New products are on the way from Fenghuolun…1. The Past and Present of Raspberry PiSince its launch in 2012, the Raspberry Pi has maintained a dominant position in the single-board computer (SBC) market due to its extremely low entry cost, comprehensive software ecosystem, and strong community support. However, in recent years, competitors such as Orange Pi, NanoPi, RockPi, and our own self-developed SBCs—Youyeetoo R1 and X1 have indeed posed challenges in specific areas.1.1 Raspberry Pi Foundation vs Raspberry Pi Ltd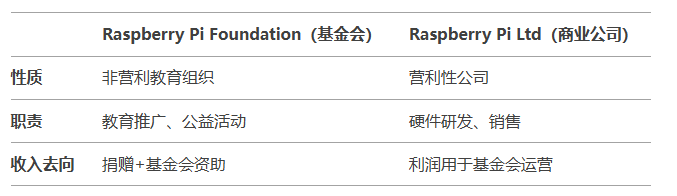 The Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer developed and launched by the Raspberry Pi Foundation.
The Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer developed and launched by the Raspberry Pi Foundation.
-
Raspberry Pi Foundation
Established: 2009, a registered charity in the UK, founders: Eben Upton, Rob Mullins, and other computer scientists from the University of Cambridge. Its original intention was to address the decline in computer science education by providing low-cost, programmable hardware to inspire students’ interest in technology.
-
Commercial Operating Company: Raspberry Pi Ltd
Due to the massive sales of Raspberry Pi (over 40 million units globally), the foundation established a wholly-owned subsidiary, Raspberry Pi Ltd, in 2013 in Cambridge, UK, responsible for the design, production, and sales of hardware. CEO: Eben Upton (one of the co-founders).
1.2 The Soul of Raspberry Pi—Founder Eben’s Interview at Cambridge University in 2012 (Text Summary Version) (Those interested can check out the complete video below to feel the passion and thought process of a leader skilled at turning ideals into reality)
1.2.1 The Origin and Mission of Raspberry Pi
The Raspberry Pi is a credit card-sized computer that has all the functions of a traditional computer but is smaller and cheaper.
This concept originated from the Computer Laboratory at the University of Cambridge. For the past 50 years, this lab has been dedicated to training computer scientists, but about five years ago (the same as five years before 2012), researchers found that the number of 17-18 year old students applying for computer science majors had been continuously declining—from about 500 per year in the mid-1990s (competing for 80 spots) to about 250.
At the same time, the actual programming skills of new students have significantly deteriorated: students in 1995 generally mastered assembly language or graphical programming, while many recent newcomers have only been exposed to basic web design.
This trend poses a dual challenge to universities and the industry: universities need extra time to make up for students’ foundational skills, while the industry faces a talent shortage. The original intention of Raspberry Pi was to stimulate young people’s interest in programming through low-cost hardware, thereby reversing this situation. (Editor’s note: This shows that good businesses often start from a sense of social responsibility.)
1.2.2 The Emergence of Unexpected New Markets
Although the initial target audience was children, after the project was made public in 2011, Raspberry Pi unexpectedly attracted two other types of users:
-
Makers Community: Adult tech enthusiasts (such as Arduino and BeagleBoard users) see it as a “high cost-performance development board” due to its combination of performance (similar to the $150 BeagleBoard) and low price (close to Arduino’s price range).
-
Developing Countries: In places like Russia, Brazil, and Africa, people view Raspberry Pi as a solution to “turning a TV into a computer” (similar to the Commodore 64 of the 1980s), using existing TVs as monitors to achieve low-cost digital access.

1.2.3 Challenges and Decisions in Commercialization
Despite the team’s technical capabilities, transforming Raspberry Pi into a scalable product faced numerous challenges:
-
Manufacturing Location: The team initially hoped to produce in the UK, but the global electronics supply chain is highly concentrated in southern China. Attempting local manufacturing would lead to skyrocketing costs (barely breaking even), ultimately opting for Chinese OEM to ensure profits and support the foundation’s educational mission.
-
Brand and Operations: Through EMBA courses, the founder learned to systematically think about brand building, partner management, and the capital constraints of non-profit organizations.
1.2.4 Future Outlook
The current products of Raspberry Pi (16-pound and 22-pound versions) have demonstrated strong multimedia processing capabilities (outstanding graphics and video performance). Future plans include launching products with performance close to modern desktop computers, but careful planning is still required—avoiding premature disclosure of new projects that could impact existing sales (similar to the failure case of Osborne in the 1980s). In the short term (2012), no new products are planned, but the team is confident about the long-term development of low-cost high-performance computing.
2. Historical Challengers2.1 How Competitors Attack to Capture Raspberry Pi’s Market Share
| Competitors’Impact Points | Orange Pi 5 (Rockchip RK3588S) | NanoPi R6S (Rockchip RK3588) | Radxa Rock 5B (RK3588) |
| Hardware Performance Superiority (In high-performance computing, AI, and network applications, these boards are clearly superior to Raspberry Pi) | 8-core Cortex-A76/A55, performance far exceeds Raspberry Pi 5 (4-core A76)
16GB memory option (RPi 5 max 8GB) NPU 6TOPS computing power (suitable for AI edge computing) |
Dual 2.5G network ports, suitable for soft routing/NAS applications | PCIe 3.0 x4 interface, can connect high-speed NVMe SSD (RPi 5 only PCIe 2.0 x1) |
| Price and Supply Stability (Higher cost-performance ratio, more stable supply, especially during shortages capturing part of the market) | Supply chain issues from 2020-2023 led users to turn to domestic alternatives | Orange Pi 5 (4GB) about ¥***, while RPi 5 (4GB) official price $*** (actual premium to ¥***) | NanoPi Neo3 (within ¥***) dominates the low-cost IoT market. |
| Specific Scenario Optimization (Better solutions for niche markets in AI, routing, and multimedia) | Orange Pi 5: NPU suitable for AI inference (e.g., YOLO object detection) | NanoPi R4S: Dual Gigabit network ports, becoming a popular choice for OpenWRT soft routing | Khadas Edge2: Supports Android TV, suitable for media box applications |
(Note: Prices are redacted)For example, the AI Studio Pro from Orange Pi currently on pre-sale at JD.com is based on domestic Huawei Ascend technology and boasts a maximum of 352 TOPS high computing power. It can be seen as a new species growing from the seeds of the West in the soil of the East.
2.2 Why Raspberry Pi is Still Hard to Replace?
Raspberry Pi is not just a single-board computer; the board is only part of its strategy. Interested friends can refer to the link below for the “Raspberry Pi Foundation 2025 Strategy”:
https://static.raspberrypi.org/files/about/RaspberryPiFoundationStrategy2025.pdf
 Netizens’ Opinions:
Netizens’ Opinions:

Despite competitors having superior hardware, Raspberry Pi’s ecological moat remains very deep:
| Raspberry Pi | Competitors’ Issues | |
| Software and System Support | Official system Raspberry Pi OS is ready to use out of the boxwith the most comprehensive third-party OS support: Ubuntu, Kali Linux, RetroPie, etc. all have official adaptationsARM64 software ecosystem: 90% of Linux software is prioritized for Raspberry Pi | Orange Pi and others often require manual driver compilation, with poorer stability |
| Community and Educational Resources | The largest global developer community (forums, GitHub, Stack Overflow).
Monopoly in the school/education market: 70% of programming education globally uses Raspberry Pi. Vast tutorials/project cases (such as smart homes, robotics). |
Less documentation, higher learning costs for beginners |
| Industrial and Commercial Applications | Raspberry Pi CM4 (Compute Module) is widely used in industrial automation and medical devices.
Long-term supply commitment (7-10 years) |
Rapid hardware iteration, old models are quickly phased out |
2.3 Real Cases that Pose a Threat to Raspberry Pi
(1) The Rise of Orange Pi 5 in AI Edge Computing: With the RK3588’s NPU, it has become the preferred low-cost AI development board, partially replacing the Raspberry Pi + USB accelerator solution.
(2) The Dominance of NanoPi R4S in the Soft Routing Market: The single network port design of Raspberry Pi is not suitable for routing, while NanoPi R4S has become the standard for OpenWRT players.
(3) The Replacement of Radxa Rock 5B in High-Performance Scenarios: PCIe 3.0 x4 makes it more popular than Raspberry Pi in NAS/storage server fields.
2.4 Conclusion
Raspberry Pi’s advantages: education, general development, stability. Domestic SBC opportunities: AI computing (NPU integration), network devices (multiple network ports, 2.5G), industrial embedded (long-term supply + customization).
Orange Pi/NanoPi and others have surpassed Raspberry Pi in specific fields (AI, routing, high performance), but the overall ecosystem still cannot shake its dominant position.
If you need:
Learning programming/general projects → Raspberry Pi (unmatched ecosystem).
AI/network/storage → Domestic boards are better (stronger hardware).
In the future, as the software ecosystem of domestic SBCs improves (such as official adaptation of Ubuntu), the competitive landscape may further change. But currently, Raspberry Pi remains the first choice for most people.
3. New Challengers (The Main Character of This Article

 Feeling the heat is being stolen)Now, the Pi family has added a new challenger—RUBIK Pi 3
Feeling the heat is being stolen)Now, the Pi family has added a new challenger—RUBIK Pi 3
RUBIK Pi 3 is a lightweight single-board development board based on Qualcomm’s QCS6490 platform, the first “Pi” product built on Qualcomm’s AI platform, supporting multiple operating systems including open-source Qualcomm Linux.
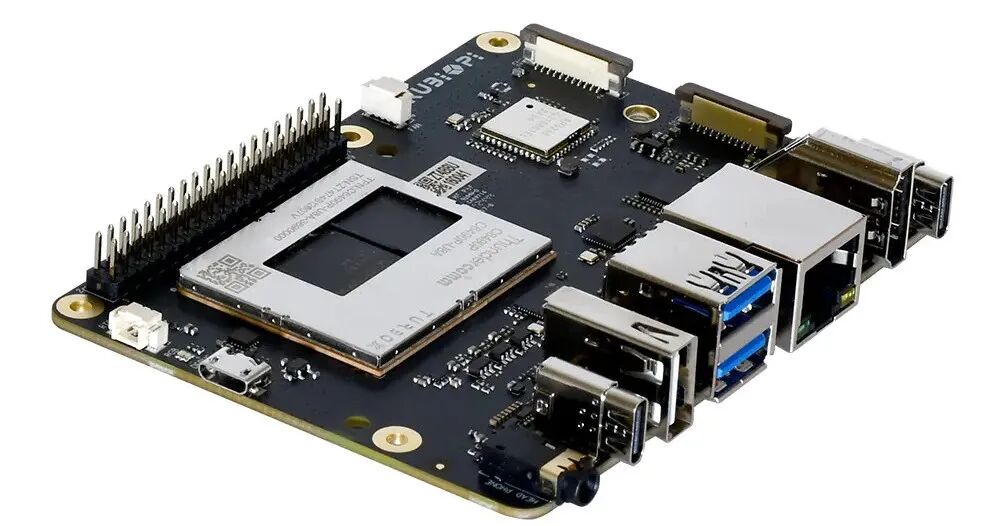

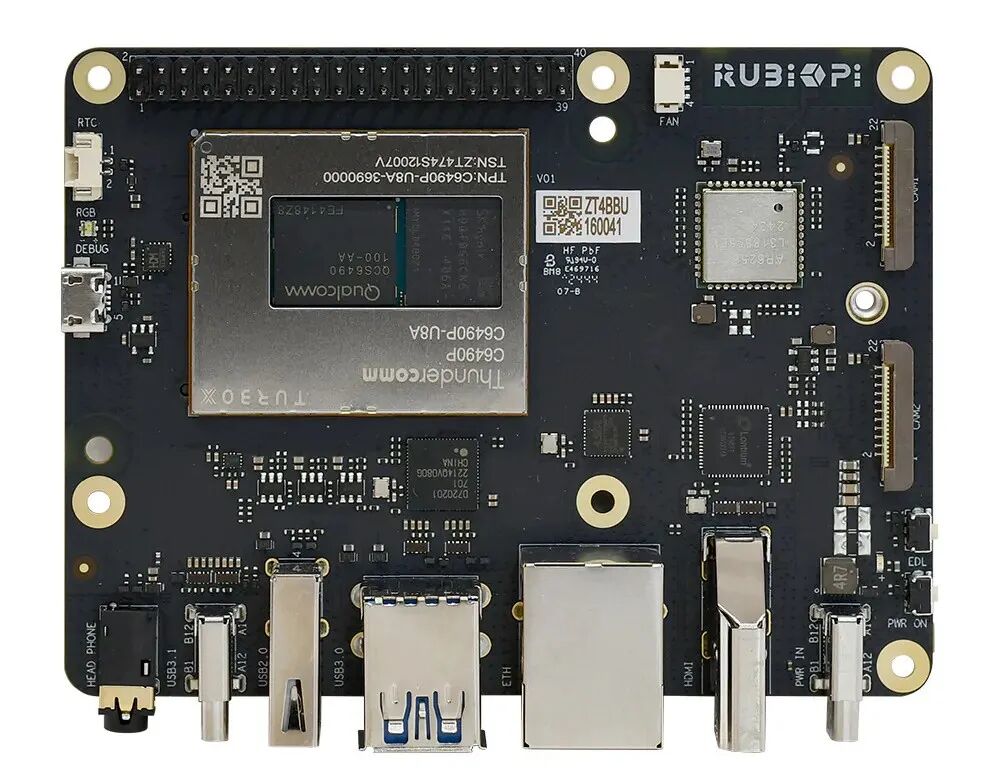 Interface Resources:
Interface Resources:
| Category | RUBIK Pi 3 Feature |
| Platform | Qualcomm Dragonwing™ QCS6490 |
| Memory | RAM 8 GB LPDDR4xROM 128 GB UFS 2.2 |
| Video | 1 x HDMI 1.4 output (up to 4K 30 Hz)1 x DP over USB Type-C (up to 4K 60 Hz)2 x camera connector (4-lane MIPI CSI D-PHY) |
| Audio | 1 x 3.5mm headphone jack |
| Connectivity | 1 x USB Type-C (USB 3.1 Gen 1)2 x USB Type-A (USB 3.0)1 x USB Type-A (USB 2.0)1 x 1000M Ethernet (RJ45)1 x UART for debug (over Micro USB)1 x M.2 Key M connector (PCIe 3.0 2-lane)40-pin LS connector supporting various interface options:– Up to 28 x GPIO– Up to 2 x I2C– Up to 3 x UART– Up to 3 x SPI– 1 x I2S (PCM)– 1 x PWM channel |
| Others | 1 x Power on button1 x EDL button1 x RGB LED2-pin RTC battery connector4-pin PWM fan connector |
| Wireless connection | Wi-Fi: IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n/acBluetooth: BT 5.2On-board PCB antenna |
| Power supply | Power Delivery over Type-C, 12V 3A |
| Operating environment | Operating temperature: 0 ~ 70°C |
| Dimensions | 100mm x 75mm x 25mm |
| OS support | Android 13Qualcomm® Linux®Debian 12*Canonical Ubuntu for Qualcomm platforms* |
Future Rich Documentation Future Active Community
Future Active Community Future High-Rated GitHub
Future High-Rated GitHub 4. Which Challenger May Stand Out in the Future
4. Which Challenger May Stand Out in the Future