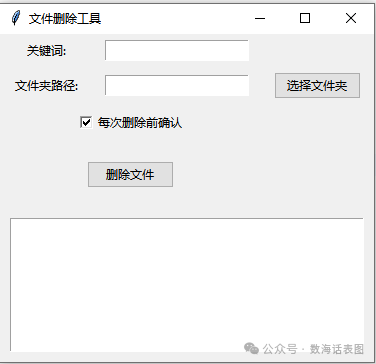
 In real work, we often encounter situations where batch deletion is required, such as temporary files, files containing specific keywords, or documentation files. Today, I will share a small program for batch deletion of files containing specified keywords (but before deleting files, it is essential to understand: Deletion carries risks, and operations must be performed with caution.):1. RequirementsOpen the Deepseek program and enter specific requirements in the input box. As shown in the figure below:
In real work, we often encounter situations where batch deletion is required, such as temporary files, files containing specific keywords, or documentation files. Today, I will share a small program for batch deletion of files containing specified keywords (but before deleting files, it is essential to understand: Deletion carries risks, and operations must be performed with caution.):1. RequirementsOpen the Deepseek program and enter specific requirements in the input box. As shown in the figure below: 2. Code Display
2. Code Display
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox, ttk, filedialog
import os
import logging
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
def center_window(window):
window.update_idletasks()
width = window.winfo_width()
height = window.winfo_height()
x = (window.winfo_screenwidth() - width) // 2
y = (window.winfo_screenheight() - height) // 2
window.geometry(f'{width}x{height}+{x}+{y}')
def select_folder():
folder = filedialog.askdirectory()
if folder:
folder_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
folder_entry.insert(0, folder)
def delete_files():
keyword = entry.get()
folder = folder_entry.get()
if not keyword or not folder:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Please enter a keyword and select a folder path")
return
if not os.path.exists(folder):
messagebox.showerror("Error", "The specified folder does not exist")
return
should_confirm = confirm_var.get()
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(folder):
for file in files:
if keyword in file:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
if should_confirm:
result = messagebox.askyesno("Confirm Deletion", f"Do you want to delete the file: {file_path}")
if result:
try:
os.remove(file_path)
logging.info(f"Deleted file: {file_path}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error deleting file {file_path}: {e}")
else:
try:
os.remove(file_path)
logging.info(f"Deleted file: {file_path}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error deleting file {file_path}: {e}")
# Create main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("File Deletion Tool")
# Keyword input box
tk.Label(root, text="Keyword:").grid(row=0, column=0, padx=10, pady=5)
entry = tk.Entry(root)
entry.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
# Folder path selection
tk.Label(root, text="Folder Path:").grid(row=1, column=0, padx=10, pady=5)
folder_entry = tk.Entry(root)
folder_entry.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
select_button = ttk.Button(root, text="Select Folder", command=select_folder)
select_button.grid(row=1, column=2, padx=10, pady=5)
# Confirmation deletion radio button
confirm_var = tk.IntVar(value=1)
tk.Checkbutton(root, text="Confirm before each deletion", variable=confirm_var).grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=10, pady=5)
# Delete button
delete_button = ttk.Button(root, text="Delete Files", command=delete_files)
delete_button.grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=10, pady=20)
# Log display box
log_text = tk.Text(root, height=10, width=50)
log_text.grid(row=4, column=0, columnspan=3, padx=10, pady=10)
# Configure log output to text box
class TextHandler(logging.Handler):
def __init__(self, text):
logging.Handler.__init__(self)
self.text = text
def emit(self, record):
msg = self.format(record)
def append():
self.text.insert(tk.END, msg + '\n')
self.text.see(tk.END)
self.text.after(0, append)
text_handler = TextHandler(log_text)
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.addHandler(text_handler)
# Center window
center_window(root)
# Run main loop
root.mainloop()
3. Code Analysis
1. Import Necessary Modules
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox, ttk, filedialog
import os
import logging<span>tkinter: The standard GUI library for Python, used to create graphical user interfaces.</span><span>messagebox: A submodule of </span><code><span>tkinter</span>used to display various message boxes, such as confirmation dialogs and error prompts.<span>ttk: A themed widget set for </span><code><span>tkinter</span>that provides more aesthetically pleasing and consistent interface components.<span>filedialog: A submodule of </span><code><span>tkinter</span>used to display file and folder selection dialogs.<span>os: A built-in Python module for interacting with the operating system, such as file and directory operations.</span><span>logging: The logging module in Python, used to record information during program execution.</span>
2. Configure Logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')<span>level=logging.INFO: Sets the logging level to </span><code><span>INFO</span>, meaning only log messages of level<span>INFO</span>and above will be recorded.<span>format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s': Sets the log format to include timestamps, log levels, and log messages.</span>
3. Define Center Window Function
def center_window(window):
window.update_idletasks()
width = window.winfo_width()
height = window.winfo_height()
x = (window.winfo_screenwidth() - width) // 2
y = (window.winfo_screenheight() - height) // 2
window.geometry(f'{width}x{height}+{x}+{y}')
- window.update_idletasks(): Updates the window’s geometry information to ensure accurate width and height are obtained.
<span>width = window.winfo_width() and height = window.winfo_height(): Retrieves the width and height of the window.</span><span>x = (window.winfo_screenwidth() - width) // 2 and y = (window.winfo_screenheight() - height) // 2: Calculates the coordinates to center the window on the screen.</span><span>window.geometry(f'{width}x{height}+{x}+{y}'): Sets the position and size of the window to display it centered.</span>
4. Define Select Folder Function
def select_folder():
folder = filedialog.askdirectory()
if folder:
folder_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
folder_entry.insert(0, folder)
<span>folder = filedialog.askdirectory(): Pops up a folder selection dialog, allowing the user to choose a folder and returns the selected folder path.</span><span>if folder: Checks if the user has selected a folder.</span><span>folder_entry.delete(0, tk.END): Clears the content in the folder path input box.</span><span>folder_entry.insert(0, folder): Inserts the user-selected folder path into the input box.</span>
5. Define Delete Files Function
def delete_files():
keyword = entry.get()
folder = folder_entry.get()
if not keyword or not folder:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Please enter a keyword and select a folder path")
return
if not os.path.exists(folder):
messagebox.showerror("Error", "The specified folder does not exist")
return
should_confirm = confirm_var.get()
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(folder):
for file in files:
if keyword in file:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
if should_confirm:
result = messagebox.askyesno("Confirm Deletion", f"Do you want to delete the file: {file_path}")
if result:
try:
os.remove(file_path)
logging.info(f"Deleted file: {file_path}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error deleting file {file_path}: {e}")
else:
try:
os.remove(file_path)
logging.info(f"Deleted file: {file_path}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error deleting file {file_path}: {e}")
- keyword = entry.get() and folder = folder_entry.get(): Retrieves the user-input keyword and selected folder path.
<span>if not keyword or not folder: Checks if the user has entered a keyword and selected a folder path; if not, displays an error message and returns.</span><span>if not os.path.exists(folder): Checks if the selected folder exists; if not, displays an error message and returns.</span><span>should_confirm = confirm_var.get(): Retrieves the state of the confirmation deletion radio button.</span><span>for root, dirs, files in os.walk(folder): Iterates through all files in the specified folder and its subfolders.</span><span>if keyword in file: Checks if the filename contains the user-input keyword.</span><span>if should_confirm: If the confirmation deletion radio button is selected, pops up a confirmation dialog.</span><span>result = messagebox.askyesno("Confirm Deletion", f"Do you want to delete the file: {file_path}"): Pops up a confirmation dialog asking the user if they want to delete the file.</span><span>os.remove(file_path): Deletes the file.</span><span>logging.info(f"Deleted file: {file_path}"): Records a log message indicating the file was successfully deleted.</span><span>logging.error(f"Error deleting file {file_path}: {e}"): Records a log message indicating an error occurred while deleting the file.</span>
6. Create Main Window and Interface Components
# Create main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("File Deletion Tool")
# Keyword input box
tk.Label(root, text="Keyword:").grid(row=0, column=0, padx=10, pady=5)
entry = tk.Entry(root)
entry.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
# Folder path selection
tk.Label(root, text="Folder Path:").grid(row=1, column=0, padx=10, pady=5)
folder_entry = tk.Entry(root)
folder_entry.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
select_button = ttk.Button(root, text="Select Folder", command=select_folder)
select_button.grid(row=1, column=2, padx=10, pady=5)
# Confirmation deletion radio button
confirm_var = tk.IntVar(value=1)
tk.Checkbutton(root, text="Confirm before each deletion", variable=confirm_var).grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=10, pady=5)
# Delete button
delete_button = ttk.Button(root, text="Delete Files", command=delete_files)
delete_button.grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=10, pady=20)
# Log display box
log_text = tk.Text(root, height=10, width=50)
log_text.grid(row=4, column=0, columnspan=3, padx=10, pady=10)
- root = tk.Tk(): Creates the main window.
<span>root.title("File Deletion Tool"): Sets the title of the main window.</span><span>tk.Label(root, text="Keyword:") and entry = tk.Entry(root): Creates a keyword input box and its corresponding label.</span><span>tk.Label(root, text="Folder Path:") and folder_entry = tk.Entry(root) and select_button = ttk.Button(root, text="Select Folder", command=select_folder): Creates a folder path input box, its corresponding label, and a button to select the folder.</span><span>confirm_var = tk.IntVar(value=1) and tk.Checkbutton(root, text="Confirm before each deletion", variable=confirm_var): Creates a confirmation deletion radio button.</span><span>delete_button = ttk.Button(root, text="Delete Files", command=delete_files): Creates a button to delete files.</span><span>log_text = tk.Text(root, height=10, width=50): Creates a log display box.</span>
7. Configure Log Output to Text Box
# Configure log output to text box
class TextHandler(logging.Handler):
def __init__(self, text):
logging.Handler.__init__(self)
self.text = text
def emit(self, record):
msg = self.format(record)
def append():
self.text.insert(tk.END, msg + '\n')
self.text.see(tk.END)
self.text.after(0, append)
text_handler = TextHandler(log_text)
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.addHandler(text_handler)- class TextHandler(logging.Handler): Defines a custom logging handler to output log information to the text box.
<span>def __init__(self, text): Initializes the logging handler, receiving a text box object as a parameter.</span><span>def emit(self, record): Overrides the emit method to insert log information into the text box.</span><span>text_handler = TextHandler(log_text): Creates an instance of the custom logging handler.</span><span>logger = logging.getLogger(): Retrieves the root logger.</span><span>logger.addHandler(text_handler): Adds the custom logging handler to the root logger.</span>
8. Center Window and Run Main Loop
# Center window
center_window(root)
# Run main loop
root.mainloop()- center_window(root): Calls the function to center the main window.
<span>root.mainloop(): Enters the main event loop, waiting for user actions and processing events.</span>
For how to use the code, please refer to the article “Python Automation: Creating a Batch Text Replacement Program with Python and Deepseek” in step four.In conclusion: Deletion carries risks, and operations must be performed with caution. If not handled properly, it may lead to the direct deletion of your data. If important files are involved, be sure to back them up to prevent accidental operations.