Source: MedRobot; Edited by: Tang Zijie
Reprint Requirements: Can be reprinted 24 hours after the first release, with source acknowledgment
This article reviews five orthopedic navigation and surgical robot products that received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) from January 2022 to the end of August, from three American companies: Surgalign (NASDAQ: SRGA), Stryker (NYSE: SYK), Novarad, and two Chinese companies: Shanghai MicroPort Robotics and Point Robotics from Taiwan.
Surgalign’s Holo Portal

On January 18, 2022, Surgalign announced that its HOLO Portal surgical navigation system for lumbar surgery had received FDA 510(k) clearance. Surgalign claims that the HOLO Portal system is the world’s first AI-driven augmented reality (AR) navigation system for spinal surgery, and it is also the first clinical application of the HOLO AI digital health platform.
1. Three Major Functions of HOLO Portal
(1) Autonomous Anatomy Segmentation
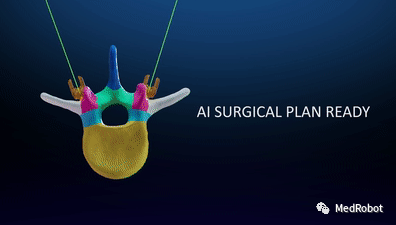
HOLO Portal can segment and group the patient’s anatomical structures based on intraoperative CT scans. It generates a patient-specific 3D model that automatically labels anatomical structures for use during surgery: pedicles, vertebral bodies, spinal canals, articular processes, transverse processes, laminae, spinous processes, ribs, and pelvis.
(2) Automatic Surgical Planning
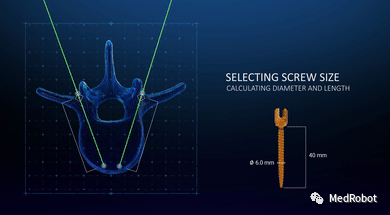
HOLO Portal automatically suggests screw trajectories and measures pedicle sizes based on the patient-specific 3D model. Then, HOLO Portal recommends appropriate screw sizes based on the pedicle fill rate defined by the surgeon. The surgical plan aims to maximize construct stability and eliminate the time spent on manual trajectory planning and screw size measurement.
(3) AR Augmented Reality
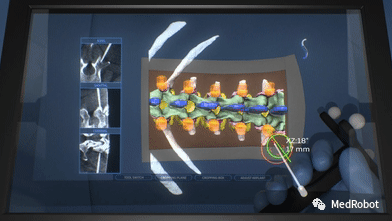
HOLO Portal displays the surgical plan in intraoperative interactive AR screens, providing 3D guidance overlays on the patient’s anatomical structures. The 3D trajectories and targets are overlaid in real-time on the surgical instruments within the surgical area. This innovative design alleviates the cognitive burden on surgeons by providing intuitive guidance, allowing them to focus on the surgical field.
Stryker’s Q Guidance System
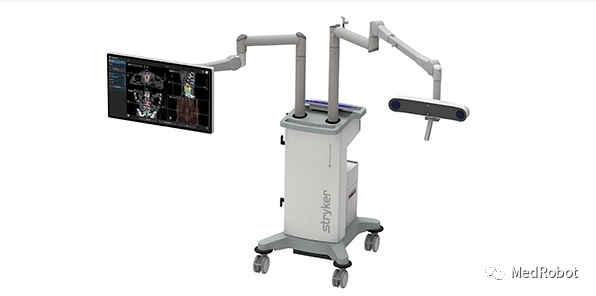
On June 1, 2022, Stryker (NYSE: SYK) announced that its Q Guidance System received FDA 510(k) clearance. This system is used alongside spinal navigation software and is an advanced planning and intraoperative navigation system designed for open or percutaneous robot-assisted surgery.
Reportedly, this is the first FDA-approved spinal navigation software that can be used for pediatric patients aged 13 and older.
The Q Guidance System is designed to provide surgical spine planning and navigation capabilities through various tracking options, complex software algorithms, and intelligent instruments. It employs high-performance navigation cameras based on the company’s 20 years of experience in developing navigation technology. Q Guidance features a completely redesigned software application, semi-automated and automated segmentation capabilities, gesture recognition, and broad compatibility with various types of image sets. When used with the Airo TruCT mobile CT scanner, this ecosystem provides automatic image registration, combining high-performance tracking capabilities with cutting-edge intraoperative image quality and scanning volume.
Novarad’s VisAR
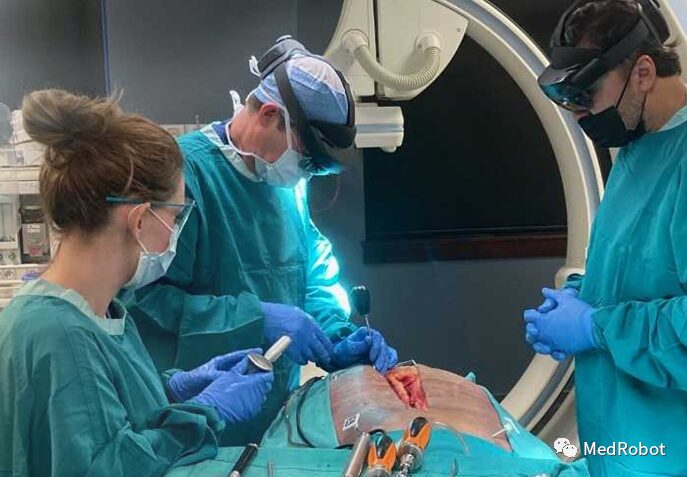
Novarad’s VisAR augmented reality surgical guidance system has received FDA clearance for intraoperative spinal surgery. This system converts imaging data into a 3D hologram that is visible and overlaid on the patient.
VisAR uses the Novarad graphics engine to render any modality’s 2D, 3D, and 4D digital images into highly detailed holograms in real-time. Using patented virtual tool technology with integrated targeting systems, the hologram is accurately overlaid directly onto the patient’s body.
MicroPort Navibot’s U.S. Company
SkyWalker by MicroPort Navibot
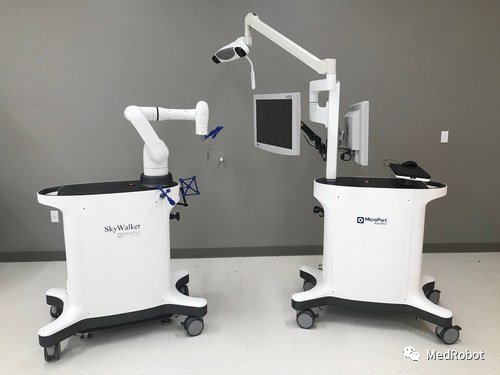
On July 12, 2022, Shanghai MicroPort Medical Robotics (Group) Co., Ltd. (02252.HK) announced that its wholly-owned subsidiary Suzhou MicroPort Changxing Robot Co., Ltd. and its U.S. Massachusetts-based MicroPort NaviBot International LLC independently developed the Honghu® orthopedic surgical robot, which received FDA 510(k) certification, becoming the first and only Chinese surgical robot certified by the FDA.
The SkyWalker System will provide a robot-assisted total knee replacement solution compatible with the Evolution Medial-Pivot total knee system.
Related link: Chinese surgical robot approved by the FDA!
MicroPort NaviBot is designed based on clinical needs and has built a fully equipped research facility with medical industry design capabilities, benefiting from self-developed, highly dexterous, lightweight robotic arms combined with intelligent planning and navigation algorithms as core technological advantages. The SkyWalker System features precise operation, efficient coordination, and a safety-first technological advantage.
The SkyWalker™ system can provide surgeons with information that helps achieve the desired joint line reconstruction while providing data to optimally balance soft tissues. MicroPort NaviBot plans to develop additional orthopedic applications with MicroPort Orthopedics in the near future to obtain a more comprehensive orthopedic product line.
Point Robotics from Taiwan
Point Kinguide System
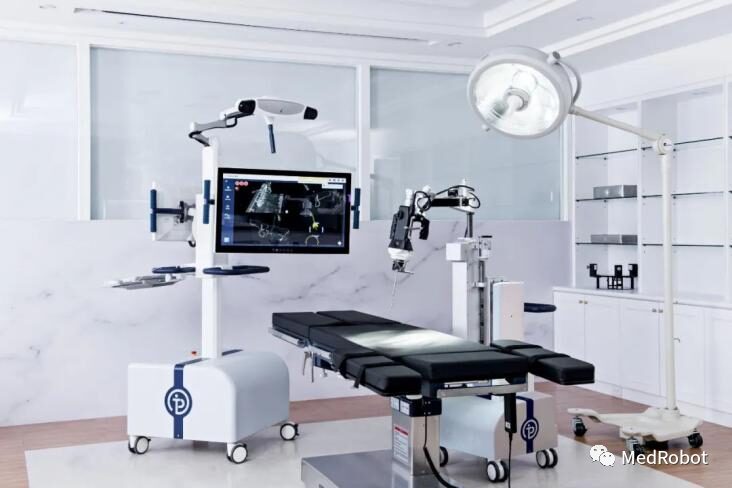
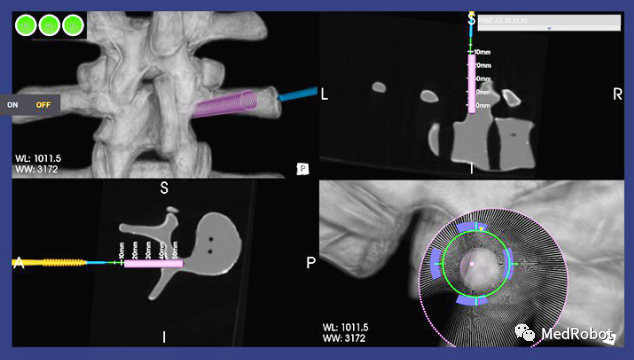
On August 23, 2022, Point Robotics announced that its minimally invasive surgical robot POINT™ Kinguide robot-assisted surgical system received FDA 510(k) clearance.
The “Kinguide robot-assisted surgical system” integrates its high-precision and unique handheld machine, helping surgeons drill and implant screws more efficiently than ever before. With a fully integrated surgical system that includes a navigation system and handheld drilling system.
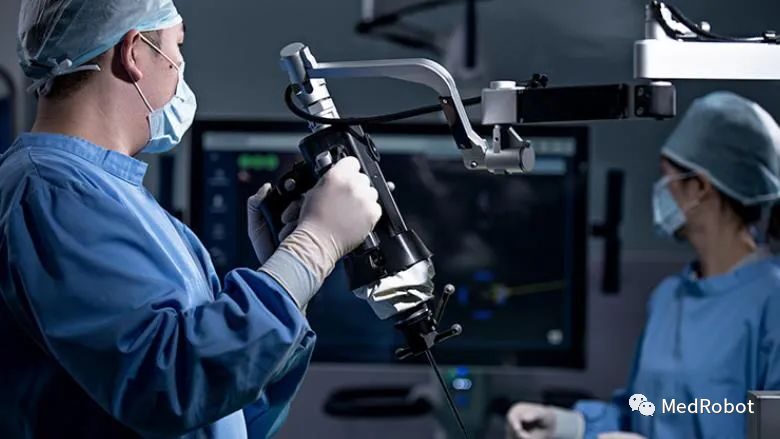

The “Kinguide robot-assisted surgical system” simplifies surgical tasks and significantly reduces the burden on surgeons during implant procedures. It also features high accuracy, low radiation exposure, a unique robotic hand, optical tracking and real-time navigation, automatic safety mechanisms, smooth intraoperative image registration, mobility, and efficient settings that allow surgeons to adapt to different surgical procedures, 3D imaging reconstruction, intraoperative planning, and integrated operating room solutions connecting surgical instruments.
Previously, Dr. Luo Wencheng, head of neurosurgery at the leading medical center Taipei Medical University Hospital, had performed over 8,000 spinal surgeries. He commented, “There is still a huge unmet clinical demand for spinal surgical robots. Once a revolutionary new product with high degrees of freedom and multifunctionality can significantly reduce the burden on surgeons for clinical procedures like implant placement and meet the growing demand for decompression surgeries, it will be a milestone in minimally invasive spinal surgical methods.”
