light flashes.
b) Air discharge on the LCD display panel, without releasing an arc, can cause the operation panel to freeze and restart.
3. Product Problem Analysis
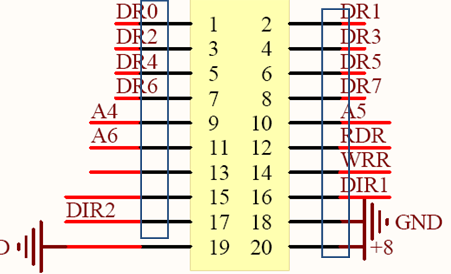
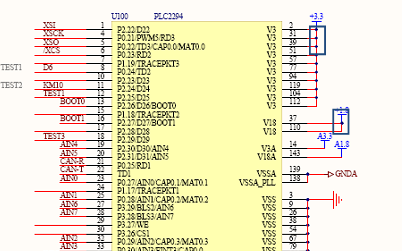
3) The power pins of the CPU lack capacitive filtering, making it susceptible to static interference, causing freezes.
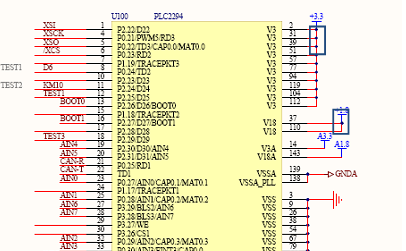
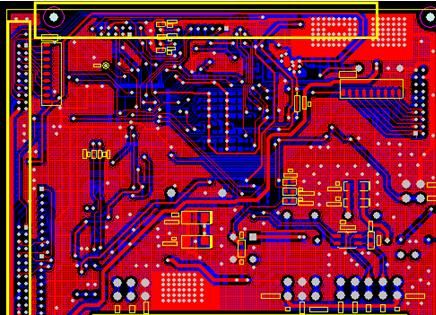
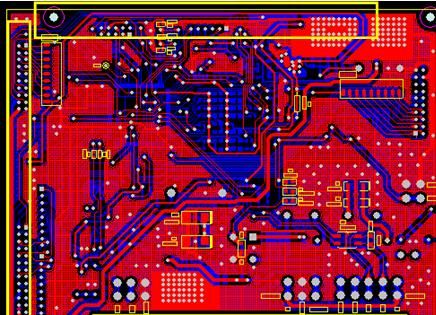
4. Product Rectification Plan and Test Data
5. Case Summary
(1) Static interference is mainly common-mode interference, and the shortest path for static interference should be released to ground.Contact discharge directly releases interference to the product, mainly using discharge protection.Discharge is to release static interference to the ground through the nearest path.Prevent interference from subsequent stages.Protective devices mainly include TVS diodes, capacitors, inductors, etc.
(2) For air discharge, the main interference comes from indirect discharge and spatial field interference.Measures against indirect discharge include isolation and discharge protection.Isolation increases the distance and insulation of discharge points so that the product has no release points.Spatial field interference is a serious static interference.Subsequent rectification is also challenging.It mainly relates to the overall PCB design, including PCB layer distribution, power, and ground design.
(3) The static issues of this project mainly involve the discharge of static electricity from the shell, large circuit board loops, and long wiring, which easily couple static interference.

Beijing August 23-24 “Board-Level EMC Design” Course is Coming!!
Qingdao August 23-24 “Hardware Circuit Design, Fault Location, and Engineering Case Analysis” Course is Coming!!
Wuhan September 6-7 “Advanced PCB-EMC Design” Course is Coming!!

